Podcast
Questions and Answers
Quel organe est principalement responsable de la circulation sanguine chez le chien ?
Quel organe est principalement responsable de la circulation sanguine chez le chien ?
- Les reins
- Le foie
- Le cœur (correct)
- Les poumons
Quel système est impliqué dans le filtrage des déchets du sang chez le chien ?
Quel système est impliqué dans le filtrage des déchets du sang chez le chien ?
- Système digestif
- Système respiratoire
- Système excréteur (correct)
- Système nerveux
Quelle partie du système nerveux connecte le cerveau au reste du corps ?
Quelle partie du système nerveux connecte le cerveau au reste du corps ?
- Le système digestif
- Les nerfs périphériques
- La moelle épinière (correct)
- Le cœur
Quel organe est responsable de l'absorption des nutriments ?
Quel organe est responsable de l'absorption des nutriments ?
Quel type de neurones est responsable du contrôle des mouvements chez le chien ?
Quel type de neurones est responsable du contrôle des mouvements chez le chien ?
Quel type de squelette compose le système musculosquelettique canin ?
Quel type de squelette compose le système musculosquelettique canin ?
Quelle est la fonction principale des tendons dans le système musculosquelettique des chiens ?
Quelle est la fonction principale des tendons dans le système musculosquelettique des chiens ?
Qu'est-ce qui facilite l'échange de gaz et de nutriments entre le sang et les tissus dans le système circulatoire canin ?
Qu'est-ce qui facilite l'échange de gaz et de nutriments entre le sang et les tissus dans le système circulatoire canin ?
Pourquoi le système musculosquelettique est-il essentiel pour les chiens ?
Pourquoi le système musculosquelettique est-il essentiel pour les chiens ?
Quel composant du sang est responsable du transport de l'oxygène ?
Quel composant du sang est responsable du transport de l'oxygène ?
Quels sont les os principaux des membres avant chez le chien ?
Quels sont les os principaux des membres avant chez le chien ?
Comment les articulations contribuent-elles à la mobilité des chiens ?
Comment les articulations contribuent-elles à la mobilité des chiens ?
Quel est le rôle principal du cœur dans le système circulatoire canin ?
Quel est le rôle principal du cœur dans le système circulatoire canin ?
Flashcards
Système nerveux du chien
Système nerveux du chien
Un réseau complexe de nerfs recevant et transmettant l'information dans le corps du chien.
Fonction du cerveau du chien
Fonction du cerveau du chien
Le centre des fonctions cognitives élevées telles que la pensée, l'apprentissage et la mémoire chez le chien.
Système nerveux périphérique du chien
Système nerveux périphérique du chien
Transmet des signaux entre le système nerveux central (cerveau et moelle épinière) et le reste du corps, y compris les organes des sens.
Différents types de neurones
Différents types de neurones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rôle du système nerveux dans le corps du chien
Rôle du système nerveux dans le corps du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Système squelettique du chien
Système squelettique du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Système musculaire du chien
Système musculaire du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articulations du chien
Articulations du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Système circulatoire canin
Système circulatoire canin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fonction du cœur
Fonction du cœur
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role du sang
Role du sang
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membres antérieurs du chien
Membres antérieurs du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membres postérieurs du chien
Membres postérieurs du chien
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
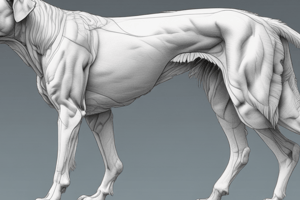
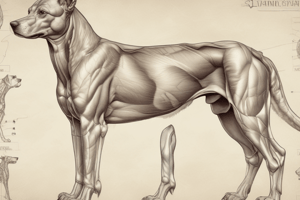
Anatomie du chien - Système Musculosquelettique
- The canine skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, and ligaments, providing support and structure.
- The dog's skeletal system is adapted for running, jumping, and other activities.
- Bones are divided into axial skeleton (skull, vertebrae, ribs) and appendicular skeleton (limbs).
- Muscles are responsible for movement, and are attached to bones via tendons.
- Muscles are of various shapes and sizes, tailored for specific functions within the body.
- Joints are points where two or more bones meet, allowing for movement and flexibility.
- Joints contain cartilage and synovial fluid, which cushion and lubricate the joint.
- Ligaments connect bones to bones, while tendons connect muscles to bones.
- Examples of bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and various vertebrae.
- Muscles include the quadriceps, pectorals, and gastrocnemius.
- Healthy musculoskeletal systems are crucial for proper posture and movement in dogs.
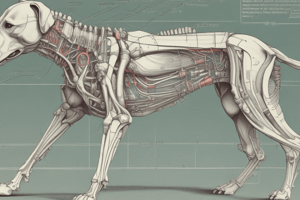
Anatomie du chien - Système Circulatoire
- The canine circulatory system is a closed system of blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries).
- The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body.
- The heart rate varies based on the dog's activity level and overall health.
- Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body.
- Blood also removes waste products like carbon dioxide.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the body.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries facilitate the exchange of gases and nutrients between blood and tissues.
- Blood consists of red blood cells (transport oxygen), white blood cells (fight infection), and platelets (blood clotting).
- The cardiovascular system plays a vital role in delivering essential substances and removing waste materials in dogs.
Anatomie du chien - Anatomie Des Membres
- Dog limbs are adapted for various locomotion styles (walking, running, jumping).
- Forelimbs include the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges (digits).
- Hindlimbs include the femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges (digits).
- Muscles in the limbs are crucial for movement and support, demonstrating specialization for particular functions.
- Joints in the limbs are designed for flexibility and stability during locomotion.
- Ligaments and tendons in the limbs provide support and allow for specific range of motion.
Anatomie du chien - Anatomie Interne
- Internal organs of the dog include the lungs, heart, liver, kidneys, and stomach.
- Each organ serves specific functions relating to respiration, circulation, digestion, excretion, and more.
- The location and precise arrangement of these internal organs vary according to the dog breeds
- The respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange, breathing in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
- The digestive system breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
- The excretory system filters waste products from the blood and eliminates them from the body.
- The nervous system controls bodily functions, and this can be broadly divided.
Anatomie du chien - Système Nerveux
- The canine nervous system is a complex network of nerves for receiving and transmitting information around the body.
- The brain and spinal cord are central components, processing and coordinating information.
- The brain is responsible for higher-level functions, such as thought processes, learning, and memory.
- The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body and relays nerve impulses.
- Peripheral nerves carry signals to and from various parts of the body.
- Sensory neurons transmit external stimuli, while motor neurons control movement and other actions.
- The nervous system is involved in regulating almost all bodily functions.
- Sensory organs like the eyes, ears, and nose are extensions of the nervous system, allowing dogs to interact with the environment.
- The nervous system's effectiveness in dogs ensures smooth bodily operations and appropriate responses to stimuli.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.