Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two distinct types of human cells that form a zygote?
What are the two distinct types of human cells that form a zygote?
- Skin cells and bone cells
- Red blood cells and white blood cells
- Sperm and egg (correct)
- Nerve cells and muscle cells
What is the unique chromosome configuration of sperm?
What is the unique chromosome configuration of sperm?
- 23 pairs of chromosomes (diploid)
- Half a set of chromosomes (haploid) (correct)
- No chromosomes
- Double the chromosomes of egg cells
Where do egg cells fully mature before being fertilized?
Where do egg cells fully mature before being fertilized?
- Fallopian tubes
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Ovaries (correct)
What is the immediate result of the fusion of sperm with an egg?
What is the immediate result of the fusion of sperm with an egg?
Where does fertilization occur in the female reproductive system?
Where does fertilization occur in the female reproductive system?
Which sex cell has all 23 pairs of chromosomes before fertilization?
Which sex cell has all 23 pairs of chromosomes before fertilization?
What is the first step in the process of fertilization?
What is the first step in the process of fertilization?
During fertilization, what happens after the acrosome reaction?
During fertilization, what happens after the acrosome reaction?
What characterizes cleavage division following fertilization?
What characterizes cleavage division following fertilization?
Which event signifies completion of fertilization?
Which event signifies completion of fertilization?
In what part of the egg does the sperm nucleus migrate after penetration?
In what part of the egg does the sperm nucleus migrate after penetration?
What is formed by rapidly dividing cells post-fertilization by day five?
What is formed by rapidly dividing cells post-fertilization by day five?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Zygotic Beginnings: Understanding the Formation of Zygotes
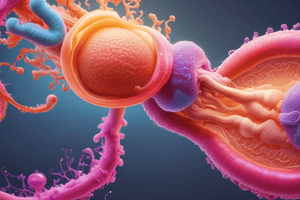
Zygotes—the tiny yet profoundly important cells at the very start of our developmental journey—are formed through the union of two distinct types of human cells: spermatozoa (sperm) from males and ovum (eggs) from females. Let's delve into this fascinating process and uncover how zygotes come into existence.
Sex Cells and their Unique Configuration
Before discussing the formation of zygotes, it's essential first to understand sex cells, also known as gametes. In humans, male sex cells are called sperms while female ones are eggs.
Sperm contain half a set of chromosomes (haploid), and they spend much of their time outside the body within semen before being fertilized with an egg cell. Egg cells, however, have all 23 pairs of chromosomes (diploid), and unlike sperm, only one is released during a woman's menstrual cycle once she reaches sexual maturity.
Prior to fertilization, both sperm and egg undergo certain processes that prepare them for combining into a zygote. Sperm must mature inside the testes and gain motility, whereas eggs grow and develop inside the ovaries until reaching full maturation when they travel down the fallopian tube waiting to encounter sperm.
Fertilization Process
Fertilization occurs when sperm fuses with the egg, creating a single diploid cell known as a zygote. This fusion event involves several steps. First, sperm must swim upstream toward the awaiting egg cell inside the fallopian tubes. Second, sperm bind to specific receptors on the outer surface of the egg cell. Third, acrosome reaction occurs where enzyme-containing granules rupture, enabling the sperm to penetrate the protective layers surrounding the egg.. Fourth, after successfully penetrating the egg, the sperm nucleus begins to migrate towards the center of the egg cell. Finally, the sperm head disintegrates, releasing its genetic material (nucleus containing 23 chromosomes) into the cytoplasm of the egg, completing fertilization.
Cleavage Division
Following fertilization, the newly created zygote undergoes rapid divisions via mitosis, which results in the production of multiple smaller cells, each of which contains the complete set of parental genes. These repeated cell divisions without any increase in size characterize cleavage division. Eventually, these rapidly dividing cells form what we call an embryo by day five post-fertilization.
The zygote serves as the foundation upon which life grows and develops. As scientific advancements continue to expand our understanding of biology, we can better appreciate and respect this remarkable beginning of every new individual born on Earth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.