Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary source of the urogenital system's development?
What is the primary source of the urogenital system's development?
- Ectoderm
- Intermediate mesoderm (correct)
- Endoderm
- Mesothelial layer
What is the function of the metanephric diverticulum (ureteric bud) in the development of the ureter?
What is the function of the metanephric diverticulum (ureteric bud) in the development of the ureter?
- It creates major calyces only.
- It forms the urinary bladder.
- It develops the mesonephric ducts.
- It elongates and becomes the ureter. (correct)
Which part of the cloaca contributes to the urinary bladder's formation?
Which part of the cloaca contributes to the urinary bladder's formation?
- Ventral urogenital sinus (correct)
- Dorsal rectum
- Cloacal membrane
- Hindgut diverticulum
How does the renal pelvis form during ureter development?
How does the renal pelvis form during ureter development?
Which structure is formed from the urogenital sinus during bladder development?
Which structure is formed from the urogenital sinus during bladder development?
What happens to the mesonephric ducts during the development process?
What happens to the mesonephric ducts during the development process?
What is the role of the urorectal septum in developing the cloaca?
What is the role of the urorectal septum in developing the cloaca?
How many times may the new buds from each calyx subdivide during development?
How many times may the new buds from each calyx subdivide during development?
What is the caudal phallic part of the urogenital sinus responsible for?
What is the caudal phallic part of the urogenital sinus responsible for?
What primarily distinguishes the major calyces in ureter development?
What primarily distinguishes the major calyces in ureter development?
What structure forms the urachus after becoming a thick fibrous cord?
What structure forms the urachus after becoming a thick fibrous cord?
Which embryonic tissue contributes to the development of the smooth muscles of the bladder?
Which embryonic tissue contributes to the development of the smooth muscles of the bladder?
At what age does the urinary bladder begin to enter the greater pelvis?
At what age does the urinary bladder begin to enter the greater pelvis?
Which part of the male urethra is derived from the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus?
Which part of the male urethra is derived from the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus?
What anomaly occurs due to the incomplete division of the metanephric diverticulum?
What anomaly occurs due to the incomplete division of the metanephric diverticulum?
From which part of the urogenital sinus is the entire female urethra derived?
From which part of the urogenital sinus is the entire female urethra derived?
What is a potential cystic anomaly that can occur related to the urachus?
What is a potential cystic anomaly that can occur related to the urachus?
Which fold unites to form the greater part of the male urethra?
Which fold unites to form the greater part of the male urethra?
What is the role of the outer fold known as the genital fold?
What is the role of the outer fold known as the genital fold?
The part of the penile urethra in the glans of the penis is derived from which tissue?
The part of the penile urethra in the glans of the penis is derived from which tissue?
What describes a urachal fistula?
What describes a urachal fistula?
Which congenital anomaly results in the urethral opening being on the ventral surface of the penis?
Which congenital anomaly results in the urethral opening being on the ventral surface of the penis?
What condition is characterized by the posterior bladder wall protruding through a defect in the abdominal wall?
What condition is characterized by the posterior bladder wall protruding through a defect in the abdominal wall?
Which congenital condition is very rare and allows urine to escape from the umbilicus?
Which congenital condition is very rare and allows urine to escape from the umbilicus?
In which condition does the external urethral orifice appear on the dorsal surface of the penis?
In which condition does the external urethral orifice appear on the dorsal surface of the penis?
A congenital recto-urethral fistula generally results in which of the following complications?
A congenital recto-urethral fistula generally results in which of the following complications?
Which anatomical structure is predominantly involved in the development of urachal conditions?
Which anatomical structure is predominantly involved in the development of urachal conditions?
What condition characteristically exposes the trigone of the bladder?
What condition characteristically exposes the trigone of the bladder?
What is a notable characteristic of a urachal sinus?
What is a notable characteristic of a urachal sinus?
Flashcards
Urachal Sinus
Urachal Sinus
A remnant of the lumen of the urachus that persists in the inferior part of the urachus.
Urachal Fistula
Urachal Fistula
The entire urachus remains patent, creating a connection between the bladder and the umbilicus, allowing urine to escape from the umbilicus.
Ectopia Vesica
Ectopia Vesica
A condition where the posterior bladder wall protrudes through a defect in the anterior abdominal wall, below the umbilicus.
