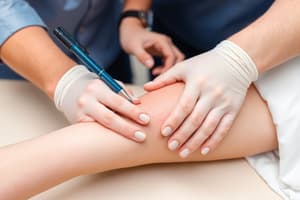
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the LEAST likely color to indicate a healthy wound bed?
Which of the following is the LEAST likely color to indicate a healthy wound bed?
- Beefy red
- Yellow (correct)
- Moist
- Shiny
A nurse is assessing a chronic wound and observes a lack of epithelial tissue regeneration at the wound edges. Which factor is LEAST likely to be preventing wound healing?
A nurse is assessing a chronic wound and observes a lack of epithelial tissue regeneration at the wound edges. Which factor is LEAST likely to be preventing wound healing?
- Complete closure (correct)
- Maceration
- Further tissue breakdown
- Signs of infection
A patient reports increased pain and distress during wound dressing changes. Besides premedication, which intervention is LEAST effective in managing wound-related pain?
A patient reports increased pain and distress during wound dressing changes. Besides premedication, which intervention is LEAST effective in managing wound-related pain?
- Appropriate dressing selection
- Protection of surrounding tissue
- Infrequent dressing changes (correct)
- Aggressive infection treatment
A patient with a chronic wound is experiencing significant pain that is impacting their quality of life. Which outcome is LEAST likely to be associated with this unresolved pain?
A patient with a chronic wound is experiencing significant pain that is impacting their quality of life. Which outcome is LEAST likely to be associated with this unresolved pain?
During a wound assessment, the nurse notes a foul odor and purulent drainage. These findings MOST likely indicate which of the following complications?
During a wound assessment, the nurse notes a foul odor and purulent drainage. These findings MOST likely indicate which of the following complications?
A nurse uses the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing (PUSH) tool. What three characteristics MOST influence the PUSH score?
A nurse uses the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing (PUSH) tool. What three characteristics MOST influence the PUSH score?
Which aspect of wound assessment provides the MOST reliable indication of the patient's pain experience?
Which aspect of wound assessment provides the MOST reliable indication of the patient's pain experience?
A nurse is using the Wound Characteristic Instrument (WCI). The WCI is designed to assess which type of wound?
A nurse is using the Wound Characteristic Instrument (WCI). The WCI is designed to assess which type of wound?
A patient with chronic tissue hypoxia is likely to experience impaired wound healing due to which of the following physiological changes?
A patient with chronic tissue hypoxia is likely to experience impaired wound healing due to which of the following physiological changes?
The microvascular and macrovascular changes associated with diabetes mellitus impede wound healing primarily by:
The microvascular and macrovascular changes associated with diabetes mellitus impede wound healing primarily by:
Why is protein important in wound healing?
Why is protein important in wound healing?
Deficiencies in which of the following nutrients would most significantly impair collagen synthesis and overall wound healing?
Deficiencies in which of the following nutrients would most significantly impair collagen synthesis and overall wound healing?
How does advanced age typically affect the body’s inflammatory response and subsequent wound healing?
How does advanced age typically affect the body’s inflammatory response and subsequent wound healing?
How does infection affect the wound healing process?
How does infection affect the wound healing process?
What is the primary characteristic of wound dehiscence?
What is the primary characteristic of wound dehiscence?
Which complication of wound healing involves the protrusion of visceral organs through the incision site?
Which complication of wound healing involves the protrusion of visceral organs through the incision site?
What is a key characteristic of fistula formation?
What is a key characteristic of fistula formation?
How does chronic tissue hypoxia interfere with collagen synthesis?
How does chronic tissue hypoxia interfere with collagen synthesis?
An alarm on a patient's NPWT system is sounding. What is the most appropriate initial action?
An alarm on a patient's NPWT system is sounding. What is the most appropriate initial action?
During a dressing change, the AP notices increased wound drainage, a foul odor, and the patient reports tenderness. What should the AP do FIRST?
During a dressing change, the AP notices increased wound drainage, a foul odor, and the patient reports tenderness. What should the AP do FIRST?
What is the rationale for using caution when positioning a patient with NPWT?
What is the rationale for using caution when positioning a patient with NPWT?
