Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the rubber bulb used with a pipette?
What is the primary function of the rubber bulb used with a pipette?
- To apply suction and draw liquid into the pipette (correct)
- To regulate the temperature of the liquid
- To measure the viscosity of the liquid
- To secure the pipette in place
When using a pipette, what should be done after raising the pipet tip out of the liquid?
When using a pipette, what should be done after raising the pipet tip out of the liquid?
- Shake the pipette gently to mix the liquid
- Stop the suction and cover the top with an index finger (correct)
- Remove the pipette from the laboratory
- Immediately drain the liquid into the receiving vessel
Which statement correctly describes the position in which the pipette should be held during usage?
Which statement correctly describes the position in which the pipette should be held during usage?
- At a 45-degree angle to facilitate flow
- Directly horizontal for maximum control
- Inverted to capture any residual liquid
- Upright to ensure accurate liquid transfer (correct)
What accuracy is a typical fixed-volume pipette known for?
What accuracy is a typical fixed-volume pipette known for?
What is the purpose of wiping the tip of the pipette after filling it with liquid?
What is the purpose of wiping the tip of the pipette after filling it with liquid?
Which type of pipette typically allows the user to select multiple volumes?
Which type of pipette typically allows the user to select multiple volumes?
What should you ensure about the position of the pipette tip when draining into a receiving vessel?
What should you ensure about the position of the pipette tip when draining into a receiving vessel?
What should be done if a variable pipette is being used before measurement?
What should be done if a variable pipette is being used before measurement?
What is the primary function of the additive Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate (SPS) found in yellow blood collection tubes?
What is the primary function of the additive Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate (SPS) found in yellow blood collection tubes?
Which blood collection tube color is specifically designed for routine CBC and ESR tests?
Which blood collection tube color is specifically designed for routine CBC and ESR tests?
What does the additive Sodium Fluoride do in gray blood collection tubes?
What does the additive Sodium Fluoride do in gray blood collection tubes?
Which tube requires a blood-to-anticoagulant ratio of 9:1 for optimal test results?
Which tube requires a blood-to-anticoagulant ratio of 9:1 for optimal test results?
What is the primary role of lithium heparin in green collection tubes?
What is the primary role of lithium heparin in green collection tubes?
What is the required inversion for the light green separator tube after collection?
What is the required inversion for the light green separator tube after collection?
Which additive is found in orange blood collection tubes?
Which additive is found in orange blood collection tubes?
What is the role of K2EDTA in royal blue collection tubes?
What is the role of K2EDTA in royal blue collection tubes?
Which blood collection tube is primarily used for glucose determination?
Which blood collection tube is primarily used for glucose determination?
What type of specimen is the lavender tube specifically used for?
What type of specimen is the lavender tube specifically used for?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
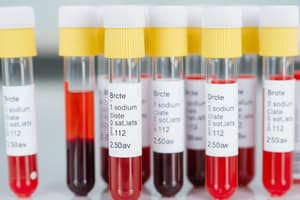
Blood Collection Tubes
- Blood collection tubes can be used with both the ETS (Evacuated Tube System) and syringe methods.
- Tubes are designed to collect small blood amounts from capillary punctures.
- Each tube is color-coded, indicating specific additives or properties, commonly made from glass or plastic.
Additives in Blood Collection Tubes
- Additives are substances integrated into evacuated tubes.
- Anticoagulants prevent blood clotting during sample collection.
- Chelates are additives that bind specific substances.
Stopper Color and Additives
Yellow Tube
- Contains Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate (SPS) and Acid Citrate Dextrose.
- Used in microbiology for blood cultures and blood banking.
- Requires 8 inversions to prevent coagulation.
Light Blue Tube
- Contains 3.2% Buffered Citrate, supporting a blood to anticoagulant ratio of 9:1.
- Used in hematology for coagulation studies including PT and aPTT.
- Requires 3-4 gentle inversions.
Red Tube
- Silicone-coated for clot activation.
- Used in chemistry for serum determinations, blood bank, and immunoserology.
- Five inversions if using clot activator; no inversion needed for glass tubes.
Gold Plastic Tube
- No additive, features a gel separator promoting clotting.
- Used for chemistry, blood banking, and immunoserology.
- Requires five inversions for adequate mixing.
Light Green Tube
- Contains Lithium Heparin with a gel separator to prevent clotting.
- Used for plasma determination in chemistry.
- Requires 8-10 inversions.
Green Tube
- May contain Lithium or Sodium Heparin.
- Used for blood gas analysis and hematology testing.
- Requires 8-10 inversions.
Lavender Tube
- Contains 1.5 mg/mL EDTA, inhibiting coagulation.
- Primarily used for chemistry (HBA1C), hematology (CBC, ESR), and blood banking.
- Requires 8-10 inversions and samples must be tested within 4 hours for optimal results.
Gray Tube
- Contains Potassium Oxalate (anticoagulant) and Sodium Fluoride (antiglycolytic agent).
- Prevents clotting by binding calcium and preserves glucose levels.
- Can be stored for up to 3 days, requiring 8-10 inversions.
Orange Tube
- Contains Thrombin which acts as a clot activator.
- Used for STAT chemistry determinations with a quick clotting time of 5 minutes.
Royal Blue Tube
- May have no additive, K2EDTA, or Heparin, used for trace elements and toxicology.
- Requires 8 inversions.
Tan Tube
- Contains Sodium Heparin (glass) or K2EDTA (plastic) used for lead determination.
Pink Tube
- Features spray-coated K2EDTA; used for blood bank testing and donor screening.
Pipetting Techniques
- Utilize fixed-volume or variable pipettes, ensuring proper technique for accurate measurement.
- Hold the pipet upright and use a rubber bulb for suction above the desired graduation line.
- Wipe the pipet tip to remove excess liquid, ensuring no bubbles when transferring contents.
- Thumb controls the bulb, while the index finger stops the flow of liquid.
Key Operating Instructions
- For variable pipettes, adjust the knob for the desired volume.
- Maintain a vertical position while draining and ensure half of the pipet tip is submerged to avoid air bubbles.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.