Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the transversalis fascia?
What is the function of the transversalis fascia?
- To form the rectus sheath
- To line the inner surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall
- To provide additional support to the pyramidalis muscle
- To cover the deep surface of the transversus abdominis (correct)
What is the characterization of the extraperitoneal fascia?
What is the characterization of the extraperitoneal fascia?
- A layer of loose connective tissue with a variable amount of fat (correct)
- A fibrous band that extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis
- A layer of dense connective tissue
- A serous membrane that lines the inner surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall
How many muscles are present on each side of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
How many muscles are present on each side of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
- 2 broad and thin muscles
- 5 broad and thin muscles
- 3 broad and thin muscles (correct)
- 4 broad and thin muscles
What is the name of the muscle present anterior to the lower part of the rectus abdominis?
What is the name of the muscle present anterior to the lower part of the rectus abdominis?
What is the function of the aponeuroses of the 3 flat muscles?
What is the function of the aponeuroses of the 3 flat muscles?
What is the origin of the external oblique muscle?
What is the origin of the external oblique muscle?
What is the direction of the fibers of the external oblique muscle on an anterior view?
What is the direction of the fibers of the external oblique muscle on an anterior view?
What is the structure formed by the fusion of the aponeuroses of the 3 right flat muscles and the 3 left flat muscles?
What is the structure formed by the fusion of the aponeuroses of the 3 right flat muscles and the 3 left flat muscles?
Which of the following nerves does not enter the rectus sheath?
Which of the following nerves does not enter the rectus sheath?
What is the level of the T10 dermatome?
What is the level of the T10 dermatome?
What is the purpose of mapping out regions on the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What is the purpose of mapping out regions on the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What is the level of the subcostal plane?
What is the level of the subcostal plane?
What is the function of the nerves of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What is the function of the nerves of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What is the midclavicular plane?
What is the midclavicular plane?
What is the posterior wall of the rectus sheath formed by?
What is the posterior wall of the rectus sheath formed by?
What is the location of the arcuate line?
What is the location of the arcuate line?
How many regions are formed by the 2 midclavicular planes and 2 horizontal planes (subcostal and transtubercular)?
How many regions are formed by the 2 midclavicular planes and 2 horizontal planes (subcostal and transtubercular)?
Which artery supplies the upper central part of the anterior abdominal wall?
Which artery supplies the upper central part of the anterior abdominal wall?
What is the lower part of the anterolateral abdominal wall composed of?
What is the lower part of the anterolateral abdominal wall composed of?
What is the significance of the arcuate line?
What is the significance of the arcuate line?
What is the deepest layer of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What is the deepest layer of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
What are the three aponeuroses that pass anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle in the lower 1/4 of the anterior abdominal wall?
What are the three aponeuroses that pass anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle in the lower 1/4 of the anterior abdominal wall?
What is Camper's fascia?
What is Camper's fascia?
What is the purpose of the deep (investing) fascia?
What is the purpose of the deep (investing) fascia?
What is the origin of the superior epigastric artery?
What is the origin of the superior epigastric artery?
What is the attachment of the posterior wall of the rectus sheath?
What is the attachment of the posterior wall of the rectus sheath?
What is the function of Scarpa's fascia?
What is the function of Scarpa's fascia?
What is the relationship between the transtubercular plane and the body of L5?
What is the relationship between the transtubercular plane and the body of L5?
What is the insertion point of the lower fibers of the external oblique muscle?
What is the insertion point of the lower fibers of the external oblique muscle?
What is the function of the pyramidalis muscle?
What is the function of the pyramidalis muscle?
What is the action of the transversus abdominis muscle on trunk movements?
What is the action of the transversus abdominis muscle on trunk movements?
What is the boundary between the abdomen and thigh formed by?
What is the boundary between the abdomen and thigh formed by?
What is the location of the superficial inguinal ring?
What is the location of the superficial inguinal ring?
What is the origin of the rectus abdominis muscle?
What is the origin of the rectus abdominis muscle?
What is the function of the anterolateral abdominal muscles in increasing intra-abdominal pressure?
