Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of the body is composed of water?
What percentage of the body is composed of water?
- 60% (correct)
- 40%
- 70%
- 50%
Which of the following is NOT a regulated route of water loss?
Which of the following is NOT a regulated route of water loss?
- Sweating
- Evaporation from the lungs
- Renal excretion (correct)
- Defecation
When the intake of water is greater than the loss of water, what is the resulting water balance?
When the intake of water is greater than the loss of water, what is the resulting water balance?
- Negative water balance
- Osmotic equilibrium
- Positive water balance (correct)
- Neutral water balance
What is the osmolarity of urine when the kidneys conserve water?
What is the osmolarity of urine when the kidneys conserve water?
What percentage of the body is composed of intracellular fluid (ICF)?
What percentage of the body is composed of intracellular fluid (ICF)?
When the kidneys conserve water, what is the resulting urine volume?
When the kidneys conserve water, what is the resulting urine volume?
What percentage change in body fluid osmolarity can alter the secretion of ADH?
What percentage change in body fluid osmolarity can alter the secretion of ADH?
Where are the osmoreceptors located that sense changes in body fluid osmolarity?
Where are the osmoreceptors located that sense changes in body fluid osmolarity?
What happens to circulating ADH levels when secretion is inhibited?
What happens to circulating ADH levels when secretion is inhibited?
What is the normal range of set point for plasma osmolarity in individuals?
What is the normal range of set point for plasma osmolarity in individuals?
What can affect the set point of the ADH secretion system?
What can affect the set point of the ADH secretion system?
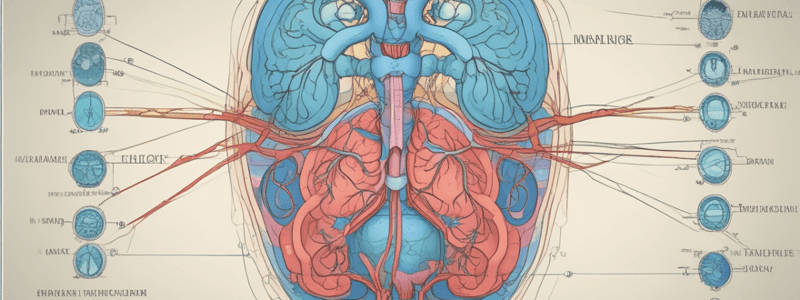
What is the primary function of the kidneys in terms of water balance?
What is the primary function of the kidneys in terms of water balance?
What is the main mechanism by which the kidneys regulate urine concentration and volume?
What is the main mechanism by which the kidneys regulate urine concentration and volume?
What is the osmotic gradient in the interstitial fluid of the kidneys?
What is the osmotic gradient in the interstitial fluid of the kidneys?
What is the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidneys?
What is the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidneys?
What is the solute load of body fluids that the kidneys aim to maintain?
What is the solute load of body fluids that the kidneys aim to maintain?
What is the name of the process by which the kidneys concentrate urine?
What is the name of the process by which the kidneys concentrate urine?
What is the primary function of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the primary function of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the osmolarity of the new fluid that enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the osmolarity of the new fluid that enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the result of the 'single effect' in the countercurrent multiplier?
What is the result of the 'single effect' in the countercurrent multiplier?
What is the purpose of the countercurrent multiplier in the loop of Henle?
What is the purpose of the countercurrent multiplier in the loop of Henle?
What happens to the high osmolarity fluid in the descending limb as a result of the flow of tubular fluid?
What happens to the high osmolarity fluid in the descending limb as a result of the flow of tubular fluid?
What happens to the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid and descending limb in LoH Step 3?
What happens to the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid and descending limb in LoH Step 3?
What is the direction of water flow in the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the direction of water flow in the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the osmolarity of the new fluid that enters the descending limb from the PT in LoH Step 4?
What is the osmolarity of the new fluid that enters the descending limb from the PT in LoH Step 4?
What is the constant difference in filtrate concentration between the 2 limbs of the LoH?
What is the constant difference in filtrate concentration between the 2 limbs of the LoH?
What happens to the fluid in the ascending limb as a result of the fluid shift in LoH Step 4?
What happens to the fluid in the ascending limb as a result of the fluid shift in LoH Step 4?
What is the role of the NaCl pumps in the ascending limb?
What is the role of the NaCl pumps in the ascending limb?
What is the result of the fluid shift in LoH Step 4 on the gradient of osmolarity?
What is the result of the fluid shift in LoH Step 4 on the gradient of osmolarity?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying