What are the differences and similarities between cellulose, starch, and glycogen based on their structure and properties?
Understand the Problem
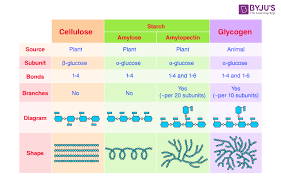
The image compares cellulose, starch (including amylose and amylopectin), and glycogen by depicting their sources, subunits, bonds, branching, diagrams, and shapes. This indicates a focus on understanding the structural differences and similarities among these carbohydrates.
Answer
Cellulose is unbranched and uses β-glucose; starch and glycogen are branched and use α-glucose.
Cellulose, starch, and glycogen are polysaccharides composed of glucose units. Cellulose uses β-glucose forming a straight chain, while starch and glycogen use α-glucose. Starch (amylose and amylopectin) and glycogen are branched, but glycogen is more densely branched, stored in animals.
Answer for screen readers
Cellulose, starch, and glycogen are polysaccharides composed of glucose units. Cellulose uses β-glucose forming a straight chain, while starch and glycogen use α-glucose. Starch (amylose and amylopectin) and glycogen are branched, but glycogen is more densely branched, stored in animals.
More Information
Cellulose, being a β-glucose polymer, is more rigid and forms plant cell walls, while starch (in plants) and glycogen (in animals) serve as energy storage molecules due to their α-glucose structure allowing easier breakdown.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the unbranched structure of cellulose with the branched structures of starch and glycogen.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information