What is the function of the anterolateral abdominal muscles in increasing intra-abdominal pressure?
What is the contents of the rectus sheath?
What is the contents of the rectus sheath?
What is the action of the oblique muscles on the trunk?
What is the action of the oblique muscles on the trunk?
What is the location of the inguinal ligament?
What is the location of the inguinal ligament?
Which artery anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery?
Which artery anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery?
Which vein drains into the axillary vein?
Which vein drains into the axillary vein?
Which lymph node receives lymph drainage from the superficial lymph vessels below the level of the umbilicus?
Which lymph node receives lymph drainage from the superficial lymph vessels below the level of the umbilicus?
Which artery supplies the lower lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall?
Which artery supplies the lower lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall?
Which vein accompanies the deep circumflex iliac artery?
Which vein accompanies the deep circumflex iliac artery?
Which artery originates from the distal part of the external iliac artery?
Which artery originates from the distal part of the external iliac artery?
Which lymph node receives lymph drainage from the deep lymph vessels that follow the arteries and deep veins?
Which lymph node receives lymph drainage from the deep lymph vessels that follow the arteries and deep veins?
Which vein drains into the azygos vein?
Which vein drains into the azygos vein?
What is the main content of the spermatic cord in males?
What is the main content of the spermatic cord in males?
What is the location of the deep inguinal ring in relation to the ASIS and pubic tubercle?
What is the location of the deep inguinal ring in relation to the ASIS and pubic tubercle?
What is the feature of the neck of a hernia sac in relation to an indirect inguinal hernia?
What is the feature of the neck of a hernia sac in relation to an indirect inguinal hernia?
What percentage of abdominal hernias occur in the inguinal region?
What percentage of abdominal hernias occur in the inguinal region?
What is the term used to describe the relationship of the stomach to its peritoneal covering?
What is the term used to describe the relationship of the stomach to its peritoneal covering?
What is the neck of the hernial sac in a direct inguinal hernia?
What is the neck of the hernial sac in a direct inguinal hernia?
What is the boundary of the inguinal triangle?
What is the boundary of the inguinal triangle?
What is the name of the peritoneal fold that connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
What is the name of the peritoneal fold that connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
What is the term used to describe the relationship of the duodenum to its peritoneal covering?
What is the term used to describe the relationship of the duodenum to its peritoneal covering?
What is the origin of an indirect inguinal hernia?
What is the origin of an indirect inguinal hernia?
What is the function of the hepatoduodenal ligament?
What is the function of the hepatoduodenal ligament?
What is the name of the peritoneal fold that hangs down from the greater curvature of the stomach?
What is the name of the peritoneal fold that hangs down from the greater curvature of the stomach?
What type of fold is the greater omentum?
What type of fold is the greater omentum?
What is the key relationship of the greater omentum?
What is the key relationship of the greater omentum?
What type of intestines have a mesentery?
What type of intestines have a mesentery?
What is the function of the mesentery?
What is the function of the mesentery?
What is the transverse mesocolon?
What is the transverse mesocolon?
What is formed by the space between the 2 anterior and 2 posterior layers of the greater omentum?
What is formed by the space between the 2 anterior and 2 posterior layers of the greater omentum?
What happens to some parts of the digestive tract during development?
What happens to some parts of the digestive tract during development?
What is the main characteristic of secondary retroperitoneal organs?
What is the main characteristic of secondary retroperitoneal organs?
What is the communication between the lesser sac and the greater sac called?
What is the communication between the lesser sac and the greater sac called?
What is the purpose of the mesentery?
What is the purpose of the mesentery?
What is the name of the part of the peritoneal cavity located posterior to the lesser omentum and stomach?
What is the name of the part of the peritoneal cavity located posterior to the lesser omentum and stomach?
What is the superior extension of the lesser sac called?
What is the superior extension of the lesser sac called?
What structure forms the posterior boundary of the epiploic foramen?
What structure forms the posterior boundary of the epiploic foramen?
Which of the following nerves innervates the peritoneum that covers the peripheral part of the undersurface of the diaphragm?
