Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the origin of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the origin of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
- Ribs 4-13 and thoracolumbar fascia (correct)
- Ribs 1-3 and thoracolumbar fascia
- Costal arch, rectus abdominis, and linea alba
- Tuber coxae, thoracolumbar fascia and inguinal ligament
What is the action of the external abdominal oblique muscle in relation to the vertebral column?
What is the action of the external abdominal oblique muscle in relation to the vertebral column?
- Rotation of the vertebral column
- Extension of the vertebral column
- Stabilization of the vertebral column
- Flexion of the vertebral column (correct)
What is the insertion of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the insertion of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
- Costal arch and rectus abdominis
- Prepubic tendon and inguinal ligament
- Tuber coxae and thoracolumbar fascia
- Linea alba by a wide aponeurosis (correct)
What is the direction of the fibers of the internal abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the direction of the fibers of the internal abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the origin of the internal abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the origin of the internal abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the common innervation of the muscles of the abdominal walls?
What is the common innervation of the muscles of the abdominal walls?
What is the fiber orientation of the external abdominal oblique m?
What is the fiber orientation of the external abdominal oblique m?
What is the function of the external abdominal oblique muscle in relation to respiration?
What is the function of the external abdominal oblique muscle in relation to respiration?
What is the main function of the abdominal muscles?
What is the main function of the abdominal muscles?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the abdominal wall layers?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the abdominal wall layers?
What is the purpose of the inguinal canal (for males specifically).
What is the purpose of the inguinal canal (for males specifically).
What is the name of the structure that forms the boundary of the inguinal canal?
What is the name of the structure that forms the boundary of the inguinal canal?
What is the primary function of the cremaster muscle?
What is the primary function of the cremaster muscle?
What is the origin of the cremaster muscle?
What is the origin of the cremaster muscle?
What is the innervation of the cremaster muscle?
What is the innervation of the cremaster muscle?
What is the significance of the inguinal canal in clinical importance?
What is the significance of the inguinal canal in clinical importance?
What is the structure that contains the spermatic cord in males?
What is the structure that contains the spermatic cord in males?
What is the feminine counterpart of the vaginal tunic?
What is the feminine counterpart of the vaginal tunic?
What is the anatomical structure that courses through the superficial inguinal ring? (Hint: noted in males)
What is the anatomical structure that courses through the superficial inguinal ring? (Hint: noted in males)
Which of the following structures is NOT present in the inguinal canal (for both males and females)?
Which of the following structures is NOT present in the inguinal canal (for both males and females)?
What forms the rectus sheath?
What forms the rectus sheath?
What is the clinical importance of the rectus sheath?
What is the clinical importance of the rectus sheath?
What is the linea alba?
What is the linea alba?
What is the inguinal ligament?
What is the inguinal ligament?
What is the caudal limit of the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the caudal limit of the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
What is the prepubic tendon?
What is the prepubic tendon?
What is the function of the aponeuroses of the external and internal abdominal oblique muscles and transversus abdominis muscle?
What is the function of the aponeuroses of the external and internal abdominal oblique muscles and transversus abdominis muscle?
What is the superficial inguinal ring?
What is the superficial inguinal ring?
The abdomen is divided into three main regions. What are they? (State in order)
The abdomen is divided into three main regions. What are they? (State in order)
What region(s) make up the cranial abdomen?
What region(s) make up the cranial abdomen?
What regions make up the middle abdominal topographic region?
What regions make up the middle abdominal topographic region?
What regions make up the caudal abdominal region?
What regions make up the caudal abdominal region?
Match the direction of the fibers to it’s correct muscle
Match the direction of the fibers to it’s correct muscle
Match insertion to correct muscles
Match insertion to correct muscles
Match the origins to correct muscle
Match the origins to correct muscle
Which muscle of the abdominal wall is the deepest abdominal muscle?
Which muscle of the abdominal wall is the deepest abdominal muscle?
What 3 borders make up the deep Inguinal ring?
What 3 borders make up the deep Inguinal ring?
What muscle participates/contributes to the cranial border of the deep Inguinal ring?
What muscle participates/contributes to the cranial border of the deep Inguinal ring?
The ___________ m. is the muscle considered to be the medial border that contributes to forming the deep Inguinal ring
The ___________ m. is the muscle considered to be the medial border that contributes to forming the deep Inguinal ring
The _____________ is considered the latero-caudal border that participates in forming the deep Inguinal ring.
