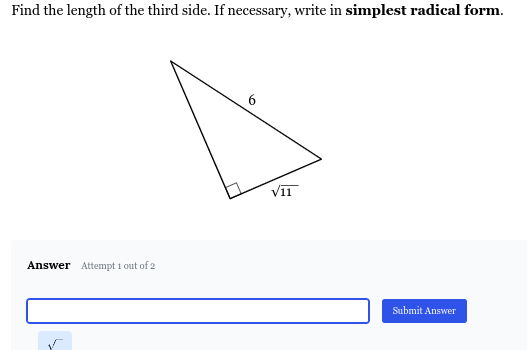
Find the length of the third side of the right triangle. If necessary, write in simplest radical form.
Understand the Problem
The question asks to find the length of the third side of a right-angled triangle given the length of the hypotenuse and one other side. We can use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the length of the missing side. We are also requested to give the answer in simplest radical form.
Answer
5
Answer for screen readers
$5$
Steps to Solve
- Recall the Pythagorean theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be written as:
$a^2 + b^2 = c^2$, where $c$ is the hypotenuse, and $a$ and $b$ are the other two sides.
- Identify the knowns and unknowns
We are given:
Hypotenuse ($c$) = 6 One side ($a$) = $\sqrt{11}$ We need to find the other side ($b$).
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem
Substitute the known values into the Pythagorean theorem:
$(\sqrt{11})^2 + b^2 = 6^2$
- Solve for $b^2$
Simplify the equation:
$11 + b^2 = 36$
Subtract 11 from both sides:
$b^2 = 36 - 11$ $b^2 = 25$
- Solve for $b$
Take the square root of both sides:
$b = \sqrt{25}$ $b = 5$
$5$
More Information
The length of the third side of the triangle is 5. The answer is an integer, so no radical form is necessary.
Tips
- Forgetting to square the numbers when applying the Pythagorean theorem.
- Incorrectly identifying the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is always the longest side and opposite the right angle.
- Not simplifying the radical correctly or leaving the answer in decimal form when the question asks for simplest radical form.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information