Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following conditions can cause both round macrocytosis and an increase in central pallor?
Which of the following conditions can cause both round macrocytosis and an increase in central pallor?
- Folate deficiency
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Reticulocytosis (correct)
- Ethanol abuse
A patient presents with microcytosis and hypochromia. Which of the following conditions is most likely responsible for these findings?
A patient presents with microcytosis and hypochromia. Which of the following conditions is most likely responsible for these findings?
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Reticulocytosis
- Ethanol abuse
- Iron deficiency anemia (correct)
Which of these conditions is associated with a lower-than-normal MCV?
Which of these conditions is associated with a lower-than-normal MCV?
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Thalassemia
- Sideroblastic anemia
- All of the above (correct)
Which of the following conditions is associated with spherocytes, lacking central pallor, and can be caused by alcohol withdrawal?
Which of the following conditions is associated with spherocytes, lacking central pallor, and can be caused by alcohol withdrawal?
How is the size of a normal red blood cell typically described in relation to a lymphocyte?
How is the size of a normal red blood cell typically described in relation to a lymphocyte?
A patient presents with target cells, which are characterized by an increased staining area in the central pallor. What could be a possible explanation for this finding?
A patient presents with target cells, which are characterized by an increased staining area in the central pallor. What could be a possible explanation for this finding?
What is the term used to describe the presence of both microcytes and macrocytes in the same field of view?
What is the term used to describe the presence of both microcytes and macrocytes in the same field of view?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of macrocytosis?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of macrocytosis?
Under what conditions do microcytes typically have a normal central pallor?
Under what conditions do microcytes typically have a normal central pallor?
Which of the following conditions is LEAST likely to cause oval macrocytes?
Which of the following conditions is LEAST likely to cause oval macrocytes?
A patient with a high reticulocyte count is likely to exhibit which of the following morphological changes in their red blood cells?
A patient with a high reticulocyte count is likely to exhibit which of the following morphological changes in their red blood cells?
Which of these is a potential cause of abnormal red blood cell morphology, leading to the presence of microcytes?
Which of these is a potential cause of abnormal red blood cell morphology, leading to the presence of microcytes?
What is the average diameter of a normal red blood cell?
What is the average diameter of a normal red blood cell?
Which of these conditions are most likely to cause an increase in MCV?
Which of these conditions are most likely to cause an increase in MCV?
What term describes red blood cells that are larger than normal?
What term describes red blood cells that are larger than normal?
What is the typical range of MCV for microcytes?
What is the typical range of MCV for microcytes?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with the presence of nucleated red blood cells in a peripheral smear?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with the presence of nucleated red blood cells in a peripheral smear?
Which of the following conditions is MOST LIKELY to be associated with the appearance of acanthocytes on a peripheral blood smear?
Which of the following conditions is MOST LIKELY to be associated with the appearance of acanthocytes on a peripheral blood smear?
What is the predominant morphological characteristic of Howell-Jolly bodies?
What is the predominant morphological characteristic of Howell-Jolly bodies?
Which of the following conditions is MOST LIKELY associated with the presence of siderotic granules (Pappenheimer bodies) within red blood cells?
Which of the following conditions is MOST LIKELY associated with the presence of siderotic granules (Pappenheimer bodies) within red blood cells?
Which of the following conditions can lead to the observation of red blood cells with an irregular clumped appearance, specifically due to cold agglutinins?
Which of the following conditions can lead to the observation of red blood cells with an irregular clumped appearance, specifically due to cold agglutinins?
What is the characteristic morphology of keratocytes, and what are the conditions associated with their presence?
What is the characteristic morphology of keratocytes, and what are the conditions associated with their presence?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with red blood cells with an abnormal shape, as seen in sickle cell anemia, acanthocytosis, or roueleaux formation?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with red blood cells with an abnormal shape, as seen in sickle cell anemia, acanthocytosis, or roueleaux formation?
Which of the following conditions is most likely to present with red blood cell morphology resembling a stack of coins?
Which of the following conditions is most likely to present with red blood cell morphology resembling a stack of coins?
Which of the following is NOT a condition associated with basophilic stippling?
Which of the following is NOT a condition associated with basophilic stippling?
Which of the following statements about Heinz bodies is TRUE?
Which of the following statements about Heinz bodies is TRUE?
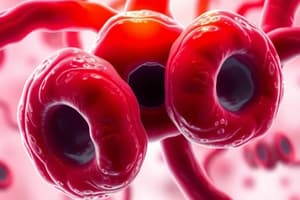
What is the likely cause of the red cell changes seen in the image on the left?
What is the likely cause of the red cell changes seen in the image on the left?
Which of the following is TRUE about Cabot rings?
Which of the following is TRUE about Cabot rings?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of avian malaria?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of avian malaria?
Which condition is NOT commonly associated with ovalocytes or elliptocytes?
Which condition is NOT commonly associated with ovalocytes or elliptocytes?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by red blood cells with a central linear slit or stoma, giving the cell a mouth-shaped appearance?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by red blood cells with a central linear slit or stoma, giving the cell a mouth-shaped appearance?
Which cell morphology is most commonly associated with Microangiopathic Haemolytic Anemia (MAHA)?
Which cell morphology is most commonly associated with Microangiopathic Haemolytic Anemia (MAHA)?
Which cell morphology is characterized by red blood cells with uniformly spaced, pointed projections on their surface, also known as Echinocytes?
Which cell morphology is characterized by red blood cells with uniformly spaced, pointed projections on their surface, also known as Echinocytes?
A patient presents with a blood smear showing red blood cells with a central hollow area. Which condition is most likely?
A patient presents with a blood smear showing red blood cells with a central hollow area. Which condition is most likely?
Which condition is NOT typically associated with red blood cell fragmentation (Schistocytes)?
