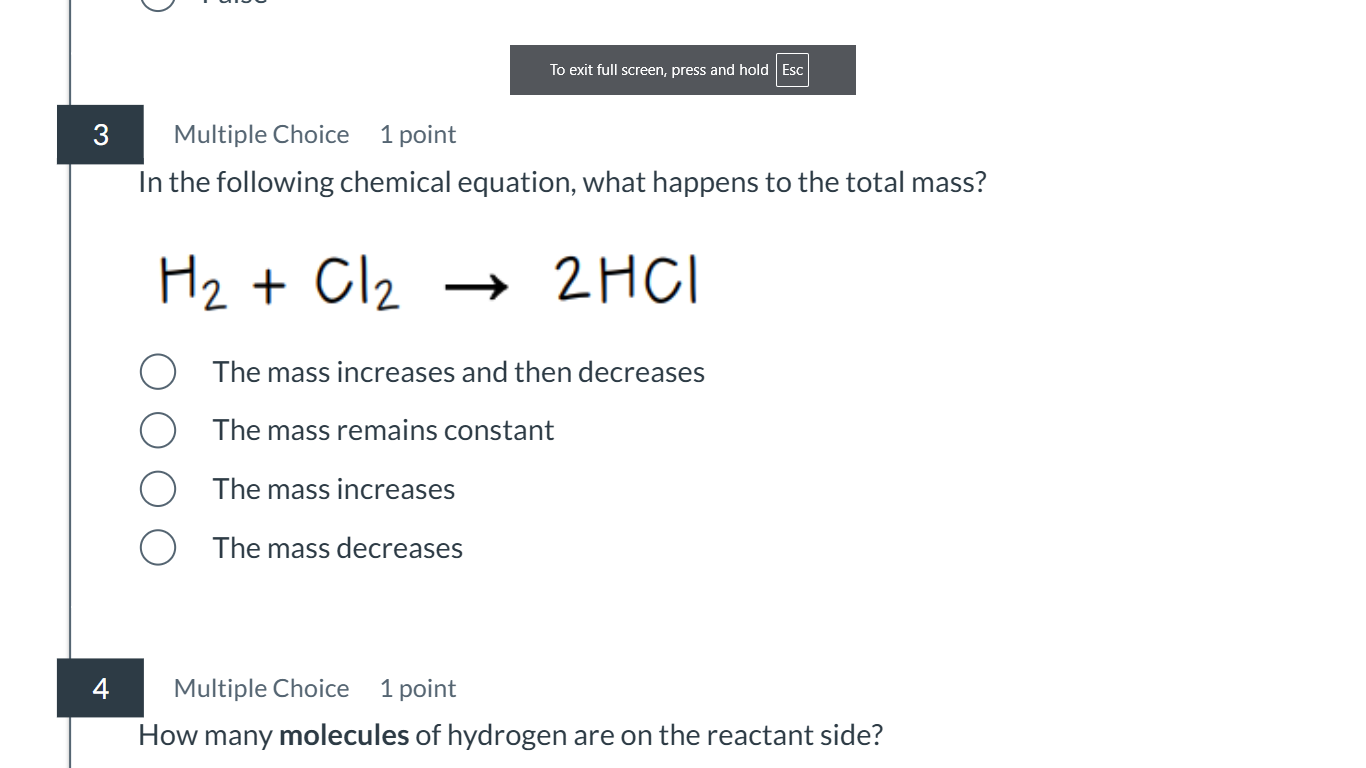
1) In the following chemical equation, what happens to the total mass? H2 + Cl2 -> 2HCl. 2) How many molecules of hydrogen are on the reactant side?
Understand the Problem
The first question asks about mass conservation during a chemical reaction. The second questions asks about counting the number of hydrogen molecules on the reactant side of a given chemical equation.
Answer
The total mass remains constant. There is one molecule of hydrogen on the reactant side.
In a chemical equation, the total mass remains constant because matter is conserved. There is one molecule of hydrogen ($H_2$) on the reactant side.
Answer for screen readers
In a chemical equation, the total mass remains constant because matter is conserved. There is one molecule of hydrogen ($H_2$) on the reactant side.
More Information
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, the total mass of the reactants will be equal to the total mass of the products.
Tips
Make sure the equation is balanced before determining any mass changes.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information