Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the most common cause of acute cholecystitis, and what percentage of cases does it account for?
What is the most common cause of acute cholecystitis, and what percentage of cases does it account for?
The most common cause of acute cholecystitis is complete cystic duct obstruction due to impacted gallstones, accounting for about 90 percent of cases.
According to O’Rourke et al. (2023), what percentage of patients with acute cholecystitis have gallstones?
According to O’Rourke et al. (2023), what percentage of patients with acute cholecystitis have gallstones?
About 95 percent of patients with acute cholecystitis have gallstones.
What is the estimated percentage of patients with asymptomatic gallstones that will develop symptoms within 20 years?
What is the estimated percentage of patients with asymptomatic gallstones that will develop symptoms within 20 years?
Only about 20 percent of patients with asymptomatic gallstones will develop symptoms within 20 years.
What is considered the most appropriate management for symptomatic patients with cholecystitis?
What is considered the most appropriate management for symptomatic patients with cholecystitis?
What risk factors are particularly significant in the diagnosis of acute calculous cholecystitis?
What risk factors are particularly significant in the diagnosis of acute calculous cholecystitis?
How do chronic conditions, such as hypertension, complicate the management of patients undergoing surgery for acute cholecystitis?
How do chronic conditions, such as hypertension, complicate the management of patients undergoing surgery for acute cholecystitis?
What classic symptoms are associated with acute cholecystitis?
What classic symptoms are associated with acute cholecystitis?
What is the significance of individualized management plans in the context of patients with acute cholecystitis and hypertension?
What is the significance of individualized management plans in the context of patients with acute cholecystitis and hypertension?
What significant health event did Patient T experience in 2013?
What significant health event did Patient T experience in 2013?
When did Patient T undergo a surgical procedure for a gallbladder issue, and what was the reason for it?
When did Patient T undergo a surgical procedure for a gallbladder issue, and what was the reason for it?
What was the recorded respiratory rate of Patient T on October 14, 2024, and is it within normal limits?
What was the recorded respiratory rate of Patient T on October 14, 2024, and is it within normal limits?
What symptoms did Patient T experience post-operatively related to her respiratory function?
What symptoms did Patient T experience post-operatively related to her respiratory function?
What was Patient T's oxygen saturation levels measured at, and what does this indicate?
What was Patient T's oxygen saturation levels measured at, and what does this indicate?
What notable family health conditions contribute to Patient T's medical history?
What notable family health conditions contribute to Patient T's medical history?
How much did Patient T smoke before her hospital admission, and what is the significance of this statistic?
How much did Patient T smoke before her hospital admission, and what is the significance of this statistic?
What intervention was administered to Patient T to assist with her respiratory condition?
What intervention was administered to Patient T to assist with her respiratory condition?
What is the chief complaint of Patient T upon admission to the hospital?
What is the chief complaint of Patient T upon admission to the hospital?
What significant chronic conditions does Patient T have in her medical history?
What significant chronic conditions does Patient T have in her medical history?
What diagnostic imaging was performed on Patient T, and what did it reveal?
What diagnostic imaging was performed on Patient T, and what did it reveal?
What was the patient's blood pressure upon admission, and how is it classified?
What was the patient's blood pressure upon admission, and how is it classified?
What surgical procedure was scheduled for Patient T, and why?
What surgical procedure was scheduled for Patient T, and why?
What is the first step in managing a patient with acute calculous cholecystitis?
What is the first step in managing a patient with acute calculous cholecystitis?
How is Patient T's respiratory support being managed?
How is Patient T's respiratory support being managed?
What specific nursing interventions are included in Patient T's care plan?
What specific nursing interventions are included in Patient T's care plan?
Why is closely monitoring vital signs important in patients with acute calculous cholecystitis?
Why is closely monitoring vital signs important in patients with acute calculous cholecystitis?
What factors contributed to Patient T's abdominal pain, as reported by her family?