Which condition is NOT typically associated with red blood cell fragmentation (Schistocytes)?
Which of the following cell morphologies is often associated with a bone marrow disorder characterized by excessive scar tissue formation?
Which of the following cell morphologies is often associated with a bone marrow disorder characterized by excessive scar tissue formation?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by red blood cells with two or three horn-like projections, often described as 'horn cells'?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by red blood cells with two or three horn-like projections, often described as 'horn cells'?
Flashcards
Normal RBC Morphology
Normal RBC Morphology
Normal red blood cells are round, non-nucleated bi-concave discs with central pallor covering 1/3 of the cell.
Anisocytosis
Anisocytosis
Variation in the size of red blood cells, indicating the presence of microcytes and macrocytes.
Microcytes
Microcytes
Red blood cells smaller than normal, typically less than 7µm in diameter.
Macrocytes
Macrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypochromasia
Hypochromasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poikilocytosis
Poikilocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inclusion Bodies
Inclusion Bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperchromic
Hyperchromic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normochromic
Normochromic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spherocytosis
Spherocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Target Cells
Target Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrocytosis
Macrocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovalocytes/Elliptocytosis
Ovalocytes/Elliptocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tear Drop Cells
Tear Drop Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blister Cell
Blister Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Schistocytosis
Schistocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomatocytosis
Stomatocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Burr (Crenation) Cell
Burr (Crenation) Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratocytes (Horn Cell)
Keratocytes (Horn Cell)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conditions linked to Ovalocytes
Conditions linked to Ovalocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophilic Stippling
Basophilic Stippling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heinz Bodies
Heinz Bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cabot Rings
Cabot Rings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasites of Red Cell
Parasites of Red Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Siderotic Inclusions
Siderotic Inclusions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratocyte
Keratocyte
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acanthocytes
Acanthocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sickle Cells
Sickle Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleated Red Blood Cells
Nucleated Red Blood Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rouleaux Formation
Rouleaux Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Red Cell-Agglutination
Red Cell-Agglutination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Howell-Jolly Bodies
Howell-Jolly Bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Siderotic Granules
Siderotic Granules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Abnormal Morphology of Red Blood Cells
- Presentation: The presentation is about abnormal morphology of red blood cells (RBCs).
Learning Objectives
- Morphology of Normal RBCs: Includes shape, size, and hemoglobin content.
- Morphology of RBCs - size: Describes the variation in size, including microcytes (smaller) and macrocytes (larger) than normal.
- Morphology of RBCs - Hb content (color): Discusses alterations in hemoglobin content leading to variations in color, including hypochromasia (reduced hemoglobin) and hyperchromasia (increased hemoglobin).
- Types of poikilocytosis (shape of RBC): Explores different abnormal shapes besides the normal biconcave disc shape.
- Inclusion bodies: Covers inclusions (e.g. Howell-Jolly bodies) that can be present within the RBC.
Normal RBCs
- Structure: Round, elastic, non-nucleated, biconcave discs with a central pallor (covering about 1/3 of the cell).
- Size: Approximately the same size as the nucleus of a small lymphocyte, with an average diameter of 7.2 microns (range of 6-9 microns).
- Purpose: Normal mature red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
Disease and Abnormal RBC Morphology
- Causes of Abnormal Morphology: Four main causes:
- Abnormal erythropoiesis (effective or ineffective production of RBC).
- Inadequate hemoglobin (Hb) formation (hypo- or hyperchromic).
- Damage/changes to RBCs after leaving the bone marrow (e.g., hereditary spherocytosis).
- Bone marrow attempts to compensate for anemia through increased erythropoiesis.
Abnormal RBC Morphology: Further Detailed Information
- Size Variations (Anisocytosis):
- Microcytes: Smaller than normal RBCs.
- Macrocytes: Larger than normal RBCs.
- Anisocytosis: Presence of both microcytes and macrocytes within the same field of view.
- Hemoglobin Content Variations:
- Hypochromasia: Increased central pallor, less hemoglobin.
- Hyperchromasia: Decreased central pallor, more hemoglobin.
- Anisochromasia: A combination of hyper- and hypochromasia.
- Shape Variations (Poikilocytosis):
- Various abnormal shapes (e.g., spherocytes, target cells, sickle cells, tear drop cells, blister cells).
- Inclusion Bodies:
- Howell-Jolly bodies: Small, round cytoplasmic inclusions appearing similar to nuclei.
- Siderotic granules (Pappenheimer bodies): Iron containing cytoplasmic inclusions.
- Basophilic stippling: Small clumps of ribosomal RNA.
- Heinz bodies: Denatured hemoglobin precipitates.
- Cabot rings: Reddish-blue threadlike remnants of the nuclear membrane.
- Parasites (e.g., malaria): Can be identified within red blood cells.
Specialized Classifications of Abnormal RBC Morphology
- Spherocytosis: Spherical, lack central pallor.
- Target Cells: Increased staining with an area of central pallor.
- Ovalocytes/Elliptocytes: Oval or elliptical in shape, respectively.
- Tear Drop Cells: Shaped like a tear drop or pear.
- Blister Cells: Eccentric hollow area inside the cell.
- Schistocytes: Fragmented red blood cells.
- Stomatocytes: Central linear slit or stoma.
- Burr/Crenation Cells: Uniformly spaced, pointed projections on surface.
- Keratocytes (horn cells): Cell fragments with horn-like projections.
- Acanthocytes: Irregularly spaced projections, mostly rounded ends.
- Nucleated RBCs: Presence of nuclei in red blood cells, an indication of early release from the bone marrow.
- Rouleaux Formation: Stacks of RBCs resembling a stack of coins.
- Red Cell Agglutination: Irregular clumps of red blood cells.
- Sickle cells: Crescent or sickle-shaped cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.