Which of the following nerves innervates the peritoneum that covers the peripheral part of the undersurface of the diaphragm?
What is the name of the fibrous cord that extends from the apex of the urinary bladder to the umbilicus?
What is the name of the fibrous cord that extends from the apex of the urinary bladder to the umbilicus?
What is the name of the compartment located below the transverse colon and its mesentery?
What is the name of the compartment located below the transverse colon and its mesentery?
Which of the following statements is true about pain originating from the parietal peritoneum?
Which of the following statements is true about pain originating from the parietal peritoneum?
What is the name of the fold formed by the peritoneum that covers the median umbilical ligament?
What is the name of the fold formed by the peritoneum that covers the median umbilical ligament?
Match the following organs with their classification based on their relationship to the peritoneum:
Match the following organs with their classification based on their relationship to the peritoneum:
The contents of the inguinal canal in females include the round ligament of uterus, genital branch of genitofemoral nerve, and ilioinguinal nerve.
The contents of the inguinal canal in females include the round ligament of uterus, genital branch of genitofemoral nerve, and ilioinguinal nerve.
The structure that lies parallel and immediately above the medial part of the inguinal ligament is known as the [blank].
The structure that lies parallel and immediately above the medial part of the inguinal ligament is known as the [blank].
Is the statement true: Above the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains upward toward the anterior axillary lymph nodes, and below the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains downward toward the superficial inguinal lymph nodes?
Is the statement true: Above the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains upward toward the anterior axillary lymph nodes, and below the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains downward toward the superficial inguinal lymph nodes?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Regions of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- The anterolateral abdominal wall is divided into 4 quadrants: upper right, upper left, lower right, and lower left quadrants, by a vertical plane and a horizontal plane that intersect at the umbilicus.
- The 4 quadrants are further divided into 9 regions by 2 midclavicular planes and 2 horizontal planes (subcostal and transtubercular planes).
Regions of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall (continued)
- The upper part (above subcostal plane) consists of: epigastric region (center), right and left hypochondriac regions.
- The middle part (between subcostal and transtubercular planes) consists of: umbilical region (center), right and left lateral regions (lumbar regions or flanks).
- The lower part (below transtubercular plane) consists of: pubic region, hypogastric region (center), and right and left inguinal (iliac) regions.
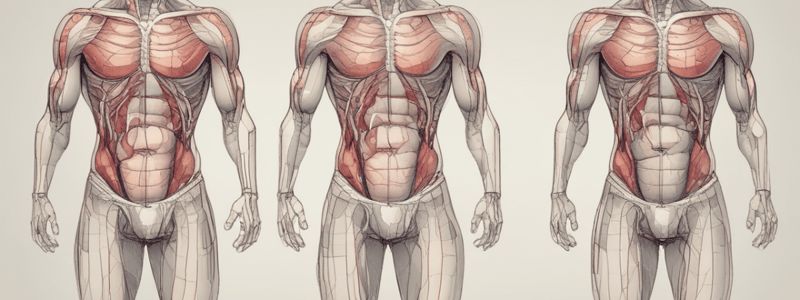
Layers of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- From superficial to deep: skin, superficial fascia, muscles with their deep (investing) fasciae, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fascia, and parietal peritoneum.
Superficial Fascia
- Divided into 2 layers in the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall: superficial, fatty layer (Camper's fascia), and deep, membranous layer (Scarpa's fascia).
Abdominal Muscles
- 3 flat muscles on each side: external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis.
- On each side of the anterior midline, there is a long, vertical muscle (rectus abdominis) and a small muscle (pyramidalis) anterior to the lower part of rectus abdominis (absent in about 20% of people).
Muscles of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall (continued)
- The 3 flat muscles are muscular (fleshy) posterolaterally and aponeurotic (fibrous) anteromedially.
- Their aponeuroses pass medially and enclose rectus abdominis (and pyramidalis, if present) to form the rectus sheath.
- In the midline of the anterior abdominal wall, the aponeuroses of the 3 right flat muscles join the aponeuroses of the 3 left flat muscles to form the linea alba.
External Oblique
- Origin: outer surface of the lower 8 ribs.