A patient receiving NPWT reports increased pain at the wound site. After reporting it to the nurse, which intervention is MOST appropriate for the AP to assist with initially?
A patient receiving NPWT reports increased pain at the wound site. After reporting it to the nurse, which intervention is MOST appropriate for the AP to assist with initially?
During a routine check, you notice wound fluid leaking around the edges of the adhesive drape. What is the priority action?
During a routine check, you notice wound fluid leaking around the edges of the adhesive drape. What is the priority action?
What is the primary purpose of a sterile safety pin when used with an open-drain system like a Penrose drain?
What is the primary purpose of a sterile safety pin when used with an open-drain system like a Penrose drain?
An assistive personnel (AP) reports to the nurse that a patient's closed drainage container needs to be emptied more frequently than once per shift. What is the most appropriate nursing action?
An assistive personnel (AP) reports to the nurse that a patient's closed drainage container needs to be emptied more frequently than once per shift. What is the most appropriate nursing action?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a wound drain. Which of the following findings should the nurse immediately report to the health care provider?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a wound drain. Which of the following findings should the nurse immediately report to the health care provider?
A patient with a wound drain reports pain at the insertion site. After medicating the patient as ordered, what additional intervention should the nurse prioritize?
A patient with a wound drain reports pain at the insertion site. After medicating the patient as ordered, what additional intervention should the nurse prioritize?
A nurse assesses a patient's drainage suction device and notes that it is not accumulating drainage. What should be the nurse's initial action?
A nurse assesses a patient's drainage suction device and notes that it is not accumulating drainage. What should be the nurse's initial action?
What is the primary mechanism by which Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) facilitates wound healing?
What is the primary mechanism by which Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) facilitates wound healing?
Which task associated with wound drainage management cannot be delegated to assistive personnel (AP)?
Which task associated with wound drainage management cannot be delegated to assistive personnel (AP)?
Following abdominal surgery, a patient has a Jackson-Pratt drain. The nurse observes that the drainage has a sudden increase in blood. What is the most appropriate initial nursing intervention?
Following abdominal surgery, a patient has a Jackson-Pratt drain. The nurse observes that the drainage has a sudden increase in blood. What is the most appropriate initial nursing intervention?
During wound assessment, which element provides the LEAST direct information about potential infection?
During wound assessment, which element provides the LEAST direct information about potential infection?
A nurse is documenting a wound. What is the MOST accurate way to record undermining?
A nurse is documenting a wound. What is the MOST accurate way to record undermining?
If multiple wounds are present on a patient, why is it essential to number them on a diagram?
If multiple wounds are present on a patient, why is it essential to number them on a diagram?
Which nursing diagnosis is MOST directly supported by the data: 'pressure injury on left buttocks, paralysis below the waist, weight loss, albumin 2.5 g/dL'?
Which nursing diagnosis is MOST directly supported by the data: 'pressure injury on left buttocks, paralysis below the waist, weight loss, albumin 2.5 g/dL'?
When planning wound care, what should a healthcare provider do FIRST to integrate person-centered care?
When planning wound care, what should a healthcare provider do FIRST to integrate person-centered care?
What is the PRIMARY reason for respecting a patient's privacy during dressing changes?
What is the PRIMARY reason for respecting a patient's privacy during dressing changes?
A patient expresses concerns about blood during a dressing change, stating it is a bad omen. What is the MOST appropriate nursing intervention?
A patient expresses concerns about blood during a dressing change, stating it is a bad omen. What is the MOST appropriate nursing intervention?
In certain cultures, hair should not be shaved. When providing wound care, what is the BEST approach?
In certain cultures, hair should not be shaved. When providing wound care, what is the BEST approach?
What is the significance of documenting the 'type of tissue present in the wound' (granulation, slough, eschar)?
What is the significance of documenting the 'type of tissue present in the wound' (granulation, slough, eschar)?
A patient reports pain in the wound area as 8 out of 10. Beyond medication, what NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL intervention demonstrates person-centered care?
A patient reports pain in the wound area as 8 out of 10. Beyond medication, what NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL intervention demonstrates person-centered care?
A patient has a burn that involves the epidermis and part of the dermis, with noticeable blisters. Which classification best describes this burn?