What factors contributed to Patient T's abdominal pain, as reported by her family?
What role does pain assessment play in the care plan for these patients?
What role does pain assessment play in the care plan for these patients?
What are some diagnoses included in the individualized care plan for this condition?
What are some diagnoses included in the individualized care plan for this condition?
What strategies can be implemented to prevent infection in a patient with acute calculous cholecystitis?
What strategies can be implemented to prevent infection in a patient with acute calculous cholecystitis?
How should dietary modifications be approached for patients recovering from acute calculous cholecystitis?
How should dietary modifications be approached for patients recovering from acute calculous cholecystitis?
Why is encouraging mobility important for patients with this condition?
Why is encouraging mobility important for patients with this condition?
What is emphasized in providing emotional support to these patients?
What is emphasized in providing emotional support to these patients?
What are the primary symptoms associated with gallstones?
What are the primary symptoms associated with gallstones?
How does acute cholecystitis differ from chronic gallbladder disease?
How does acute cholecystitis differ from chronic gallbladder disease?
What nutritional considerations are important for patients with gallbladder disease?
What nutritional considerations are important for patients with gallbladder disease?
What is the first-line treatment for acute cholecystitis according to recent guidelines?
What is the first-line treatment for acute cholecystitis according to recent guidelines?
What role does patient education play in managing gallstone disease?
What role does patient education play in managing gallstone disease?
What are the potential complications of untreated gallstones?
What are the potential complications of untreated gallstones?
How do lifestyle factors contribute to the development of gallstones?
How do lifestyle factors contribute to the development of gallstones?
What postoperative care strategies are important for patients after gallbladder surgery?
What postoperative care strategies are important for patients after gallbladder surgery?
What is the primary focus of the discharge plan for Patient T following her surgery?
What is the primary focus of the discharge plan for Patient T following her surgery?
Why is it important for Patient T to recognize signs of potential complications post-surgery?
Why is it important for Patient T to recognize signs of potential complications post-surgery?
Describe the significance of nursing care in the context of Patient T's case.
Describe the significance of nursing care in the context of Patient T's case.
What role does medication adherence play in Patient T's recovery?
What role does medication adherence play in Patient T's recovery?
How do dietary modifications contribute to Patient T's health management?
How do dietary modifications contribute to Patient T's health management?
What does a collaborative healthcare approach entail in the care of Patient T?
What does a collaborative healthcare approach entail in the care of Patient T?
Identify two specific health risks Patient T faces post-surgery and suggest how they can be addressed.
Identify two specific health risks Patient T faces post-surgery and suggest how they can be addressed.
What educational aspects were emphasized to Patient T and her caregiver?
What educational aspects were emphasized to Patient T and her caregiver?
Flashcards
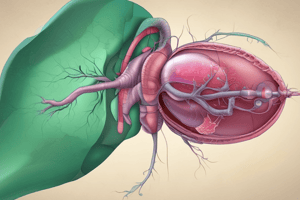
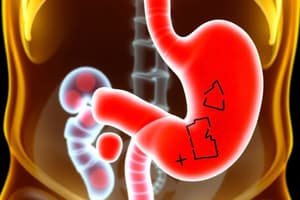
Acute Cholecystitis
Acute Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct.
Gallstones
Gallstones
Hardened deposits that can form in the gallbladder.