- Insertion: into the xiphoid process, linea alba, and pubic bone.
- Inguinal (Poupart's) ligament: lower border of the external oblique aponeurosis that extends from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the pubic tubercle.
Transversus Abdominis
- Lies deep to the internal oblique.
- Origin: deep surface of the lower 6 costal cartilages, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and lateral ⅓ of the inguinal ligament.
- Insertion: into the xiphoid process, linea alba, and pubic bone.
Rectus Abdominis
- Long strap muscle that extends along the whole length of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Divided into segments by 3 transverse fibrous bands (tendinous intersections or inscriptions).
Actions of the Anterolateral Abdominal Muscles
- Their tone plays an important role in supporting and protecting abdominal organs.
- Oblique muscles are involved in flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation of the trunk.
- Rectus abdominis flexes the trunk.
- Transversus abdominis contributes little to trunk movements.
- By contracting simultaneously with the diaphragm, with the glottis of the larynx closed, anterolateral abdominal muscles increase intra-abdominal pressure, helping with evacuation of the contents of abdominal and pelvic hollow organs.
Rectus Sheath
- Formed by the aponeurosis of the 3 flat abdominal muscles.
- Contents: rectus abdominis, pyramidalis (if present), terminal parts of the lower 5 intercostal nerves and subcostal nerve, and superior and inferior epigastric vessels.
Nerves of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- Ventral rami of T7 to T11 spinal nerves (7th to 11th intercostal nerves) and ventral ramus of T12 spinal nerve (subcostal nerve).
- Ventral ramus of L1 spinal nerve (iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves).
Dermatomes of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- T7: just inferior to the tip of the xiphoid process.
- T10: level of the umbilicus.
- L1: pubic symphysis and area immediately superior to it.
Arteries of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- Superior epigastric artery: terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery.
- Inferior epigastric artery: originates from the distal part of the external iliac artery.
- Deep circumflex iliac artery: originates from the distal part of the external iliac artery.
- 10th and 11th posterior intercostal arteries, subcostal artery, and lumbar arteries.
Veins of the Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
- Superficial veins: form a network that radiates out from the umbilicus.
- Deep veins: accompany corresponding arteries and drain into internal thoracic, external iliac, posterior mediastinal, and lumbar (para-aortic) veins.
Lymphatic Drainage of the Anterior Abdominal Wall
- Superficial lymph vessels: above the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains upward toward the anterior axillary lymph nodes; below the level of the umbilicus, lymph drains downward toward the superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
- Deep lymph vessels: follow arteries and deep veins and drain into internal thoracic (parasternal), external iliac, posterior mediastinal, and lumbar (para-aortic) lymph nodes.
Inguinal Canal
- Oblique passage, approximately 4 cm in length, through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall
- Lies parallel and immediately above the medial part of the inguinal ligament
- Contents:
- In males: spermatic cord (formed by structures running between the testis and abdominopelvic cavity) and ilioinguinal nerve
- In females: round ligament of uterus (fibrous cord that extends from the uterus to the labium majus), genital branch of genitofemoral nerve, and ilioinguinal nerve
- Openings:
- Deep inguinal ring (opening in transversalis fascia) located approximately halfway between the ASIS and pubic tubercle
- Superficial inguinal ring (opening in aponeurosis of external oblique) located immediately superior to the pubic tubercle
- Walls:
- Anterior: aponeurosis of external oblique
- Posterior: transversalis fascia
- Inferior: inguinal ligament
- Superior: lower borders of internal oblique and transversus abdominis
Abdominal Hernia
- Protrusion of abdominal contents beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall
- Has three parts: hernial sac, contents of the sac, and coverings of the sac
- Sac: pouch (diverticulum) of parietal peritoneum
- Contents: may consist of any structure found within the abdominal cavity (e.g., piece of omentum, loop of small intestine, etc.)