Hypospadias
Hypospadias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epispadias
Epispadias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congenital Recto-Urethral Fistula
Congenital Recto-Urethral Fistula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urachal Anomalies
Urachal Anomalies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metanephric diverticulum (ureteric bud)
Metanephric diverticulum (ureteric bud)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patent Urachus
Patent Urachus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter
Ureter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urachal Cyst
Urachal Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal pelvis
Renal pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major calyces
Major calyces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urachal Sinus
Urachal Sinus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minor calyces
Minor calyces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cloaca
Cloaca
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urorectal septum
Urorectal septum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urogenital sinus
Urogenital sinus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vesical (vesicourethral) part of the urogenital sinus
Vesical (vesicourethral) part of the urogenital sinus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oblique entry of ureters into the bladder
Oblique entry of ureters into the bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of the Urinary Bladder
Development of the Urinary Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urachus
Urachus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Position of the Urinary Bladder
Position of the Urinary Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of Female Urethra
Development of Female Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of Male Urethra: Proximal and Distal Parts
Development of Male Urethra: Proximal and Distal Parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of Male Urethra: Penile Parts
Development of Male Urethra: Penile Parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Formation of the Urethra and Scrotum
Formation of the Urethra and Scrotum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urogenital Membrane
Urogenital Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bifid Renal Pelvis and Ureter
Bifid Renal Pelvis and Ureter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retrocaval Ureter
Retrocaval Ureter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
AL AZHAR UNIVERSITY - Anatomy & Embryology
- Faculty: Medicine for Girls
- Year: 2, Semester 3
- Academic Year: 2023/2024
- Module Name: Renal module
- Code: IPM-07-20318
- Credit Hours: 5
- Topic: Development of the Ureter, Urinary Bladder & Urethra
Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
- ILO 1: Describe the development of the ureter and its congenital anomalies.
- ILO 2: Understand the development of the urinary bladder and its congenital anomalies.
- ILO 3: Describe the development of the urethra and differentiate between its congenital anomalies.
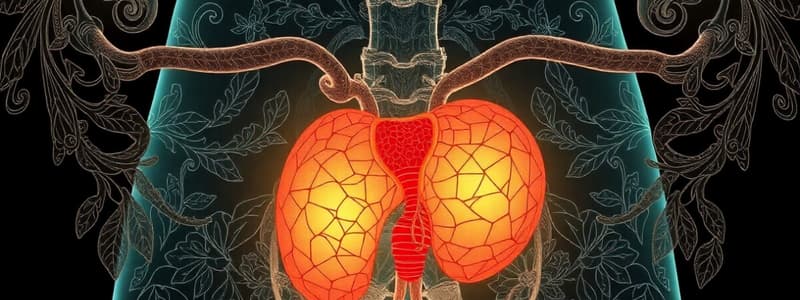
Development of the Ureter
- The urogenital system develops from the intermediate mesoderm.
- The metanephric diverticulum (ureteric bud) arises as an outgrowth from the mesonephric duct, entering the cloaca.
- It grows dorsally and cranially.
- The stalk of the ureteric bud becomes the ureter.
- The expanded cranial end of the bud forms the funnel-shaped renal pelvis.
- The renal pelvis divides into two, then into multiple parts, forming the major and minor calyces.
- These structures repeatedly divide, eventually creating the collecting ducts and renal tubules.
Development of the Urinary Bladder
- The urinary bladder develops from two sources.
- The vesical part of the urogenital sinus forms the main part of the bladder.
- The caudal ends of the mesonephric ducts form the trigone of the bladder.
- The epithelium of the bladder originates from the endoderm of the vesical part of the urogenital sinus.
- The smooth muscles of the bladder develop from adjacent mesoderm.
Development of the Urethra
- In females, the entire urethra is derived from the endoderm of the urogenital sinus.
- Connective tissue and smooth muscle derive from the splanchnic mesenchyme.
- In males, the proximal part of the prostatic urethra (as far as the ejaculatory ducts) is formed from the vesicourethral part of the urogenital sinus.
- The distal part and membranous parts of the prostatic urethra originate from the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus.
- The greater part of the penile urethra arises from the phallic part of the urogenital sinus.
- The glans of the penis is formed from surface ectoderm.
Urogenital Membrane
- There are two folds developing from the edges of the phallic part of the urogenital sinus.
- An inner fold, the urethral fold, forms the major part of the urethra.
- An outer fold, the genital fold, forms the scrotum in males and the labia in females.
- The urogenital membrane represents the ventral portion of the cloaca membrane.
- It eventually closes, incorporating the phallic part of the urogenital sinus.
Congenital Anomalies
- Ureter: Bifid renal pelvis and ureter, Retrocaval ureter, Megalo-ureter, Ureterocele
- Bladder: Urachal cysts, Urachal sinus, Urachal fistula
- Urethra: Hypospadias, Epispadias, Congenital recto-urethral fistula
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.