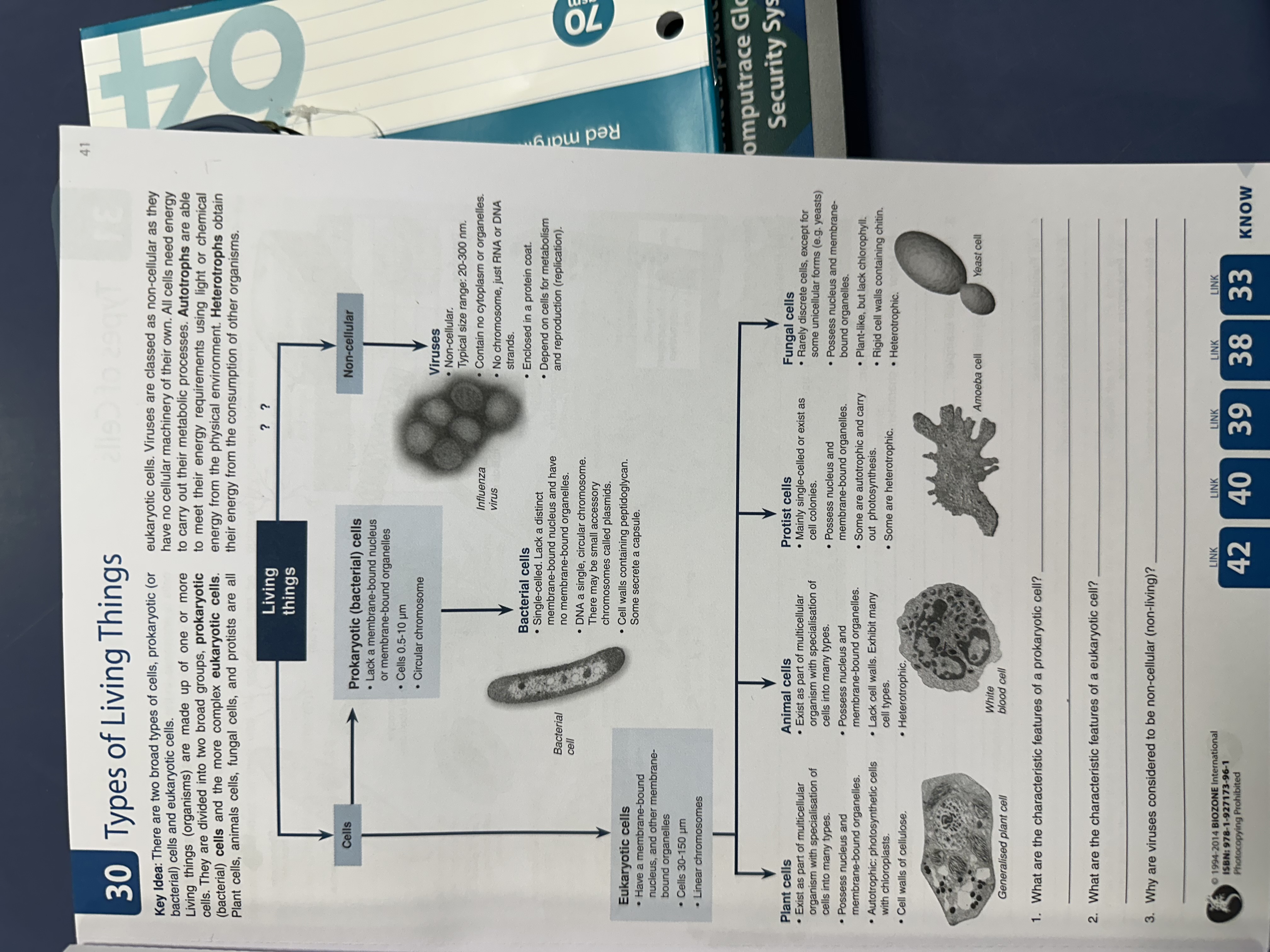
What are the characteristic features of a prokaryotic cell? What are the characteristic features of a eukaryotic cell? Why are viruses considered to be non-cellular (non-living)?
Understand the Problem
The questions are asking about the characteristics of prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and the non-cell nature of viruses. These concepts relate to the fundamental differences in cell structure and classification in biology.
Answer
Prokaryotic: no nucleus, smaller. Eukaryotic: nucleus, larger. Viruses: non-cellular, need host.
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, are usually smaller, and have circular DNA. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, are larger, and have linear chromosomes. Viruses are non-cellular because they lack cell structures, cannot reproduce independently, and need a host cell.
Answer for screen readers
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, are usually smaller, and have circular DNA. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, are larger, and have linear chromosomes. Viruses are non-cellular because they lack cell structures, cannot reproduce independently, and need a host cell.
More Information
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and include bacteria. Eukaryotic cells make up plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Viruses are not considered living as they cannot metabolize or reproduce outside of a host cell.
Tips
A common mistake is to assume all cellular life forms have a nucleus; remember that prokaryotes do not.
Sources
- 3.2 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells – Concepts of Biology - opentextbc.ca
- Prokaryotic cells (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- 7.7: Virus Characteristics - Biology LibreTexts - bio.libretexts.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information