Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the result of a slower pace of bone remodeling as we age?
What is the result of a slower pace of bone remodeling as we age?
- Increased collagen in tendons and ligaments
- Stronger bones
- Weaker, more fragile bones (correct)
- Faster healing of fractures
Which type of muscle is involved in vasoconstriction or vasodilation of blood vessels?
Which type of muscle is involved in vasoconstriction or vasodilation of blood vessels?
- Striated muscle
- Smooth muscle (correct)
- Cardiac muscle
- Skeletal muscle
What is a characteristic of skeletal muscle?
What is a characteristic of skeletal muscle?
- Involuntary tissue with branched fibers
- Uninucleate, involuntary tissue with tapered edges
- Type of tissue found in hollow organs
- Striated tissue with unbranched fibers that is voluntary (correct)
What is the result of the reduction in collagen in tendons, ligaments, and skin as we age?
What is the result of the reduction in collagen in tendons, ligaments, and skin as we age?
What is the effect of the thinning of disks between the bodies of vertebrae as we age?
What is the effect of the thinning of disks between the bodies of vertebrae as we age?
Which muscle is responsible for closing the eyelids and producing facial expressions such as smiling and squinting?
Which muscle is responsible for closing the eyelids and producing facial expressions such as smiling and squinting?
Which of the following muscles is involved in the action of protruding the lips?
Which of the following muscles is involved in the action of protruding the lips?
Which muscle is located in the lower and middle back and is responsible for adduction of the arm?
Which muscle is located in the lower and middle back and is responsible for adduction of the arm?
Which muscle is involved in the action of tilting and rotating the head to the opposite side?
Which muscle is involved in the action of tilting and rotating the head to the opposite side?
Which muscle is responsible for flexion of the elbow and supination of the forearm?
Which muscle is responsible for flexion of the elbow and supination of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for elevating the shoulder girdle?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for elevating the shoulder girdle?
Which muscle is involved in the action of rotating the arm inward?
Which muscle is involved in the action of rotating the arm inward?
What is the main characteristic of the muscular system?
What is the main characteristic of the muscular system?
Which type of muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs such as the stomach and bladder?
Which type of muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs such as the stomach and bladder?
What is the term for a type of joint that allows for rotational movement?
What is the term for a type of joint that allows for rotational movement?
What is the term for the movement of bending the elbow?
What is the term for the movement of bending the elbow?
Which muscle is responsible for extension of the knee and assists in extension of the hip?
Which muscle is responsible for extension of the knee and assists in extension of the hip?
What is the term for a type of joint that allows for movement in multiple planes?
What is the term for a type of joint that allows for movement in multiple planes?
What is the term for the movement of rotating the forearm to face the palm downward?
What is the term for the movement of rotating the forearm to face the palm downward?
What is the term for a muscle strain injury?
What is the term for a muscle strain injury?
Which muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle and inversion of the foot?
Which muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle and inversion of the foot?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
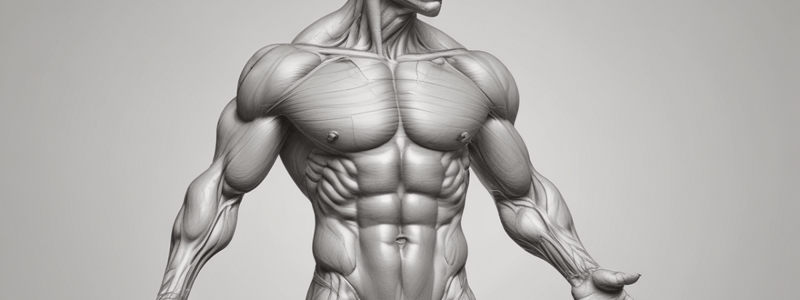
Muscle Descriptions and Basic Actions
- Orbicularis Oris: surrounds the lips, responsible for pursing, closing, protruding, and compressing lips.
- Orbicularis Oculi: surrounds the eye, responsible for closing eyelids and facial expressions.
- Sternocleidomastoid (SCM): connects the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process, responsible for flexing the neck forward and tilting/rotating the head.
