Determine if the reaction below is spontaneous at 25°C by calculating ΔS_surr: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) ΔH°_rxn = -92.6 kJ at 298.15 K S°_NH3= 193 J/(K·mol); S°_H2 = 131 J/(K·mol);... Determine if the reaction below is spontaneous at 25°C by calculating ΔS_surr: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) ΔH°_rxn = -92.6 kJ at 298.15 K S°_NH3= 193 J/(K·mol); S°_H2 = 131 J/(K·mol); S°_N2 = 192 J/(K·mol)
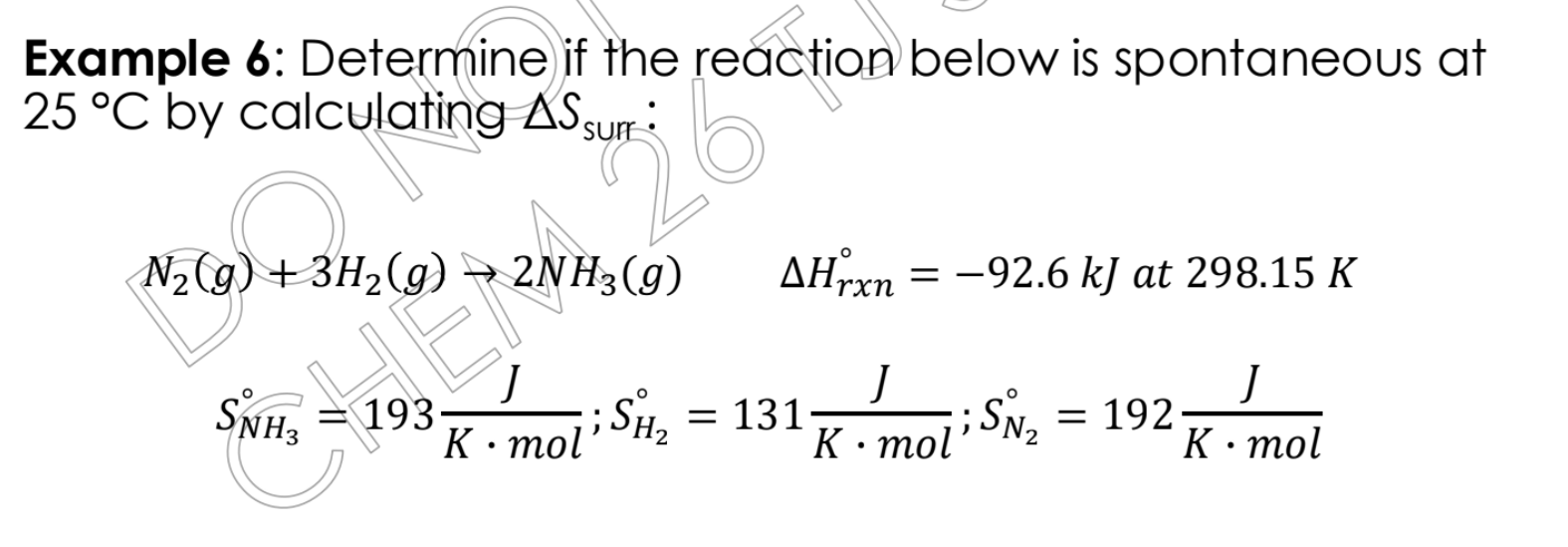
Understand the Problem
The question asks to determine if the given reaction is spontaneous at 25°C by calculating the change in entropy of the surroundings (ΔS_surr). We are given the balanced chemical equation, the change in enthalpy of the reaction (ΔH_rxn), and the standard molar entropies (S°) for each of the reactants and products.
Answer
$\Delta S_{surr} = 310.59 \frac{J}{K}$. The reaction is spontaneous.
Answer for screen readers
$\Delta S_{surr} = 310.59 \frac{J}{K}$. Since $\Delta S_{surr} > 0$, the reaction is spontaneous at 25°C.
Steps to Solve
-
Calculate $\Delta S_{sys}$ (change in entropy of the system): Use the given standard molar entropies ($S^\circ$) to calculate $\Delta S_{sys}$ using the formula: $\Delta S_{sys}^\circ = \sum nS^\circ_{products} - \sum nS^\circ_{reactants}$, where $n$ represents the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation.
-
Plug in the values: $\Delta S_{sys}^\circ = [2 \cdot S^\circ_{NH_3}] - [1 \cdot S^\circ_{N_2} + 3 \cdot S^\circ_{H_2}]$ $\Delta S_{sys}^\circ = [2 \cdot 193 \frac{J}{K \cdot mol}] - [1 \cdot 192 \frac{J}{K \cdot mol} + 3 \cdot 131 \frac{J}{K \cdot mol}]$ $\Delta S_{sys}^\circ = 386 \frac{J}{K} - (192 + 393) \frac{J}{K} = 386 \frac{J}{K} - 585 \frac{J}{K} = -199 \frac{J}{K}$
-
Calculate $\Delta S_{surr}$ (change in entropy of the surroundings): Use the formula $\Delta S_{surr} = -\frac{\Delta H_{rxn}}{T}$, where $\Delta H_{rxn}$ is the change in enthalpy of the reaction and $T$ is the temperature in Kelvin.
-
Convert $\Delta H_{rxn}$ to Joules: $\Delta H_{rxn} = -92.6 \text{ kJ} = -92600 \text{ J}$
-
Plug in the values: $\Delta S_{surr} = -\frac{-92600 \text{ J}}{298.15 \text{ K}} = \frac{92600 \text{ J}}{298.15 \text{ K}} = 310.59 \frac{J}{K}$
-
Determine spontaneity: If $\Delta S_{surr} > 0$, then the process is spontaneous.
$\Delta S_{surr} = 310.59 \frac{J}{K}$. Since $\Delta S_{surr} > 0$, the reaction is spontaneous at 25°C.
More Information
The entropy of the surroundings increases as the reaction proceeds, indicating that the heat released by the exothermic reaction increases the disorder in the surroundings.
Tips
A common mistake is not converting $\Delta H_{rxn}$ from kJ to J before calculating $\Delta S_{surr}$. Also, forgetting to multiply the molar entropies by their respective stoichiometric coefficients when calculating $\Delta S_{sys}$. Another common mistake is getting the sign wrong when calculating $\Delta S_{surr}$.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information