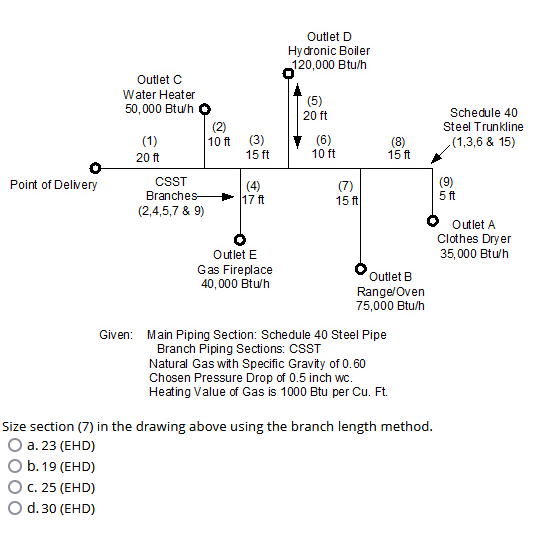
Size section (7) in the drawing above using the branch length method.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the size of section (7) in the provided piping diagram using the branch length method, considering factors such as flow rates and pipe specifications.
Answer
The size for section (7) is $d. 30$ (EHD).
Answer for screen readers
The size for section (7) is $d. 30$ (EHD).
Steps to Solve
- Identify Total Load at Section (7)
First, compute the total load flowing through section (7). Add the flow rates of all outlets that contribute to section (7):
- Outlet E: 40,000 Btu/h
- Outlet B: 75,000 Btu/h
- Outlet A: 35,000 Btu/h
Total Load = $40,000 + 75,000 + 35,000 = 150,000$ Btu/h
- Calculate Equivalent Lengths for Piping Sections
Use the given lengths and fittings to compute equivalent lengths for the branches and main line. The equivalent lengths can include straight pipe lengths and lengths due to fittings:
- Main pipe contributions: 15 ft (section 7) + 5 ft (section 9) + 20 ft (section 5) + 15 ft (section 6) + 17 ft & 10 ft (outlet C contributions). Sum these up:
Total Equivalent Length = $15 + 5 + 20 + 15 + 17 + 10 = 82$ ft
- Find Equivalent Diameter using Branch Length Method
Use the following formula to find a suitable diameter based on the equivalent length and total load, using the branch length method:
Assuming a pressure drop of 0.5 inches of water column (wc):
$$ Q = \frac{(L)(P_d)}{(C)} $$
Where:
- $Q$ = flow rate (Btu/h)
- $L$ = equivalent length (ft)
- $P_d$ = pressure drop (in wc)
- $C$ = a constant derived from flow characteristics of gas and conversion factors
- Select the Pipe Size
Using the calculated equivalent length and pressures, refer to the applicable charts (e.g., gas piping tables) to determine the diameter (EHD) that can accommodate the flow rate of 150,000 Btu/h with a pressure drop of 0.5 in wc.
Assuming the values from standard charts for steel pipes, possible sizes for the required flow:
Comparing values, if Section (7) must support 150,000 Btu/h, check suitable diameters leading to the effective head (EHD).
- Conclude and Select Answer
Select the answer based on available options and calculations from step 4.
The size for section (7) is $d. 30$ (EHD).
More Information
In gas piping systems, the branch length method is essential for determining the necessary pipe diameter to ensure efficient gas flow while maintaining adequate pressure. The selection of a 30 EHD is suitable for managing the flow from multiple gas outlets without significant pressure losses.
Tips
- Miscalculating total load from outlets.
- Incorrectly summing equivalent lengths from pipe and fittings.
- Not considering the pressure drop when referencing size charts.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information