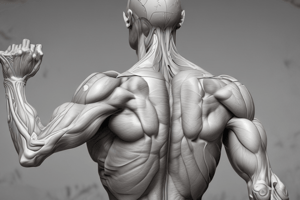
- Trapezius: located in the upper back and neck, responsible for elevating the shoulder girdle, retracting the scapula, and depressing the shoulder girdle.
- Serratus Anterior: located in the lateral aspect of the thorax, responsible for protracting the scapula and stabilizing the scapula.
- Pectoralis Major: located in the chest, responsible for adduction, medial rotation, and flexion of the shoulder.
- Latissimus Dorsi: located in the lower and middle back, responsible for adduction, extension of the shoulder, and medial rotation.
- Deltoid: located in the shoulder, responsible for flexing, abducting, and extending the shoulder joint.
- Biceps Brachii: located in the front of the upper arm, responsible for flexing the elbow and supinating the forearm.
- Triceps Brachii: located in the back of the upper arm, responsible for extending the elbow and assisting in shoulder extension.
- Flexor Carpi Muscles: located in the anterior forearm, responsible for flexing the wrist and assisting in flexing the elbow.
- Extensor Carpi Muscles: located in the posterior forearm, responsible for extending the wrist and assisting in extending the fingers.
- Rectus Abdominis: located in the anterior abdominal wall, responsible for flexing the trunk and assisting in stabilization.
- External Oblique: located in the lateral abdominal wall, responsible for flexing and rotating the trunk, and compressing the abdomen.
- Gluteus Maximus: located in the buttocks, responsible for extending the hip, externally rotating the hip, and assisting in stabilization.
- Hamstrings: located in the back of the thigh, responsible for flexing the knee and extending the hip.
- Adductor Muscles: located in the medial thigh, responsible for adducting the hip, and assisting in flexion and extension of the hip.
- Tibialis Anterior: located in the anterior lower leg, responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle and inversion of the foot.
- Gastrocnemius: located in the back of the lower leg, responsible for plantar flexion of the ankle and flexion of the knee.
Characteristics of Muscles
- Smooth Muscle: makes up walls of hollow organs, has no striations, moves involuntarily, and contracts slowly.
- Cardiac Muscle: makes up walls of the heart, has striated cells, and generates electrical impulses to contract.
- Skeletal Muscle: makes up the largest amount of body muscle tissue, has striated cells, and is stimulated by the nervous system to contract voluntarily.
Common Diseases and Conditions of the Muscles
- Strain: injury to a muscle and its surrounding tendons, causing pain, limited motion, muscle spasms, and inflammation.
- Treatment: RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation)
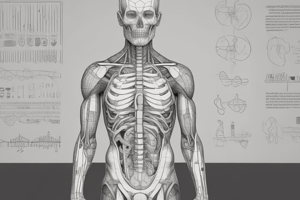
Functions of the Skeletal System
- Serves as framework for body: protects brain, spinal cord, and other structures.
- Works with muscles to produce movement: stores calcium and produces blood cells.
- Types of Joints: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
- Types of Synovial Joints: gliding, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket.
Movement and Actions
- Flexion and Extension: flexion bends the elbow, extension straightens the knee.
- Abduction and Adduction: abduction raises the arm sideways, adduction brings the leg towards the body.
- Rotation: medial rotation rotates the leg inward, lateral rotation rotates the arm outward.
- Circumduction: moving the arm in a circular motion.
- Pronation and Supination: pronation rotates the forearm to face the palm downward, supination rotates the forearm to face the palm upward.
- Dorsiflexion and Plantar Flexion: dorsiflexion bends the foot upward, plantar flexion points the toes downward.
- Inversion and Eversion: inversion turns the sole of the foot inward, eversion turns the sole of the foot outward.
Effects of Aging on the Skeletal System
- Slower pace of bone remodeling: weaker, more fragile bones.
- Osteoporosis: extreme loss of bone mass.
- Decreased ability to form proteins: fractures heal slowly.
- Reduction in collagen in tendons, ligaments, and skin: stiffness.
- Thinning of disks between bodies of vertebrae: height loss.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.