A patient has a burn that involves the epidermis and part of the dermis, with noticeable blisters. Which classification best describes this burn?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a full-thickness burn?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a full-thickness burn?
What is the primary concern regarding a full-thickness burn?
What is the primary concern regarding a full-thickness burn?
What physiological factor primarily contributes to pressure injury formation?
What physiological factor primarily contributes to pressure injury formation?
How do friction and shear forces contribute to the development of pressure injuries?
How do friction and shear forces contribute to the development of pressure injuries?
Prolonged exposure to moisture predisposes the skin to breakdown via:
Prolonged exposure to moisture predisposes the skin to breakdown via:
Which characteristic is associated with a Stage 1 pressure injury?
Which characteristic is associated with a Stage 1 pressure injury?
A wound is classified as a Stage 2 pressure injury. What anatomical structures are affected?
A wound is classified as a Stage 2 pressure injury. What anatomical structures are affected?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of a Stage 3 pressure injury?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of a Stage 3 pressure injury?
In a Stage 4 pressure injury, which of the following anatomical structures may be exposed?
In a Stage 4 pressure injury, which of the following anatomical structures may be exposed?
Why is an unstageable pressure injury not assigned a stage?
Why is an unstageable pressure injury not assigned a stage?
What is the initial presentation of a deep tissue pressure injury?
What is the initial presentation of a deep tissue pressure injury?
When assessing a wound, what does the presence of undermining indicate?
When assessing a wound, what does the presence of undermining indicate?
Why is it important to pack tunneled wounds lightly with gauze or other dressing materials?
Why is it important to pack tunneled wounds lightly with gauze or other dressing materials?
What does the presence of purulent drainage from a wound indicate?
What does the presence of purulent drainage from a wound indicate?
Flashcards
Chronic
Chronic
Long-lasting condition.
Chronic Tissue Hypoxia
Chronic Tissue Hypoxia
The body's diminished ability to supply tissues with adequate oxygen, impairing normal cellular function.
Diabetes Impact on Vessels
Diabetes Impact on Vessels
Thickening of vessel walls, decreased blood flow. Affects nutrient and oxygen supply.
Protein in Wound Healing
Protein in Wound Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamins & Minerals for Healing
Vitamins & Minerals for Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infection's Impact on Healing
Infection's Impact on Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Age's Effect on Healing
Age's Effect on Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dehiscence
Dehiscence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evisceration
Evisceration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fistula Formation
Fistula Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Burns
Burns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Burn
Superficial Burn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Partial-Thickness Burn
Partial-Thickness Burn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Full-Thickness Burn
Full-Thickness Burn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pressure Injury
Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 2 Pressure Injury
Stage 2 Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 3 Pressure Injury
Stage 3 Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 4 Pressure Injury
Stage 4 Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Undermining (wound)
Undermining (wound)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tunneling (wound)
Tunneling (wound)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serous Drainage
Serous Drainage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serosanguineous Drainage
Serosanguineous Drainage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Drainage Changes
Wound Drainage Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Edge Assessment
Wound Edge Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Bed Tissue Types
Wound Bed Tissue Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
RYB Wound Bed Code
RYB Wound Bed Code
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of Wound Pain
Impact of Wound Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assessing Wound Pain
Assessing Wound Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Managing Wound Pain
Managing Wound Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Assessment Tools
Wound Assessment Tools
Signup and view all the flashcards
NPWT & Positioning
NPWT & Positioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dressing Integrity
Dressing Integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient's Temperature/Comfort
Patient's Temperature/Comfort
Signup and view all the flashcards
NPWT: Wound Changes
NPWT: Wound Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
NPWT & Hemorrhage
NPWT & Hemorrhage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open-Drain System
Open-Drain System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed-Drain System
Closed-Drain System
Signup and view all the flashcards
AP Role with Wound Drains
AP Role with Wound Drains
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infected Drainage Site
Infected Drainage Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bleeding Around Drain
Bleeding Around Drain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain with Wound Drain
Pain with Wound Drain
Signup and view all the flashcards
No Drainage Accumulating
No Drainage Accumulating
Signup and view all the flashcards
NPWT
NPWT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Assessment Documentation
Wound Assessment Documentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Documenting Infection Signs in Wounds
Documenting Infection Signs in Wounds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Measurement Documentation
Wound Measurement Documentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multiple Wound Documentation
Multiple Wound Documentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Documenting Wound Pain
Documenting Wound Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Skin Integrity
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Skin Integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Tissue Integrity
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Tissue Integrity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Care: Minimizing Discomfort
Wound Care: Minimizing Discomfort
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cultural Sensitivity: Hair
Cultural Sensitivity: Hair
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skin Integrity and Wound Care: Part I
- Learning objectives include:
- Describing skin structure and function.
