Résoudre les inéquations suivantes: 1. 2x - 6 ≤ 4x + 10 2. √(5x - 5) ≥ 2x - 7x + √5 3. (3 - 2x)/5 - (x - 2)/10 > (5x + 2)/2 - 1/5
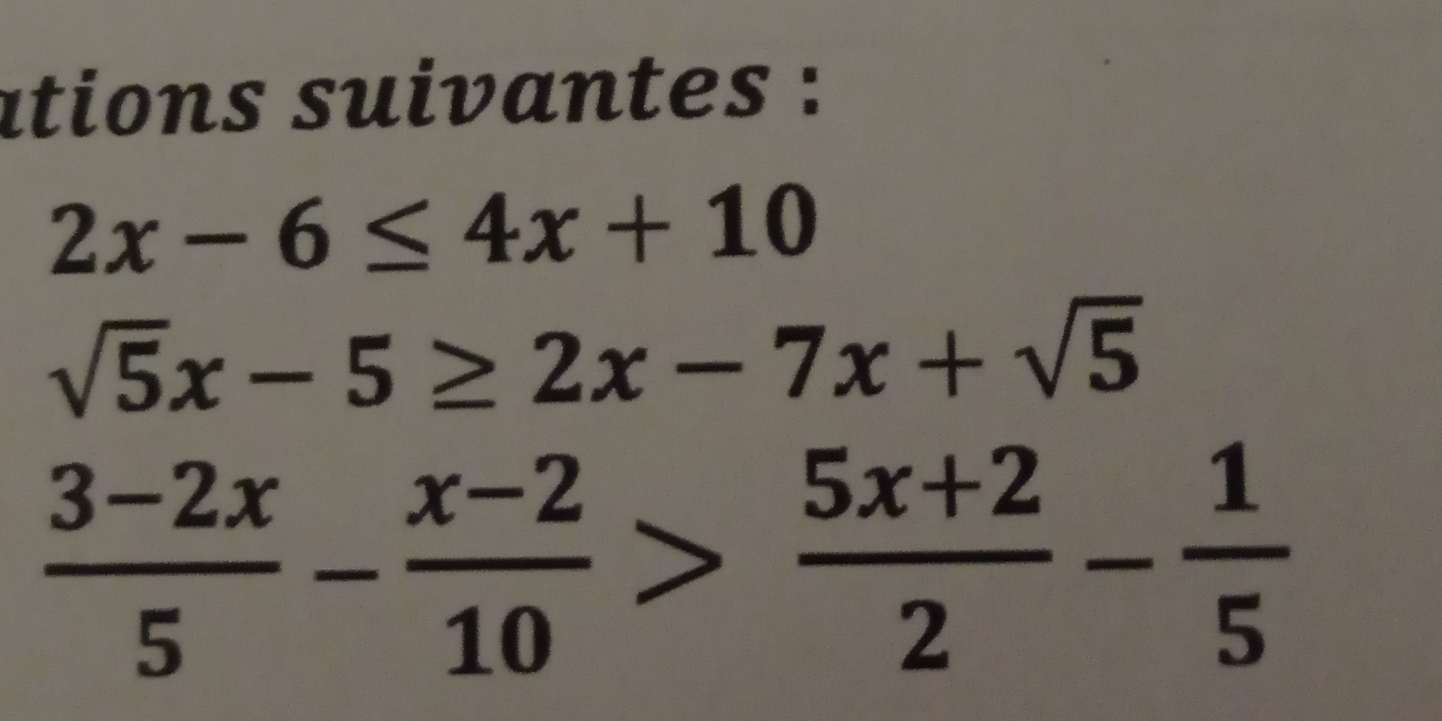
Understand the Problem
La question consiste à résoudre plusieurs inéquations. Chaque inéquation implique de trouver les valeurs de x qui satisfont la condition donnée. Nous allons donc résoudre chaque inéquation étape par étape pour trouver l'ensemble des solutions pour x.
Answer
1. $x \ge -8$ 2. $x \ge 1$ 3. $x < 0$
Answer for screen readers
- $x \ge -8$
- $x \ge 1$
- $x < 0$
Steps to Solve
- Solving the first inequality: $2x - 6 \le 4x + 10$ Isolate $x$ terms on one side and constants on the other side.
$2x - 6 \le 4x + 10$ $2x - 4x \le 10 + 6$ $-2x \le 16$ $x \ge -8$
- Solving the second inequality: $\sqrt{5x-5} \ge 2x - 7x + \sqrt{5}$
Simplify the inequality. $\sqrt{5x-5} \ge -5x + \sqrt{5}$
First, consider the domain of the square root function: $5x - 5 \ge 0$ $5x \ge 5$ $x \ge 1$
Now, consider the inequality. Since the square root is always non-negative, if $-5x + \sqrt{5}$ is negative, the inequality holds. $-5x + \sqrt{5} < 0$ $-5x < -\sqrt{5}$ $5x > \sqrt{5}$ $x > \frac{\sqrt{5}}{5} \approx 0.447$ So for $x \ge 1$, we must test some values. Let's analyze $\sqrt{5x-5} \ge -5x + \sqrt{5}$ for $x \ge 1$. If $x = 1$, $\sqrt{5(1)-5} \ge -5(1) + \sqrt{5}$ $0 \ge -5 + \sqrt{5}$ approximately $0 \ge -5 + 2.236$, $0 \ge -2.764$, which is true.
If $x = 2$, $\sqrt{5(2)-5} \ge -5(2) + \sqrt{5}$ $\sqrt{5} \ge -10 + \sqrt{5}$ which is true. If $x = 3$, $\sqrt{5(3)-5} \ge -5(3) + \sqrt{5}$ $\sqrt{10} \ge -15 + \sqrt{5}$ Approximately, $3.16 \ge -15 + 2.236$, $3.16 \ge -12.764$, which is true. Since the rate of decrease of the term on the right is higher than the term on the left, we examine where both sides can be equal. Graphing the functions might be simplest to accurately determine the solution. Let $f(x) = \sqrt{5x-5}$ and $g(x) = -5x + \sqrt{5}$. Using a graphing calculator, the intersection appears close to x=0.4. Since $x\ge 1$, the inequality holds for $x \ge 1$.
- Solving the third inequality: $\frac{3-2x}{5} - \frac{x-2}{10} > \frac{5x+2}{2} - \frac{1}{5}$
Multiply both sides by the least common multiple of the denominators (10) to eliminate the fractions.
$10 \cdot \left(\frac{3-2x}{5} - \frac{x-2}{10}\right) > 10 \cdot \left(\frac{5x+2}{2} - \frac{1}{5}\right)$ $2(3-2x) - (x-2) > 5(5x+2) - 2(1)$ $6-4x - x + 2 > 25x + 10 - 2$ $8 - 5x > 25x + 8$ $-5x - 25x > 8 - 8$ $-30x > 0$ $30x < 0$ $x < 0$
- $x \ge -8$
- $x \ge 1$
- $x < 0$
More Information
Each inequality was solved separately to determine the solution set for x. For the second inequality, both algebraic manipulation and consideration of the domain were necessary.
Tips
- Forgetting to consider the domain of the square root function.
- Not flipping the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
- Making arithmetic errors when simplifying the inequality.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information