Evaluate the limit: $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{x \tan^2(5x^2)}{\sin^5(2x)}$
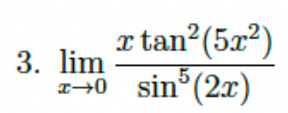
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to evaluate a limit of a function as x approaches 0. The function involves trigonometric functions (tan and sin) raised to powers and multiplied by x. We need to find the limit of this function as x approaches 0.
Answer
$\frac{25}{32}$
Answer for screen readers
$\frac{25}{32}$
Steps to Solve
-
Rewrite the expression Rewrite the given expression to prepare it for using standard limits. $$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x \tan^2(5x^2)}{\sin^5(2x)} = \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x}{\sin^5(2x)} \cdot \tan^2(5x^2) $$
-
Use standard trigonometric limits Use the fact that $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin x}{x} = 1$ and $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\tan x}{x} = 1$. We will rewrite the expression using these limits.
-
Rewrite using $\frac{\sin x}{x}$ and $\frac{\tan x}{x}$ $$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x \tan^2(5x^2)}{\sin^5(2x)} = \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x}{(2x)^5 (\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x})^5} \cdot (5x^2)^2 (\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2})^2 $$ $$ = \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x}{32x^5} \cdot (5x^2)^2 \cdot \frac{(\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2})^2}{(\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x})^5} $$
-
Simplify the expression $$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x}{32x^5} \cdot 25x^4 \cdot \frac{(\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2})^2}{(\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x})^5} $$ $$ = \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{25x^5}{32x^5} \cdot \frac{(\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2})^2}{(\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x})^5} $$
-
Evaluate the limit As $x \to 0$, $\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x} \to 1$ and $\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2} \to 1$. $$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{25x^5}{32x^5} \cdot \frac{(\frac{\tan(5x^2)}{5x^2})^2}{(\frac{\sin(2x)}{2x})^5} = \frac{25}{32} \cdot \frac{1^2}{1^5} = \frac{25}{32} $$
$\frac{25}{32}$
More Information
The limit of the given expression as $x$ approaches $0$ is $\frac{25}{32}$.
Tips
A common mistake is not correctly applying the small angle approximations $\sin(x) \approx x$ and $\tan(x) \approx x$ as $x \to 0$. Another common mistake is to incorrectly simplify the expression after applying the small angle approximations. Finally, forgetting to account for the powers of the trigonometric functions.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information