The _____________ is considered the latero-caudal border that participates in forming the deep Inguinal ring.
What 3 structures make up the deep Inguinal ring?
What 3 structures make up the deep Inguinal ring?
What feature/characteristic makes the superficial Inguinal ring distinct?
What feature/characteristic makes the superficial Inguinal ring distinct?
Flashcards
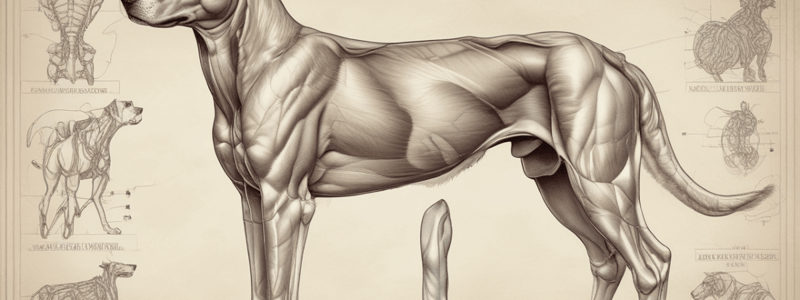
Abdominal Wall Layers
Abdominal Wall Layers
Four layers: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transversus abdominis, and rectus abdominis.
External Abdominal Oblique Origin
External Abdominal Oblique Origin
Ribs 4-13 and thoracolumbar fascia.
External Abdominal Oblique Insertion
External Abdominal Oblique Insertion
Linea alba via aponeurosis (a flat sheet).
External Abdominal Oblique Innervation
External Abdominal Oblique Innervation
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Abdominal Oblique Action
External Abdominal Oblique Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Location
Internal Abdominal Oblique Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Fiber Direction
Internal Abdominal Oblique Fiber Direction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Origin
Internal Abdominal Oblique Origin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Insertion
Internal Abdominal Oblique Insertion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Innervation
Internal Abdominal Oblique Innervation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Abdominal Oblique Action
Internal Abdominal Oblique Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus Sheath
Rectus Sheath
Signup and view all the flashcards
Linea Alba
Linea Alba
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inguinal Ligament
Inguinal Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Inguinal Ring
Superficial Inguinal Ring
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cremaster Muscle
Cremaster Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inguinal Canal
Inguinal Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prepubic Tendon
Prepubic Tendon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Abdominal Wall and Muscles
- The abdominal wall consists of four layers: external abdominal oblique muscle, internal abdominal oblique muscle, transversus abdominis muscle, and rectus abdominis muscle.
- The muscles of the abdominal wall function to compress the abdominal viscera, aid in expiration, urination, and defecation, and flex the vertebral column.
External Abdominal Oblique Muscle
- Origin: ribs 4-13 and thoracolumbar fascia
- Insertion: linea alba by a wide aponeurosis
- Innervation: ventral branches of thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves
- Action: compression of the abdominal viscera, aids in expiration, urination, defecation, parturition, and flexion of the vertebral column
Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle
- Location: medial to the external abdominal oblique muscle
- Fiber direction: cranioventrally
- Origin: tuber coxae, thoracolumbar fascia, and inguinal ligament
- Insertion: costal arch, rectus abdominis, linea alba, and prepubic tendon
- Innervation: ventral branches of thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves
- Action: compression and support of the abdominal viscera
Rectus Sheath
- Formed by aponeuroses of the external abdominal oblique muscle, internal abdominal oblique muscle, and transversus abdominis muscle
- Clinical importance: the holding layer when closing the abdomen
Linea Alba
- Midventral raphe (seam) where the aponeuroses of the left and right abdominal muscles meet
- A thick, white, fibrous structure that runs from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis
Inguinal Ligament
- Separates the inguinal canal from the vascular lacuna
- Caudal limit of the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle
Superficial Inguinal Ring
- Formed by the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique muscle
- Contains the spermatic cord, cremaster muscle, and vaginal process
Prepubic Tendon
- Strong attachment of abdominal muscles to the pelvis
- Contains several structures: external pudendal artery and vein, genitofemoral nerve, lymphatics, and the vaginal process (in females)
Inguinal Canal
- Clinical importance: neutering, cryptorchidism, and inguinal hernias
Cremaster Muscle
- Origin: caudal border of the internal abdominal oblique muscle
- Innervation: genitofemoral nerve
- Action: pulls the testis closer to the body in response to cold
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.