Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the body weight of a calf as mentioned?
What is the body weight of a calf as mentioned?
- 250 kg
- 500 kg
- 100 kg
- 75 kg (correct)
Which of the following best describes potassium sulfate?
Which of the following best describes potassium sulfate?
- A neutral compound with no charge
- An organic compound with carbon and hydrogen
- An ionic compound consisting of potassium and sulfate ions (correct)
- A molecular compound with shared electrons
How does potassium become a potassium ion in the formation of potassium sulfate?
How does potassium become a potassium ion in the formation of potassium sulfate?
- By losing one electron (correct)
- By losing two electrons
- By gaining an electron
- By gaining two electrons
What type of bond is formed in urea?
What type of bond is formed in urea?
Which elements are involved in forming the sulfate ion in potassium sulfate?
Which elements are involved in forming the sulfate ion in potassium sulfate?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes potassium sulfate from urea in terms of bonding?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes potassium sulfate from urea in terms of bonding?
What type of ions are formed during the creation of potassium sulfate?
What type of ions are formed during the creation of potassium sulfate?
In terms of body composition, which animal has a higher lipid content per kilogram of carcass as indicated in the content?
In terms of body composition, which animal has a higher lipid content per kilogram of carcass as indicated in the content?
Which statement correctly explains the formation of ionic bonds in potassium sulfate?
Which statement correctly explains the formation of ionic bonds in potassium sulfate?
What distinguishes the molecular structure of urea from that of potassium sulfate?
What distinguishes the molecular structure of urea from that of potassium sulfate?
Which of the following statements about the electronegativity in potassium sulfate is true?
Which of the following statements about the electronegativity in potassium sulfate is true?
Which of the following best characterizes the physical state of potassium sulfate?
Which of the following best characterizes the physical state of potassium sulfate?
What does the term 'lipid' refer to in the context of calf body composition?
What does the term 'lipid' refer to in the context of calf body composition?
In the formation of sulfate, how many electrons does sulfur need to gain?
In the formation of sulfate, how many electrons does sulfur need to gain?
How does the body weight of a steer compare to that of a calf?
How does the body weight of a steer compare to that of a calf?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
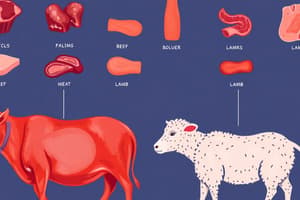
Overall Composition of Beef Animal Body
- Calf body weight: 75 kg; Steer body weight: 500 kg.
- Values are presented in grams per kilogram of beef carcass.
- Example: 66 g kg⁻¹ of lipids in a calf indicates 66 grams of lipids per kilogram of the calf’s carcass.
Chemical Composition of Fertilizers
- Discusses common inorganic fertilizers and their components.
- Highlights potential hazards and information needs in agriculture related to fertilizers.
Ionic and Covalent Compounds
- Potassium sulfate is an ionic compound, composed of potassium (K) and sulfur (S).
- Significant electronegativity difference results in electron transfer: potassium loses an electron to become K⁺, sulfur gains electrons to form SO₄²⁻.
- Formation of ionic bonds occurs through attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- Urea is an example of a covalent compound, consisting of 1 carbon, 1 oxygen, 2 nitrogen, and 4 hydrogen atoms.
- Urea contains a double bond between carbon and oxygen.
Overall Composition of Beef Animal Body
- Calf body weight: 75 kg; Steer body weight: 500 kg.
- Values are presented in grams per kilogram of beef carcass.
- Example: 66 g kg⁻¹ of lipids in a calf indicates 66 grams of lipids per kilogram of the calf’s carcass.
Chemical Composition of Fertilizers
- Discusses common inorganic fertilizers and their components.
- Highlights potential hazards and information needs in agriculture related to fertilizers.
Ionic and Covalent Compounds
- Potassium sulfate is an ionic compound, composed of potassium (K) and sulfur (S).
- Significant electronegativity difference results in electron transfer: potassium loses an electron to become K⁺, sulfur gains electrons to form SO₄²⁻.
- Formation of ionic bonds occurs through attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- Urea is an example of a covalent compound, consisting of 1 carbon, 1 oxygen, 2 nitrogen, and 4 hydrogen atoms.
- Urea contains a double bond between carbon and oxygen.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.