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy
Surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptomatic Gallstones
Symptomatic Gallstones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymptomatic Gallstones
Asymptomatic Gallstones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors for Cholecystitis
Risk Factors for Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perioperative Care
Perioperative Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Controlled Hypertension
Controlled Hypertension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Cholecystitis
Acute Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient T
Patient T
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Conditions
Chronic Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Scale 10/10
Pain Scale 10/10
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient T's Stroke
Patient T's Stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient T's Heart History
Patient T's Heart History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cotrimoxazole Allergy
Cotrimoxazole Allergy
Signup and view all the flashcards
2024 Cholecystectomy
2024 Cholecystectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Rate (2024)
Respiratory Rate (2024)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Productive Cough
Productive Cough
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smoking History
Smoking History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ideal Management for Acute Cholecystitis
Ideal Management for Acute Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Management (Cholecystitis)
Pain Management (Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infection Prevention (Cholecystitis)
Infection Prevention (Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Modifications (Cholecystitis)
Dietary Modifications (Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-operative Monitoring (Cholecystectomy)
Post-operative Monitoring (Cholecystectomy)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient Education (Cholecystitis)
Patient Education (Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vital Signs Monitoring (Acute Cholecystitis)
Vital Signs Monitoring (Acute Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallstones
Gallstones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Cholecystitis
Acute Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptomatic Gallstones
Symptomatic Gallstones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymptomatic Gallstones
Asymptomatic Gallstones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors (Cholecystitis)
Risk Factors (Cholecystitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nutritional Management (Gallbladder)
Nutritional Management (Gallbladder)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Comprehensive Patient-Centered Approach
Comprehensive Patient-Centered Approach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Discharge Plan Components
Discharge Plan Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-operative Challenges
Post-operative Challenges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medication Adherence
Medication Adherence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Potential Complications
Potential Complications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complex Medical History
Complex Medical History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collaborative Environment
Collaborative Environment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Modifications
Dietary Modifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Care
Nursing Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Issues
Chronic Issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Management
Pain Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infection Prevention
Infection Prevention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Flow
Bile Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
- A prevalent inflammatory condition of the gallbladder
- Occurs when the cystic duct is obstructed by gallstones
- Leading to irritation, inflammation, and potential necrosis of the gallbladder wall
- Risk is more prevalent in women aged 40 years and above, and can run in families
- Cholecystitis develops in up to 10% of patients with symptomatic gallstones (90% of cases caused by complete cystic duct obstruction)
- 95% of patients with acute cholecystitis have gallstones
- Asymptomatic gallstones may not be treated, as issues may arise after 20 years
- Symptomatic patients often undergo laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Comorbidities like hypertension can complicate surgical interventions and recovery
Health Profile
- Patient T is a 56-year-old female, widowed, currently living with a partner in Lower Palalan, Lumbia, Cagayan de Oro City
- History of hypertension, angina, and a previous ischemic stroke
- Chief complaint of intense abdominal pain (10/10), in the right upper quadrant (RUQ), frequent nausea, and vomiting
- Two months prior to admission, experienced intermittent sharp RUQ pain associated with vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain rated 10/10 on the pain scale, particularly in the right upper quadrant, for the previous two months, accompanied by intermittent vomiting
Comprehensive Nursing Assessment (October 14, 2024)
- Respiratory Rate: 19 cycles per minute (cpm)
- Productive Cough with yellow sputum indicative of secretions and airway obstruction.
- Oxygen saturation levels: 96% with oxygen support at 2 liters per minute
- Blood pressure recorded at 140/70 mmHg; heart rate at 57 beats per minute (bpm), indicative of bradycardia showing adequate perfusion
- Full alertness and orientation, with a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 15
- Mild body weakness, however, normal motor function and sensation with effective coordination
- Reported consuming a typical diet (e.g., fried chicken, pork chop, stir-fried vegetables)
- No issues with swallowing, indicating the absence of dysphagia.
- Patient depended on partner for daily chores.
Comprehensive Nursing Assessment (October 15, 2024)
- Respiratory Rate: 18 cycles per minute (cpm)
- Decreased discomfort from her cough, showing effectiveness of nebulization therapy from previous assessment
- Blood pressure recorded at 130/80 mmHg; heart rate improved to 68 bpm; good perfusion
- Full alertness and orientation
- Normal bowel function
- Patient still reported numbness in her lower extremities
- Patient's daily dietary intake remained consistent with a balanced consumption of three meals a day, including soups, and lessening intake of oily foods
- Patient still depended on partner for daily activities of daily living (ADLs)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.