The angle x lies in the interval π/2 ≤ x ≤ π, and sin² x = 8/9. Without using a calculator, determine the value of sin 2x, cos 2x, x/2, and sin 3x.
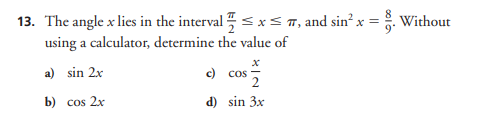
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to find the values of trigonometric functions of an angle x, given that x lies in a specific interval and its sine squared is a known value. We will use trigonometric identities to solve for the requested values without a calculator.
Answer
a) $\sin 2x = -\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9}$ b) $\cos 2x = -\frac{7}{9}$ c) $\frac{x}{2} = \frac{x}{2}$ d) $\sin 3x = \frac{22\sqrt{2}}{27}$
Answer for screen readers
a) $\sin 2x = -\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9}$
b) $\cos 2x = -\frac{7}{9}$
c) $\frac{x}{2} = \frac{x}{2}$
d) $\sin 3x = \frac{22\sqrt{2}}{27}$
Steps to Solve
- Find sin x and cos x
Given that $\sin^2 x = \frac{8}{9}$, we take the square root.
Thus,
$$ \sin x = \sqrt{\frac{8}{9}} = \frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3} $$
Since $x$ lies in the interval $\left[\frac{\pi}{2}, \pi\right]$, $\sin x$ is positive.
To find $\cos x$, we use the identity $\sin^2 x + \cos^2 x = 1$.
So,
$$ \cos^2 x = 1 - \sin^2 x = 1 - \frac{8}{9} = \frac{1}{9} $$
Therefore,
$$ \cos x = -\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = -\frac{1}{3} $$
- Calculate sin 2x
Using the double angle identity for sine,
$$ \sin 2x = 2 \sin x \cos x $$
Substituting the values:
$$ \sin 2x = 2 \left(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\right)\left(-\frac{1}{3}\right) = -\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9} $$
- Calculate cos 2x
Using the double angle identity for cosine,
$$ \cos 2x = \cos^2 x - \sin^2 x $$
Substituting the values:
$$ \cos 2x = \left(-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{9} - \frac{8}{9} = -\frac{7}{9} $$
- Calculate sin 3x
Using the identity for sine of a triple angle:
$$ \sin 3x = 3\sin x - 4\sin^3 x $$
We first find $\sin^3 x$:
$$ \sin^3 x = \left(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\right)^3 = \frac{8\sqrt{2}}{27} $$
Now substituting:
$$ \sin 3x = 3\left(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\right) - 4\left(\frac{8\sqrt{2}}{27}\right) = 2\sqrt{2} - \frac{32\sqrt{2}}{27} $$
To combine the terms:
$$ \sin 3x = \frac{54\sqrt{2}}{27} - \frac{32\sqrt{2}}{27} = \frac{22\sqrt{2}}{27} $$
- Calculate x/2
Since $\sin^2 x = \frac{8}{9}$, we can find:
$$ x = \arcsin\left(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\right) \text{ within the specified interval.} $$
Thus,
$$ \frac{x}{2} \text{ is half of the angle. } $$
Since we do not require the exact angle, we denote it as $\frac{x}{2}$.
a) $\sin 2x = -\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9}$
b) $\cos 2x = -\frac{7}{9}$
c) $\frac{x}{2} = \frac{x}{2}$
d) $\sin 3x = \frac{22\sqrt{2}}{27}$
More Information
Using trigonometric identities, we derived multiple function values based on the given sine value. The calculations utilized fundamental relationships between sine, cosine, and their double/triple angle identities, which are crucial in trigonometry.
Tips
- Confusing the signs of cosine in different quadrants. Remember that in the interval $\left[\frac{\pi}{2}, \pi\right]$, cosine is negative.
- Forgetting to apply the correct identities for double and triple angles can lead to incorrect values.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information