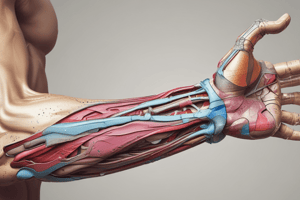
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which structure passes centrally through the cubital fossa?
Which structure passes centrally through the cubital fossa?
- Brachial artery
- Biceps tendon (correct)
- Radial nerve
- Median nerve
What is the main contents of the anatomical snuffbox?
What is the main contents of the anatomical snuffbox?
- Ulnar artery and median nerve
- Radial artery, a branch of the radial nerve, and the cephalic vein (correct)
- Median nerve and brachial artery
- Radial artery and cephalic vein
What is the function of the radial nerve in the forearm and hand?
What is the function of the radial nerve in the forearm and hand?
- Sensory function only in the posterior forearm
- Motor and sensory function in the posterior forearm and hand (correct)
- Motor function only in the anterior forearm
- Motor and sensory function in the anterior forearm and hand
How many tendons are present in the carpal tunnel?
How many tendons are present in the carpal tunnel?
What borders the adductor canal?
What borders the adductor canal?
Which of the following is NOT a tendon present in the carpal tunnel?
Which of the following is NOT a tendon present in the carpal tunnel?
What is the function of the femoral triangle?
What is the function of the femoral triangle?
What is the name of the passageway in the leg that contains the tibialis posterior tendon and the tibial nerve?
What is the name of the passageway in the leg that contains the tibialis posterior tendon and the tibial nerve?
Where is the first extensor compartment located?
Where is the first extensor compartment located?
What is the branch of the median nerve that is given off prior to the carpal tunnel?
What is the branch of the median nerve that is given off prior to the carpal tunnel?
What is the name of the compartment that transmits the tendons of the extensor digitorum and extensor indicis?
What is the name of the compartment that transmits the tendons of the extensor digitorum and extensor indicis?
What is the name of the region in the posterior compartment of the leg and thigh that contains the popliteal artery and vein?
What is the name of the region in the posterior compartment of the leg and thigh that contains the popliteal artery and vein?
What forms the floor of the inguinal canal?
What forms the floor of the inguinal canal?
Which nerve contributes to the sensory innervation of the genitalia and is most at risk of damage during an inguinal hernia repair?
Which nerve contributes to the sensory innervation of the genitalia and is most at risk of damage during an inguinal hernia repair?
What is the medial boundary of the submental triangle?
What is the medial boundary of the submental triangle?
Which structure originates from the uterine horn and travels through the inguinal canal to attach at the labia majora?
Which structure originates from the uterine horn and travels through the inguinal canal to attach at the labia majora?
What is the superior boundary of the carotid triangle?
What is the superior boundary of the carotid triangle?
What is the lateral boundary of the submental triangle?
What is the lateral boundary of the submental triangle?
Which nerve supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males?
Which nerve supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males?
What is the posterior boundary of the submandibular triangle?
What is the posterior boundary of the submandibular triangle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cubital Fossa
- A passageway for structures to pass between the upper arm and forearm.
- Contents: radial nerve, biceps tendon, brachial artery, and median nerve.
- Radial nerve: travels along the lateral border, divides into superficial and deep branches, and has motor and sensory functions.
- Biceps tendon: passes centrally, attaches to the radial tuberosity, and gives rise to the bicipital aponeurosis.
- Brachial artery: bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at the apex of the cubital fossa.
- Median nerve: travels medially, exits by passing between the two heads of the pronator teres, and has motor and sensory functions.
Carpal Tunnel
- Contains 9 tendons, surrounded by synovial sheaths, and the median nerve.
- Tendons: flexor pollicis longus, 4 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus, and 4 tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis.
- Palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve is given off prior to the carpal tunnel, traveling superficially to the flexor retinaculum.
Extensor Compartments
- 1st compartment: located on the lateral (radial) aspect of the wrist, transmits two tendons (extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus).
- 2nd compartment: contains tendons of the extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis.
- 3rd compartment: conducts the extensor pollicis longus tendon.
- 4th compartment: transmits tendons of the extensor digitorum and extensor indicis.
- 5th compartment: contains the extensor digiti minimi tendon.
- 6th compartment: located on the medial (ulnar) aspect of the wrist, conducts the tendon of the extensor carpi ulnaris.
Anatomical Snuffbox
- Contains the radial artery, a branch of the radial nerve, and the cephalic vein.
Femoral Triangle
- Contains major neurovascular structures of the lower limb.
- Contents: femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, and femoral canal.
- Femoral nerve: innervates the anterior compartment of the thigh, and provides sensory branches for the leg and foot.
- Femoral artery: responsible for the majority of the arterial supply to the lower limb.
- Femoral vein: the great saphenous vein drains into the femoral vein within the triangle.
Femoral Triangle Borders
- Roof: fascia lata.
- Floor: pectineus, iliopsoas, and adductor longus muscles.
- Superior border: inguinal ligament.
- Lateral border: medial border of the sartorius muscle.
- Medial border: medial border of the adductor longus muscle.
Femoral Canal
- Located in the anterior thigh within the femoral triangle.
- A rectangular shaped compartment with four borders and an opening.
- Borders: medial (lacunar ligament), lateral (femoral vein), anterior (inguinal ligament), and posterior (pectineal ligament, superior ramus of the pubic bone, and pectineus muscle).
Adductor Canal
- Bordered by muscular structures: anteromedial (sartorius), lateral (vastus medialis), and posterior (adductor longus and adductor magnus).
- Transmits the femoral artery, femoral vein (posterior to the artery), nerve to the vastus medialis, and the saphenous nerve.
Popliteal Fossa
- Diamond-shaped with four borders formed by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg and thigh.
- Borders: superomedial (semimembranosus), superolateral (biceps femoris), inferomedial (medial head of the gastrocnemius), and inferolateral (lateral head of the gastrocnemius and plantaris).
- Contents: popliteal artery, popliteal vein, tibial nerve, and common fibular nerve (common peroneal nerve).
Tarsal Tunnel
- Acts as a passageway for tendons, nerves, and vessels to travel between the posterior leg and the foot.
- Contents: tibialis posterior tendon, flexor digitorum longus tendon, posterior tibial artery and vein, tibial nerve, and flexor hallucis longus tendon.
Inguinal Canal
- Bordered by anterior, posterior, superior (roof), and inferior (floor) walls.
- Two openings: superficial and deep rings.
- Walls: anterior (aponeurosis of the external oblique, reinforced by the internal oblique muscle laterally), posterior (transversalis fascia), roof (transversalis fascia, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis), and floor (inguinal ligament, thickened medially by the lacunar ligament).
Inguinal Canal Contents
- Spermatic cord (biological males only): contains neurovascular and reproductive structures that supply and drain the testes.
- Round ligament (biological females only): originates from the uterine horn and travels through the inguinal canal to attach at the labia majora.
- Ilioinguinal nerve: contributes towards the sensory innervation of the genitalia.
- Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve: supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females.
Carotid Triangle
- Boundaries: superior (posterior belly of the digastric muscle), lateral (medial border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle), and inferior (superior belly of the omohyoid muscle).
Submental Triangle
- Boundaries: inferiorly (hyoid bone), medially (midline of the neck), and laterally (anterior belly of the digastric).
- A triangular region in the neck.
Submandibular Triangle
- Boundaries: superiorly (body of the mandible), anteriorly (anterior belly of the digastric muscle), and posteriorly (posterior belly of the digastric muscle).
- A triangular region in the neck.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.