- Reviewing factors that alter skin structure and function.
- Discussing components of a focused skin and wound assessment, including risk assessment tools.
- Identifying appropriate nursing diagnoses.
- Developing patient-centered goals.
- Selecting and evaluating interventions for impaired skin integrity.
Normal Skin Structure and Function: Epidermis
- Outermost and thinnest layer that regenerates every 4-6 weeks.
- Five sublayers are:
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum germinativum or basale
Normal Skin Structure and Function: Dermis
- Thicker than epidermis.
- Contains:
- Sebaceous glands
- Sweat glands
- Hair and nail follicles
- Nerves
- Lymphatics
- Epidermal and dermal layers are joined by the basal membrane
Normal Skin Structure and Function: Subcutaneous Layer
- Primarily adipose tissue.
- Attaches the dermis to underlying muscles and bone.
- Delivers blood supply to the dermis, provides insulation, and cushioning.
- Size varies based on body location, weight, sex, and age.
Additional Factors Affecting Skin Integrity
- Wounds disrupt skin integrity.
- Vascular disease impairs the skin's ability to obtain required oxygen and nutrients.
- Diabetes affects microvasculature and skin pH.
- Malnutrition comorbidity, medication and process of aging.
- Medical adhesive-related skin injuries (MARSI) occur when superficial skin layers are removed by medical adhesive.
Altered Structure and Function of the Skin
- Wound classification includes:
- Skin integrity (open vs. closed).
- Wound depth (superficial, partial-thickness, full-thickness).
- Amount of contamination (clean, clean contaminated, contaminated, infected, or colonized).
- Healing process (acute vs. chronic; primary, secondary, or tertiary intention).
Phases of Wound Healing (Full-Thickness Wounds)
- Hemostasis: blood vessels constrict and clotting factors activate coagulation pathways to stop bleeding and form a temporary barrier to bacteria, and platelets release growth factors that attract cells needed for repair.
- Inflammatory: vasodilation occurs, plus plasma and blood cells leak; leukocytes arrive and macrophages appear to regulate wound repair, resulting in a clean wound bed.
- Proliferative: Epithelialization begins, granulation tissue forms, new capillaries are created, and collagen is synthesized, which contributes to strength and structural integrity.
- Contraction occurs in open wounds, reducing the size of the wound.
- Maturation (remodeling): collagen is remodeled for strength, resulting in a well-healed scar
Other Factors impacting healing:
- Oxygenation and Tissue Perfusion: chronic tissue hypoxia is associated with a reduction in collagen formation and decreased action/proliferation of fibroblasts/leukocytes; this impairs cell migration.
- Diabetes: changes in microvascular/macrovascular systems thicken the vessel wall, occlude blood flow, and decrease nutrient/oxygen supply.
- Nutrition: protein is needed by fibroblasts for collagen; deficiencies in vitamins C and A, plus zinc/copper, significantly impact wound healing.
- Infection: prolongs the inflammatory phase, delays collagen synthesis, prevents epithelialization, and leads to further tissue destruction.
- Age: inflammatory response/macrophage & fibroblast action is decreased or delayed, which reduces collagen synthesis and slows epithelialization; comorbidities are increased.
Complications of wound healing
- Dehiscence: partial or complete separation of tissue layers during healing.
- Evisceration: separation of tissue layers allowing protrusion of visceral organs through incision.
- Fistula formation: abnormal connection between two internal organs or an organ and the outside through the skin Examples: enterovaginal, enterocutaneous.
Types of Burns:
- Superficial: damage is to only the epidermis, causing pain and erythema (redness).
- Partial-thickness: destroys the epidermis and part/all of the dermis, causes blistering and pain.
- Full-thickness: destroys the epidermis, dermis, and part of the subcutaneous tissue; area appears white/brown, charred, and lacks sensation; cannot heal without surgery.
