Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the shape of the Rotavirus capsid?
What is the shape of the Rotavirus capsid?
- Three-layer icosahedral (correct)
- Spherical
- Helical
- Filamentous
Which route is responsible for the transmission of Rotavirus?
Which route is responsible for the transmission of Rotavirus?
- Direct contact
- Fecal-oral (correct)
- Airborne
- Vector-borne
What is the effect of trypsin on Rotavirus infectivity?
What is the effect of trypsin on Rotavirus infectivity?
- No effect
- Decreases infectivity
- Unknown
- Enhances infectivity (correct)
What is the primary site of latency for Rotavirus?
What is the primary site of latency for Rotavirus?
What is the name of the vaccine used to prevent Rotavirus infection?
What is the name of the vaccine used to prevent Rotavirus infection?
What is the characteristic of the REOVIRUS in terms of pH?
What is the characteristic of the REOVIRUS in terms of pH?
How many RNA segments does the Orbivirus consist of?
How many RNA segments does the Orbivirus consist of?
Which of the following viruses is primarily an animal pathogen and acid labile?
Which of the following viruses is primarily an animal pathogen and acid labile?
What is the mode of transmission of the Kemerovo virus?
What is the mode of transmission of the Kemerovo virus?
What is the characteristic of Coltivirus in terms of its site of latency?
What is the characteristic of Coltivirus in terms of its site of latency?
What is the treatment for diseases caused by the viruses mentioned?
What is the treatment for diseases caused by the viruses mentioned?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
General Characteristics of Reoviruses
- Naked, icosahedral structure with dual-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genome
- Environmental resilience: stable under heat, infectious from pH 3-9
- Infects a wide range of mammal species and is often found in water contaminated by animal feces
Genera of Reoviruses
- Nine genera identified, with four causing diseases in humans:
- Orbivirus: Primarily animal pathogens, acid labile
- Orthoreovirus
- Rotavirus: Leading cause of gastroenteritis in children
- Coltivirus
Orbivirus
- Contains multiple species including:
- Kemerovo virus: Transmitted by Ixodes tick, causes Oklahoma tick fever and neurologic infections
- Lebombo virus: Spread by mosquitoes, causes clinical illness in Africa
- Orungovirus: Transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, presents with headache and myalgia
- Changuinola virus: Spread by Phlebotomus flies, results in acute febrile illness in Panama
- Laboratory diagnosis via cell culture (BHK) and ELISA
- Supportive treatment and insect repellent recommended
Coltivirus
- Comprises 12 RNA segments, latency sites in bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, and liver of Rhesus monkeys
- Transmitted by wood tick (Dermacentor andersoni)
- Presentation involves biphasic fever: periods of fever, temporary relief, and recurrence
- Associated symptoms: sore throat, vomiting, abdominal pain, including Colorado Tick Fever
- Diagnosed using ELISA, neutralization tests, direct fluorescent antibody tests, and RT-PCR
- Supportive treatment recommended, with avoidance of wood tick bites
Orthoreovirus
- Composed of 10 RNA segments; three known serotypes
- Stable in heat and acid, also aerosol stable
- Associated with upper respiratory tract disease and febrile exanthema in children
- Diagnosis through cell culture methods (PMK, HeLa, MLCF), serology, complement fixation, and hemagglutination inhibition
- Supportive treatment advised
Rotavirus
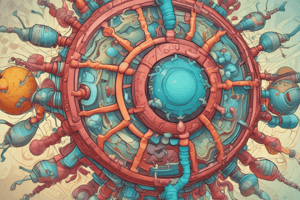
- Most common cause of gastroenteritis in children, identified by a "rim of a wheel" appearance
- Three-layered icosahedral capsid; stable in low temperatures and resistant to acid
- Major cause of infantile diarrhea, with infection enhanced by trypsin
- Major mode of transmission is fecal-oral route, latency in the small intestine
- Laboratory diagnosis via electron microscopy, direct fluorescent antibody tests, and indirect electron microscopy
- Supportive treatments, emphasized importance of personal hygiene, hand washing, and vaccination (RRV-TV - Rota shield) using a rhesus-human reassortant tetravalent vaccine
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.