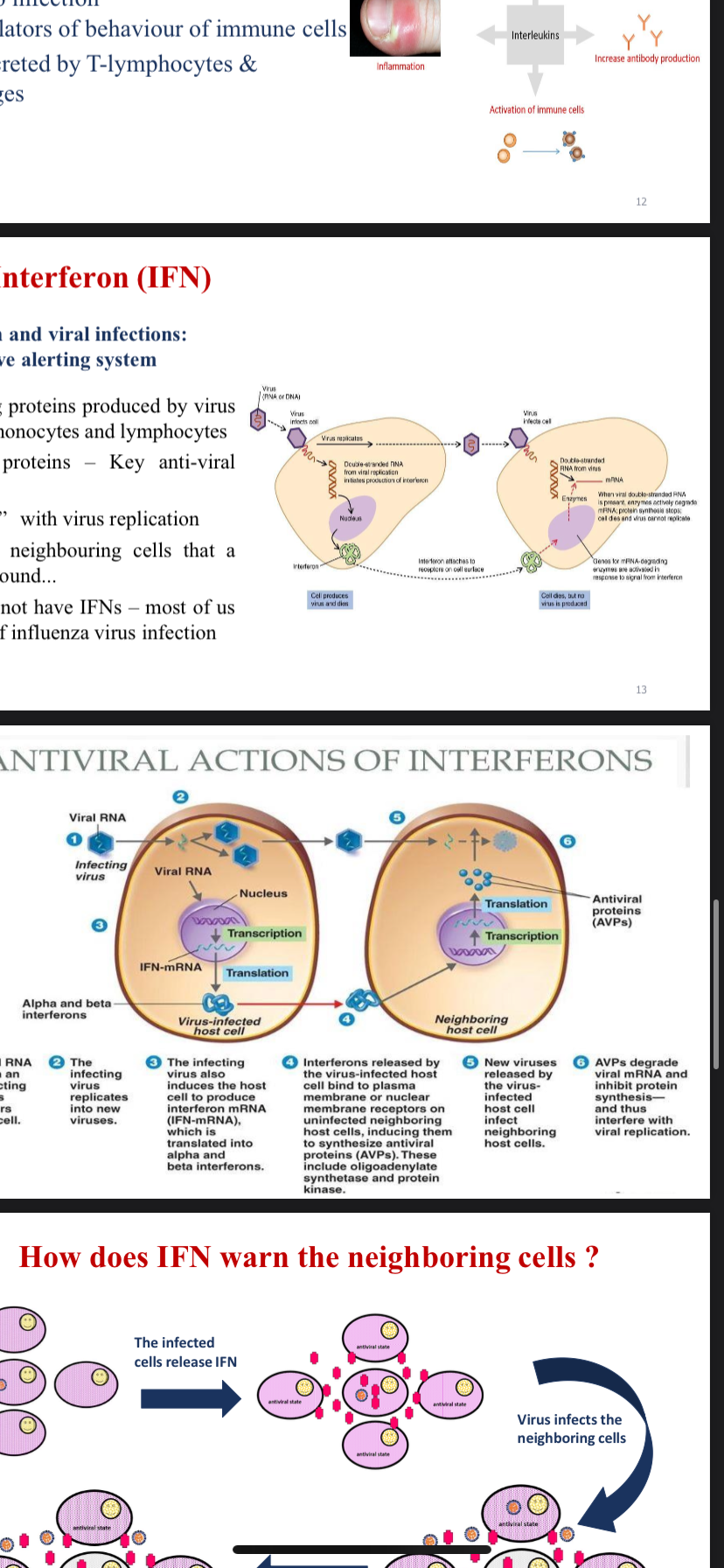
How does IFN warn the neighboring cells?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking how interferon (IFN) communicates a viral infection to neighboring cells, triggering an antiviral response in them. This involves understanding the mechanism by which infected cells release IFN to alert nearby cells.
Answer
IFNs bind to receptors on neighboring cells, inducing antiviral protein production to create an antiviral state.
Interferons (IFNs) warn neighboring cells by binding to receptors on their surface. This binding triggers a signaling cascade that induces these cells to produce antiviral proteins, creating an antiviral state that inhibits viral replication.
Answer for screen readers
Interferons (IFNs) warn neighboring cells by binding to receptors on their surface. This binding triggers a signaling cascade that induces these cells to produce antiviral proteins, creating an antiviral state that inhibits viral replication.
More Information
Interferons are a key part of the immune system's response to infections, helping to control viral spread.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming interferons directly combat the virus rather than preparing neighboring cells to resist infection.
Sources
- Interferons Overview | Thermo Fisher Scientific - thermofisher.com
- Viral recognition and the antiviral interferon response - embopress.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information