Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controller to Control the Position of a Mass
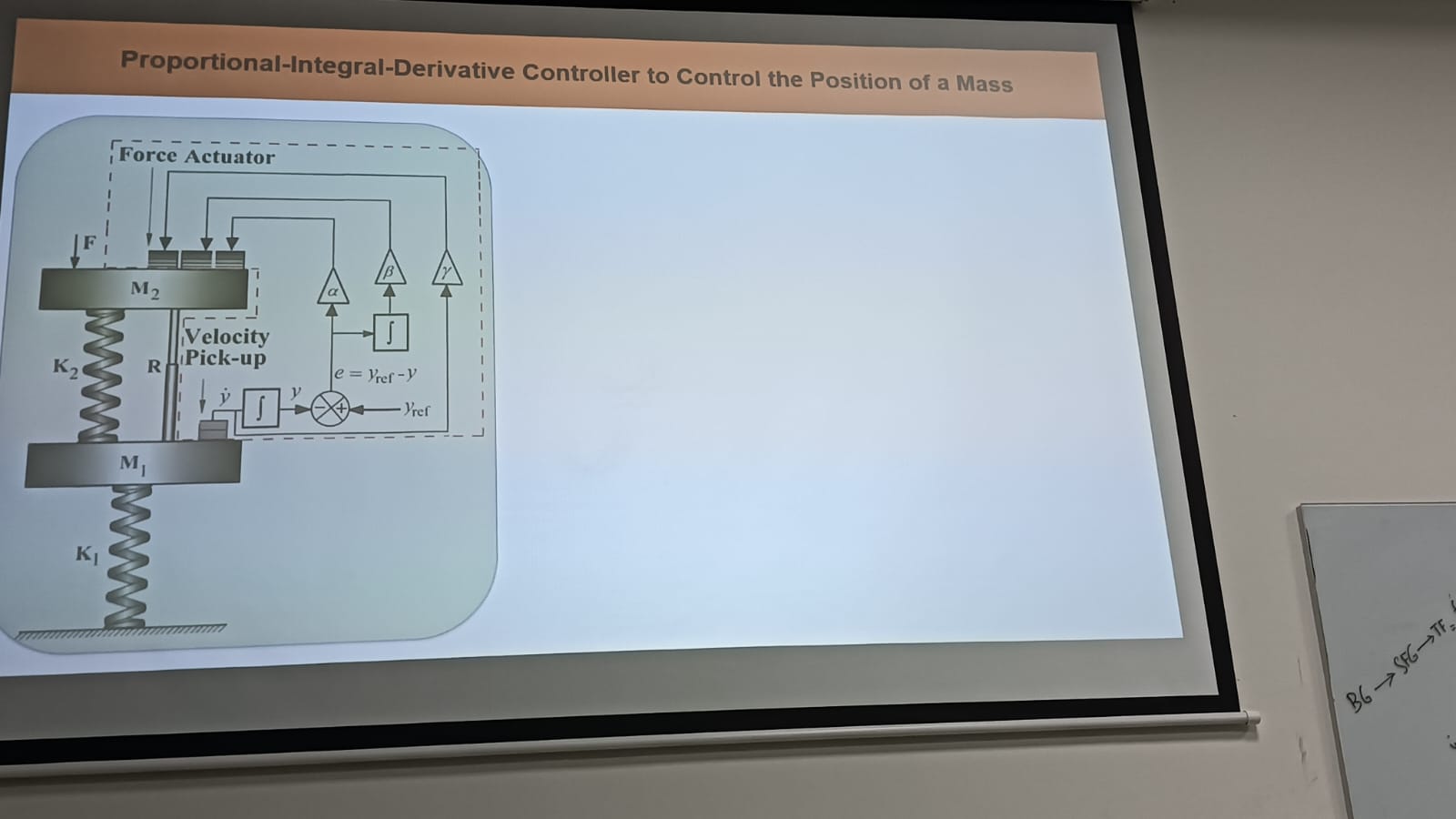
Understand the Problem
The question is focusing on the application of a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller in controlling the position of a mass, involving concepts of force, mass, springs, and motion dynamics.
Answer
The PID controller minimizes position error by adjusting the force applied by the actuator based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms.
The PID controller, through its proportional, integral, and derivative components, continuously adjusts the force applied by the actuator to minimize the position error of mass.
Answer for screen readers
The PID controller, through its proportional, integral, and derivative components, continuously adjusts the force applied by the actuator to minimize the position error of mass.
More Information
A PID controller is widely used in various industrial control applications due to its ease of implementation and ability to provide robust and stable control.
Tips
Common mistakes include tuning the PID parameters incorrectly, which can lead to instability or slow response. Proper tuning of the proportional, integral, and derivative parameters is essential for optimal performance.
Sources
- Proportional–integral–derivative controller - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
- Introduction: PID Controller Design - ctms.engin.umich.edu
- PID Controller: Types, What It Is & How It Works - Omega Engineering - omega.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information