- Coverings: formed by layers of the abdominal wall through which the hernial sac passes
- Approximately 75% of abdominal hernias occur in the inguinal region (most common type of abdominal hernia)
Types of Inguinal Hernias
- Indirect inguinal hernia:
- Most common type of inguinal hernia (2/3 to 3/4 of inguinal hernias)
- Hernial sac leaves the abdominal cavity lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, through the deep inguinal ring
- Results from a persistent processus vaginalis (outpouching of peritoneum that in the fetus is responsible for the formation of the inguinal canal)
- More common in children and young adults
- Direct inguinal hernia:
- Hernial sac leaves the abdominal cavity medial to the inferior epigastric vessels
- Hernial sac protrudes through an area of relative weakness in the posterior wall of the inguinal canal
- Inguinal (Hesselbach's) triangle is bounded by the inferior epigastric vessels (laterally), rectus abdominis (medially), and inguinal ligament (inferiorly)
Intraperitoneal and Retroperitoneal Relationships
- Intraperitoneal organ: organ that is almost totally covered with peritoneum
- Retroperitoneal organ: organ that is located posterior to the peritoneal sac and is only covered with peritoneum anteriorly
Peritoneal Folds
- Ligament: two-layered peritoneal fold that connects an organ to the abdominal wall or another organ
- Examples:
- Falciform ligament: connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
- Coronary ligament: connects the liver to the diaphragm
- Splenorenal ligament: connects the spleen to the left kidney
- Gastrosplenic ligament: connects the spleen to the stomach
- Omentum: peritoneal fold that passes from the stomach and proximal part of the duodenum to another organ
- Lesser omentum: two-layered peritoneal fold that connects the lesser curvature of the stomach and the 1st part of the duodenum to the visceral surface of the liver
- Greater omentum: hangs down from the greater curvature of the stomach, like an "apron", in front of the loops of the jejunum and ileum
- Mesentery: two-layered peritoneal fold that connects the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall
- Allows blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves to reach the intestines from the posterior abdominal wall
- Examples:
- Mesentery of small intestine (or just simply "the mesentery"): connects the loops of the jejunum and ileum to the posterior abdominal wall
- Transverse mesocolon (mesentery of transverse colon): connects the transverse colon to the posterior abdominal wall
- Sigmoid mesocolon (mesentery of sigmoid colon): connects the sigmoid colon to the posterior abdominal and pelvic walls
Secondary Retroperitoneal Organs
- Early in development, all parts of the digestive tract are intraperitoneal and have a mesentery
- With further development, some parts of the digestive tract adhere to the posterior abdominal wall, lose their mesentery, and become retroperitoneal (more fixed in position)
Lesser Sac (Omental Bursa)
- Part of the peritoneal cavity located posterior to the lesser omentum and stomach
- Superior recess: upward extension of the lesser sac, located between the liver and diaphragm
- Inferior recess: downward extension of the lesser sac between the 2 anterior and 2 posterior layers of the greater omentum
- On the left, it is closed by the spleen, gastrosplenic ligament, and splenorenal ligament
- On the right, it communicates with the greater sac via the omental (epiploic) foramen
Epiploic (Omental) Foramen (Opening of Lesser Sac, Foramen of Winslow)
- Boundaries:
- Anteriorly: right, free border of the lesser omentum (hepatoduodenal ligament)
- Posteriorly: inferior vena cava
- Superiorly: caudate lobe of the liver
- Inferiorly: 1st part of the duodenum
Peritoneal Folds in the Lower Part of the Anterior Abdominal Wall
- 1 median umbilical fold: formed by the peritoneum that covers the median umbilical ligament
- 2 medial umbilical folds (1 on each side): formed by the peritoneum that covers the medial umbilical ligaments
- 2 lateral umbilical folds (1 on each side): formed by the peritoneum that covers the inferior epigastric vessels
Other Subdivisions of the Abdominal Cavity
- The transverse colon and its mesentery (transverse mesocolon) divide the abdominal cavity into supracolic and infracolic compartments
- Supracolic compartment: located above the transverse colon and its mesentery, contains the stomach, liver, gallbladder, and spleen
- Infracolic compartment: located below the transverse colon and its mesentery, contains most of the small and large intestines
- Free communication between the supracolic and infracolic compartments via the paracolic gutters
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.