Pressure Injuries
- Factors:
- Intensity of pressure: Acceptable capillary closing pressure is exceeded in chairs or hard surfaces.
- Duration of pressure: Has a cumulative effect.
- Medical Devices: injuries result from the use of devices designed and applied for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes
- Friction and shear: opposing stresses on the skin result in hyperangulation/stretching capillaries, damaging them/ability to transport blood.
- Sensory loss/immobility lead to breakdown
- Moisture (maceration, incontinence-related dermatitis) & Nutrition
Pressure injury
- Stage 1 pressure injury is intact, non-blistered skin with non-blanchable erythema/persistent redness, area feels painful and differs in firmness or differs in temperature to surrounding tissue.
- Stage 2 pressure injury is a partial-thickness wound involving the epidermis and/or dermis, and has a shallow and superficial pink wound bed, it does not extend below the level of the dermis, with potential for intact/ruptured blisters.
- Stage 3 pressure injury Full-thickness wounds extend which extend into the subcutaneous tissue but not through fascia to muscle, bone, or connective tissue, and cause undermining or tunneling.
- Stage 4 pressure injury is a full-thickness wound with exposed muscle, bone, or connective tissue; carries high risk for osteomyelitis.
- Unstageable pressure injury is a dull-thickness wound with necrotic tissue making it impossible to assess the depth or involvement of underlying structures until necrotic tissue is removed.
- Deep tissue pressure injury Area of intact skin that can rapidy progress even when treated appropriately, is purple or maroon or a blood-filled blister.
Assessment
- Braden and Norton scales are used to predict pressure sore risk.
Wound Assessment
Important factors include:
- Location and size
- Presence of undermining or tunneling
- Drainage
- Serous drainage: clear, watery fluid from plasma.
- Serosanguineous drainage: pink or pale red with a mix of serous fluid and red, bloody fluid.
- Sanguineous drainage: indicates bleeding and is bright red.
- Purulent drainage: thick, indicates infection, and can be yellow, greenish, or beige.
- Conditions of wound edges/surrounding tissue.
- Wound bed (looking for granulation, necrotic, subcutaneous type tissues, muscle or bone)
- Red Yellow Black classification (RYB): The wound bed should be beefy red and shiny or moist in appearance Yellow is a type of slough tissue and black is necrotic tissue.
- Patient response
Wound Assessment: Tools
- The Wound Characteristic Instrument: Used to assess any open wound.
- Pressure Sore Status Tool (PSST): assigns a numerical score based on 13 wound attributes.
- Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing (PUSH): Score based on three characteristics.
Measuring a Wound
- Performed using a metric system with a facility-provided ruler with increments in centimeters or millimeters and that sterile cotton-tipped applicators can be used to measure the depth
- Wound size changes over time, so size can indicate either healing or negative progression.
- Measure laterally by determining how wide the wound is and vertically to determine the length of the the wound.
Documentation
Items that should be documented following a wound assessment are:
- Color, consistency, and odor type of drainage; as well as the type of tissue present in the wound.
- Changes in the skin surrounding the wound that may indicate infection and areas where undermining measurements taken.
- Number the wounds on a diagram to show how many are present
- Patient pain or discomfort
Wound Assessment: Anatomy
- Assessment includes:
- Periwound skin
- Wound edges
- Odor and pain
- Signs of infection
Wound Color/Tissue Classification
- Black/brown wounds/eschar is full-thickness tissue destruction and are described as necrotic or desiccated tissue. If the goal is debridement chemical debdridment may be used.
- Yellow wounds/Slough tissue represents nonviable tissue, and purulent drainage may be present. Use moisture-retentive dressings can enhance debridement process.
- Red wounds/granulation is a result of an increasing number of blood vessels in the wound and select a dressing that maintains a clean and moist wound environment.
Nursing Diagnoses
- Impaired tissue integrity
- Support: Pressure, immobility, stage 3 pressure injury.
- Impaired skin integrity
- Support: Pressure injury, loss of sensation, stage 2 pressure injury, losing weight, albumin 2.5 g/dL, prealbumin 15 mg/dL (may indicate poor nutrition).
