Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the scientific name of the heart muscle?
What is the scientific name of the heart muscle?
- Pericardium
- Myocardium (correct)
- Epicardium
- Endocardium
What is the shape of the heart?
What is the shape of the heart?
- Rectangle
- Oval
- Triangle (correct)
- Circle
How many chambers does the heart have?
How many chambers does the heart have?
- 2
- 5
- 3
- 4 (correct)
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
How many main coronary arteries are there?
How many main coronary arteries are there?
Which artery supplies blood to the left heart muscle?
Which artery supplies blood to the left heart muscle?
What is the name of the artery that branches from the left coronary artery and supplies blood to the anterior interventricular area?
What is the name of the artery that branches from the left coronary artery and supplies blood to the anterior interventricular area?
In what percentage of individuals does the left circumflex artery contribute to the posterior interventricular artery?
In what percentage of individuals does the left circumflex artery contribute to the posterior interventricular artery?
What is the average weight of a male heart?
What is the average weight of a male heart?
What is the function of the SA node in the heart?
What is the function of the SA node in the heart?
What is the normal heart rate at rest?
What is the normal heart rate at rest?
What is the purpose of the capillaries in the circulatory system?
What is the purpose of the capillaries in the circulatory system?
What is the pulmonary circuit responsible for?
What is the pulmonary circuit responsible for?
What are the two separate loops of the circulatory system?
What are the two separate loops of the circulatory system?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Heart Structure
- The heart is a triangular organ with a broad superior surface and a tapering apex.
- It consists of four chambers: left and right atria, and left and right ventricles.
- The heart has four valves: tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves.
Heart Layers
- The heart wall is composed of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
- These layers are embryologically equivalent to the three layers of blood vessels: tunica adventitia, tunica media, and tunica intima.
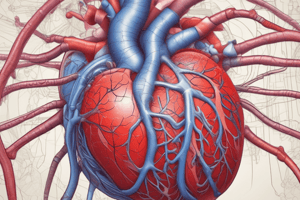
Coronary Arteries
- Coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation.
- They originate from the root of the aorta and wrap around the entire heart, supplying oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
- The two main coronary arteries are the left coronary artery (LCA) and the right coronary artery (RCA).
- LCA supplies blood to the left heart muscle (left ventricle and left atrium).
- RCA supplies blood to the right side, SA node, AV node, and bundle of His between the ventricles.
Coronary Artery Branches
- LCA branches into the left anterior descending artery (LAD), left marginal artery (LMA), and left circumflex artery (Cx).
- In 20-25% of individuals, the left circumflex artery contributes to the posterior interventricular artery (PIv).
- RCA branches into the right marginal artery (RMA) and, in 80-85% of individuals, the posterior interventricular artery (PIv).
Heart Size and Weight
- Heart length, width, and thickness are typically 12 cm, 8.5 cm, and 6 cm, respectively.
- The mean weight of the heart is 280-340 g in males and 230-280 g in females.
Heart Function
- The heart pumps blood throughout the body by contracting its muscle.
- It controls heart rate and maintains blood pressure through electrical signals produced in the SA node.
SA Node
- The SA node, also known as the sinus node, is a specialized myocardial structure that initiates electrical impulses to stimulate contraction.
- It is located in the atrial wall at the junction of the superior caval vein and the right atrium.
- The signal then passes through the AV node to the lower heart chambers (ventricles), causing them to contract or pump.
Heart Rate
- Heart rate depends on the rate at which the SA node produces action potentials.
- At rest, heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Blood Vessels
- There are five types of blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system is divided into two separate loops: the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit.
- The pulmonary circuit exchanges blood between the heart and the lungs for oxygenation.
- The systemic circuit distributes blood throughout all other systems and tissues of the body.
- Both circuits begin and end in the heart.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.