Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does the glottis play in swallowing?
What role does the glottis play in swallowing?
- It relaxes to permit airflow to the lungs.
- It closes to prevent aspiration. (correct)
- It assists in producing saliva.
- It opens to allow food to enter the trachea.
What is the function of the esophageal sphincter in swallowing?
What is the function of the esophageal sphincter in swallowing?
- It allows food to pass from the esophagus to the stomach. (correct)
- It closes to prevent backflow of food into the pharynx.
- It prevents food from entering the trachea.
- It helps produce saliva for digestion.
Which statement correctly describes the action of the salivary glands during swallowing?
Which statement correctly describes the action of the salivary glands during swallowing?
- They cover the glottis to block the airway.
- They aid in breaking down food mechanically.
- They decrease saliva production to eliminate choking risks.
- They increase saliva production to enhance taste. (correct)
Why is it important for the glottis to close during swallowing?
Why is it important for the glottis to close during swallowing?
What happens to the upper esophageal sphincter during swallowing?
What happens to the upper esophageal sphincter during swallowing?
What role does myosin light-chain phosphorylation play in muscle contraction?
What role does myosin light-chain phosphorylation play in muscle contraction?
How is swallowing controlled in the body?
How is swallowing controlled in the body?
What initiates the pressure responses in the swallowing mechanism?
What initiates the pressure responses in the swallowing mechanism?
What happens when swallowing occurs according to the control center?
What happens when swallowing occurs according to the control center?
Which of the following describes the function of gap junctions in single-unit smooth muscle?
Which of the following describes the function of gap junctions in single-unit smooth muscle?
What is the primary role of mechanoreceptors during chewing?
What is the primary role of mechanoreceptors during chewing?
In the contraction process of smooth muscle, what follows the phosphorylation of myosin?
In the contraction process of smooth muscle, what follows the phosphorylation of myosin?
What is the primary functional consequence of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
What is the primary functional consequence of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
Which nerve type is responsible for the control of chewing?
Which nerve type is responsible for the control of chewing?
What triggers a cycle of contractions in the context of swallowing and jaw movement?
What triggers a cycle of contractions in the context of swallowing and jaw movement?
What triggers peristaltic waves when food is swallowed?
What triggers peristaltic waves when food is swallowed?
What role do peristaltic waves play in digestion?
What role do peristaltic waves play in digestion?
What could happen if the lower esophageal sphincter fails to close after a meal?
What could happen if the lower esophageal sphincter fails to close after a meal?
What is the consequence of a large food bolus during swallowing?
What is the consequence of a large food bolus during swallowing?
What initiates the closure of the lower esophageal sphincter after swallowing?
What initiates the closure of the lower esophageal sphincter after swallowing?
What role does calcium play in muscle contraction?
What role does calcium play in muscle contraction?
How does the swallowing process affect the esophagus?
How does the swallowing process affect the esophagus?
Which type of channels allow calcium to enter the cell during muscle contraction?
Which type of channels allow calcium to enter the cell during muscle contraction?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the sensation when swallowing?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the sensation when swallowing?
What structural feature do thin filaments have in muscle cells?
What structural feature do thin filaments have in muscle cells?
What initiates muscle contraction in response to electrical signals?
What initiates muscle contraction in response to electrical signals?
What is a consequence of increased cytosolic calcium in muscle cells?
What is a consequence of increased cytosolic calcium in muscle cells?
How do thick and thin filaments interact to cause muscle contraction?
How do thick and thin filaments interact to cause muscle contraction?
Which component is NOT directly involved in muscle contraction?
Which component is NOT directly involved in muscle contraction?
What happens to the plasma membrane during the contraction process?
What happens to the plasma membrane during the contraction process?
Which statement about muscle contraction is true?
Which statement about muscle contraction is true?
Which factor is crucial for bridge formation during muscle contraction?
Which factor is crucial for bridge formation during muscle contraction?
What role does the sphincter play in relation to the stomach?
What role does the sphincter play in relation to the stomach?
Which substance is particularly involved in dissolving food?
Which substance is particularly involved in dissolving food?
What common condition can be exacerbated during pregnancy related to digestive issues?