- Acute pain
- Support: Trauma, pain rated at 8 of 10.
Person Centered Care: Planning stage
- Understand how cultural beliefs and practices impact wound care.
- Use gender congruent caregivers and professional translators when possible.
- Recognize family caregivers when giving information.
- Remind patients to communicate any at-home care
Goals for person-centered care in management of wounds
- Identify and respect the patients, spiritual practice or cultural practice when related to wound healing
- Dressing changes Require respect for a patient privacy.
- Identify individual measures to minimize a patient's discomfort during a dressing, change by understanding his or her values and beliefs about pain management
- Assess and try to understand the different meanings of blood and wounds and how they affect patients.
- provide an opportunity for Family caregivers to be present during dressing changes
Person-centered skin care includes recognizing:
- Skin tone.
- Providing patient and caregiver education.
- Considering the social effects of a pressure injury.
- Awareness that hair in some cultures cannot be shaved.
- Consider primary language and reading ability when using printed materials.
- Pressure injuries cause pain and resultant disability
Skin Integrity and Wound Care: Part II
- Comprehensive wound and periwound assessment aids progress of healing and promotes early identification of wound infections.
- Ongoing assessment of chronic wounds and periwound area identifies risk factors.
- Topical antimicrobial agents, polyurethane film, silicone, or foam dressings are effective in promoting wound healing.
Dressings, Bandages, and Binders: Safety Guidelines
- Perform hand hygiene and use appropriate gloves.
- Verify that Wound closure techniques are accurate
- Ensure that the proper treatment plan is in place
- Verify that wound drainage devices don't cause pressure on adjacent skin.
Applying a dressing
- Dry Gause dressings, are used to provide wound healing by little drainage do not interact with wound tissues and cause little wound irritation.
- Moist dressings, such as moisture and gauze can increase the absorptive ability of the dressing to collect exuding wound debris, and mechanically debride the wound.
Applying a dressing: Delegation
- Applying, dry and moist dressing may be delegated to assistant personnel the nurse is responsible for assessing and a evaluating patient:
- Unique modifications of change
- Reporting pain fever, bleeding,
- reporting potential contamination
Applying a dressing: Unexpected outcomes and related
- Inflammation, monitor patients inform health care provider
- Wound bleeds, observe amount of drainage contact, the patient
Applying a dressing: Unexpected outcomes and related
- If area has assess wound
- Sensation , protect if this happens cover patient lie
Application of a pressure bandage is first step in hemorrhage control. Pressure dressing exerts pressure over a bleeding site and assists temporary in controlling and anticipated bleeding The skill of applying or pressure dressing and emergency situation cannot be delegated to a AP. The nurse can direct that AP to asssit as needed. Assist the nurse is directed,. Observe the pressure dressing during activities so has to remain in place and no viable.
Applying a pressure bandage: unexpected outcomes and related interventions
- The continued bleeding of fluid can cause an electrolyte imbalance or the heart can stop
- If the pressure dressing is too tight contact and check circulation and adjust as.
Applying Transparent Dressing
- This is clear, adherents and prevents dehydration, a film
- May for people on high risk skin
Applying Transparent Dressing: Delegation
- This is delegatable if wounds are selected, nurse is responsible
Applying Transparent Dressing: Related outcomes and interventions
- Fluid accumulation, notify health care provider
- does it stay in place, make sure to evaluate size
Hydrocolloid, Hydrogle , Fome
- This is adhesion agent and wound debridement
- It's Glycerin. Water based, may require you to cannot be delegated to A.P. The nurse directs AP to
Hydrocolloid, Hydrogle: Unexpected
- And make necrotic site with tissue will start care
- Evaluate would protocol
- what's impaired
roller gauze, And is easy. the condition of any wound for A nurse
Applying roller gauze - An elastic dressing is
The skill of applying.
Abdominal binder
Abdominal BINDER, large abdominal, The skill of the.
Would Healing Process
May need is enhanced and
Would care related the
Is weak of cleaning the factors.
Irrigation
- That's Tipping in
Irrigation The wound
That.
Suture
Remove as quickly Of depend depends, the degree
Suitors delegates
Drain or temp or pay
Evacuation
And the can't be the
Is may
This has can for
Negative wound
That can.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.