Podcast
Questions and Answers
The caldera is smaller than the original crater.
The caldera is smaller than the original crater.
False (B)
What is the primary function of a volcano's vent?
What is the primary function of a volcano's vent?
- To create lava flows
- To provide access for humans
- To supply magma from underground (correct)
- To form the crater
What is the term for the largest underground pool of liquid rock beneath the Earth's crust?
What is the term for the largest underground pool of liquid rock beneath the Earth's crust?
Magma chamber
The _____ is known as the side of a volcano.
The _____ is known as the side of a volcano.
Which of the following describes pyroclastic flow?
Which of the following describes pyroclastic flow?
Volcanic bombs vary in size, with some measuring up to 64 mm in diameter.
Volcanic bombs vary in size, with some measuring up to 64 mm in diameter.
Match the features of a volcano with their descriptions:
Match the features of a volcano with their descriptions:
The _____ refers to the highest point or apex of a volcano.
The _____ refers to the highest point or apex of a volcano.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Volcano Features
- Cone: The most noticeable part of a volcano, formed from a mix of lava and pyroclastic material. The type of magma influences cone shape: Viscous granitic magma creates steep cones, while fast-moving basaltic magma creates low, flat cones.
- Vent: The opening where eruptions occur. Magma travels from the underground source to the volcano's summit through this main part. Vents can be straight or complex.
- Magma Chamber: A large underground pool of molten rock beneath the Earth's crust.
- Crater: A basin-like depression at the summit of the cone, directly above the vent.
- Caldera: A volcanic depression much larger than the original crater.
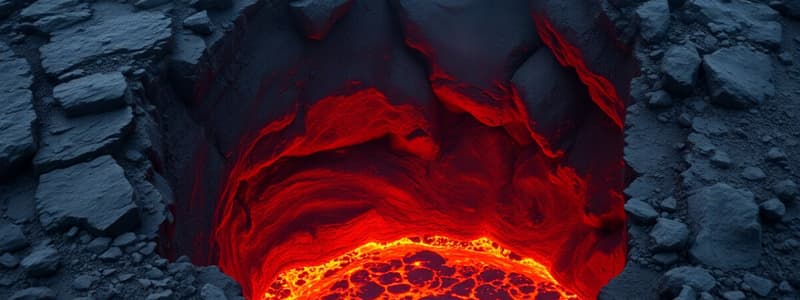
- Lava: Molten rock or magma ejected during an eruption. Lava can reach temperatures up to 700°C and flows until cooling and hardening.
- Dikes: Barriers or obstacles within a volcano. They form when magma cuts through existing rock layers under high pressure.
- Sills: Solidified lava flows that have intruded between existing layers of rock, creating sheets parallel to those layers.
- Conduit: A channel or pipe carrying magma.
- Flank: The side of a volcano.
- Summit: The highest point of a volcano.
- Throat: The entrance of a volcano.
- Ash Cloud: A cloud of pulverized rock and glass created during an eruption, expelled into the atmosphere.
- Volcanic Bombs: Chunks of lava ejected into the air that solidify before reaching the ground. They vary in size, reaching up to 64mm in diameter.
- Pyroclastic Flow: Fast-moving currents of hot gases and rock flowing downhill from a volcano. These flows can reach temperatures over 1000°C and speeds of 700 km/hr. They include pumice flow, ash flow, block and ash flow, glowing erupting clouds (nuée ardente), and avalanches.
- Tephra Fall: Fragmented material consisting of pumice, scoria, lithic materials, crystals, or a combination.
- Lahar: Flows of volcanic debris mixed with water. They are classified as primary (hot) if associated with an eruption, or cold if caused by heavy rainfall.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.