What common condition can be exacerbated during pregnancy related to digestive issues?
What function does bile serve in digestion?
What function does bile serve in digestion?
What can cause increased pressure in the abdomen during pregnancy?
What can cause increased pressure in the abdomen during pregnancy?
Which enzyme is responsible for initiating the digestion of carbohydrates?
Which enzyme is responsible for initiating the digestion of carbohydrates?
What is the primary purpose of the sphincter in the digestive system?
What is the primary purpose of the sphincter in the digestive system?
What role does saliva play in digestion?
What role does saliva play in digestion?
Flashcards
Muscle Contraction
Muscle Contraction
The process of muscle contraction, where thick and thin filaments slide past each other, causing muscle shortening.
Myosin Filaments
Myosin Filaments
Thick protein filaments found in muscle fibers, responsible for generating force during muscle contraction.
Actin Filaments
Actin Filaments
Thin protein filaments found in muscle fibers, which are pulled by myosin filaments during muscle contraction.
Dense Bodies
Dense Bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcium-Calmodulin Binding
Calcium-Calmodulin Binding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regulatory Proteins
Regulatory Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myosin Anchor Point
Myosin Anchor Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous Electrical Activity
Spontaneous Electrical Activity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitters and Hormones
Neurotransmitters and Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Contraction State
Muscle Contraction State
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myosin Contraction and Relaxation
Myosin Contraction and Relaxation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Unit Smooth Muscle
Single-Unit Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gap Junctions
Gap Junctions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation
Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristaltic Waves in Esophagus
Peristaltic Waves in Esophagus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophageal Mechanoreceptors
Esophageal Mechanoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Peristalsis
Secondary Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Esophageal Sphincter Closure
Lower Esophageal Sphincter Closure
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the glottis and why is it important during swallowing?
What is the glottis and why is it important during swallowing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the esophageal sphincter during swallowing?
What is the role of the esophageal sphincter during swallowing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of saliva in swallowing?
What is the role of saliva in swallowing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the food pharynx and what is its role in swallowing?
What is the food pharynx and what is its role in swallowing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is aspiration and how does the glottis prevent it?
What is aspiration and how does the glottis prevent it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a sphincter?
What is a sphincter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main role of the stomach in digestion?
What is the main role of the stomach in digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of enzymes in digestion?
What is the role of enzymes in digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux?
What causes heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is heartburn more common during pregnancy?
Why is heartburn more common during pregnancy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the stomach acidic?
Why is the stomach acidic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the stomach break down food?
How does the stomach break down food?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do sphincters control the movement of food?
How do sphincters control the movement of food?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Smooth Muscle
- Filaments oriented diagonally
- No striations
- Thin filaments anchored to dense bodies
- Contraction involves shortening and ballooning
Calcium Source
- Released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
- Extracellular calcium enters via channels
Smooth Muscle Contractions
- Spontaneous electrical activity
- Neurotransmitters from autonomic nerves
- Hormones
- Changes in extracellular fluid composition
- Stretch
Gap Junctions
- Single-unit smooth muscle cells are synchronized
- Action potentials spread between cells via gap junctions
Chewing
- Controlled by somatic nerves to the mouth and jaw
- Mechanical pressure of food on hard plate/gums inhibits muscles, closing the jaw
- Pressure initiates new cycles of contractions
Saliva
- Produced by salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, sublingual)
- Increased by sight, smell, taste, volume
- Parasympathetic stimulation (PNS)
- Moistens and lubricates food
- Aids in digesting carbohydrates (amylase)
- Dissolves food
- Kills bacteria
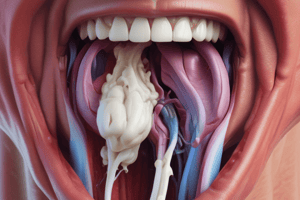
Swallowing
- Initiated by tongue pushing food to pharynx
- Soft palate elevates to close nasal passages
- Epiglottis covers glottis
- Prevents aspiration
- Upper esophageal sphincter relaxes to permit food passage
- Peristaltic waves push food into the stomach
- Esophageal mechanoreceptors signal the swallowing center
- Secondary peristalsis
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.