What is the function of enzymes and how do temperature and pH affect their activity?
Understand the Problem
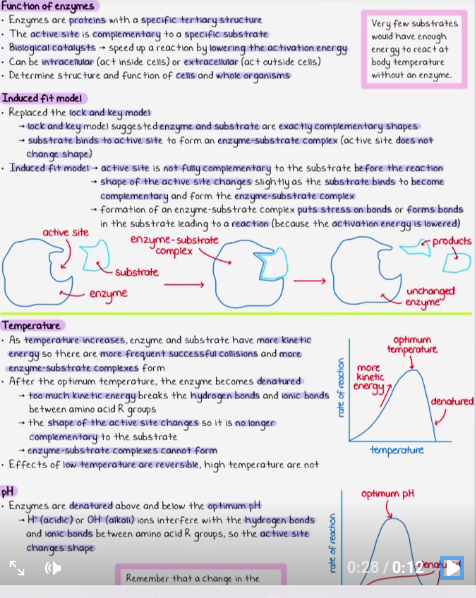
The question relates to the functions of enzymes, specifically how they interact with substrates and how factors like temperature and pH affect their activity. It outlines the induced fit model, the relationship between enzyme and substrate kinetics, and the consequences of temperature and pH on enzyme functionality.
Answer
Enzymes speed up reactions. Temperature increases activity until denaturation; pH affects enzyme shape and function.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. Temperature and pH affect enzyme activity by altering the enzyme's shape. Higher temperature increases rate until denaturation, while deviations from optimal pH reduce effectiveness.
Answer for screen readers
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. Temperature and pH affect enzyme activity by altering the enzyme's shape. Higher temperature increases rate until denaturation, while deviations from optimal pH reduce effectiveness.
More Information
Enzymes operate best under specific conditions unique to each type, which is why biological pathways are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming that higher temperatures always increase enzyme activity indefinitely; remember that enzymes denature at high temps.
Sources
- 18.7: Enzyme Activity - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
- Factors affecting enzyme action - BBC Bitesize - bbc.co.uk
- Enzymes and the active site - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information