What is the structure and function of the stomach in the human digestive system?
Understand the Problem
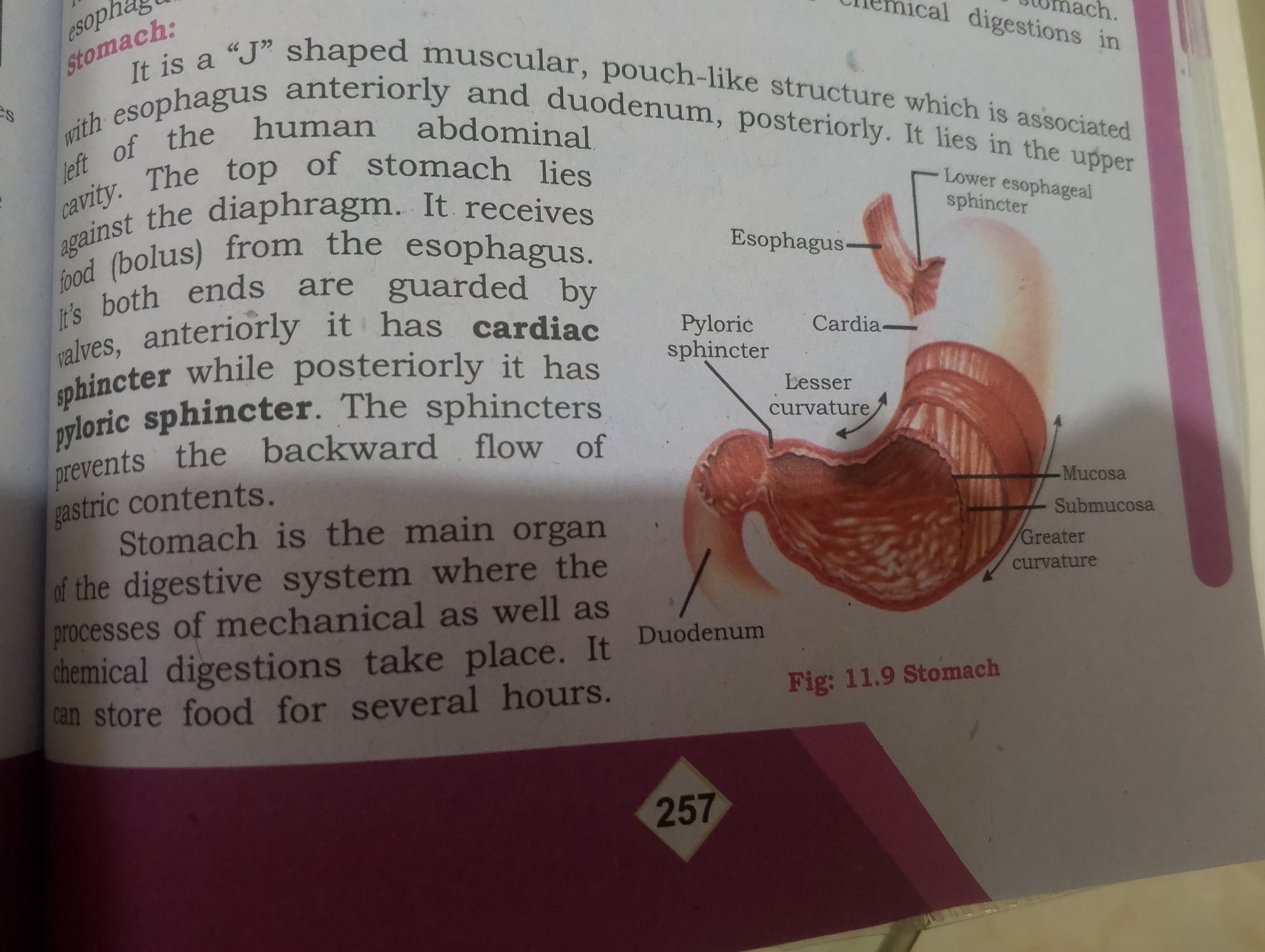
The text is describing the anatomy and physiological functions of the stomach, including its structure, associated sphincters, and the digestive processes that take place within it.
Answer
The stomach stores, mixes, and digests food using acids and enzymes.
The stomach is a J-shaped muscular organ located between the esophagus and duodenum. It stores, mixes, and digests food with acids and enzymes, and has sphincters that prevent backflow. It plays a key role in both mechanical and chemical digestion.
Answer for screen readers
The stomach is a J-shaped muscular organ located between the esophagus and duodenum. It stores, mixes, and digests food with acids and enzymes, and has sphincters that prevent backflow. It plays a key role in both mechanical and chemical digestion.
More Information
The stomach's muscular walls allow it to churn food, enhancing digestion. It also releases digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid that break down food particles.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the roles of mechanical and chemical digestion. The stomach is involved in both processes.
Sources
- Stomach | Definition, Function, Structure, Diagram, & Facts | Britannica - britannica.com
- What Does the Stomach Do? Its Anatomy and Functions - Ezra - ezra.com
- Digestive System: Function, Organs & Anatomy - Cleveland Clinic - my.clevelandclinic.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information