Podcast
Questions and Answers
Input the patient information, use first and last name, for ID use the first two letters of the ______ name, and first letter of their last name followed by their birth year.
Input the patient information, use first and last name, for ID use the first two letters of the ______ name, and first letter of their last name followed by their birth year.
first
The patient sits in the chair ______ inches away from the TV.
The patient sits in the chair ______ inches away from the TV.
36
Keep the ______ clean, use an antibacterial wipe to maintain cleanliness.
Keep the ______ clean, use an antibacterial wipe to maintain cleanliness.
goggles
Select ______ Testing. The patient’s eyes will be on the screen.
Select ______ Testing. The patient’s eyes will be on the screen.
Instruct the patient to keep their head still and only have their eyes follow the ______.
Instruct the patient to keep their head still and only have their eyes follow the ______.
Place the black goggle ______ on for spontaneous nystagmus tests.
Place the black goggle ______ on for spontaneous nystagmus tests.
Instruct the patient to imagine a dot far away from them and focus on that ______ without moving their eyes.
Instruct the patient to imagine a dot far away from them and focus on that ______ without moving their eyes.
Before you perform the test, show the patients the ______ on the TV frame.
Before you perform the test, show the patients the ______ on the TV frame.
When I say ______, you look at where the top dot was.
When I say ______, you look at where the top dot was.
Do this ______ times in each direction, holding for 1.5-2 seconds before switching.
Do this ______ times in each direction, holding for 1.5-2 seconds before switching.
For Gaze Stability, you should 'keep your eye on the ______ at all times.'
For Gaze Stability, you should 'keep your eye on the ______ at all times.'
In the Antisaccades test, when a new dot appears, look where the dot would be if it was on the ______ side.
In the Antisaccades test, when a new dot appears, look where the dot would be if it was on the ______ side.
If the cursor is not staying on the ______, the patient’s eyelashes may be causing a disturbance.
If the cursor is not staying on the ______, the patient’s eyelashes may be causing a disturbance.
If at any point, the patient gets ______ or nauseous, pause the test and wait for them to improve.
If at any point, the patient gets ______ or nauseous, pause the test and wait for them to improve.
During the VNG, check up on the patient to see if they need to take a ______ and feel ok to continue.
During the VNG, check up on the patient to see if they need to take a ______ and feel ok to continue.
For the OPK test, ask the patient if they have a history of ______.
For the OPK test, ask the patient if they have a history of ______.
What should you do if the calibration is stuck on a dot for more than 7 seconds during the VNG setup?
What should you do if the calibration is stuck on a dot for more than 7 seconds during the VNG setup?
Why is it important to have the patient's eyes at the same level as the green dot during the VNG set-up?
Why is it important to have the patient's eyes at the same level as the green dot during the VNG set-up?
What is the purpose of the Ocular Counter Roll test in the VNG procedure?
What is the purpose of the Ocular Counter Roll test in the VNG procedure?
What action should be taken during the test if there is a calibration error?
What action should be taken during the test if there is a calibration error?
How often should you check on the patient for feelings of discomfort during the VNG procedure?
How often should you check on the patient for feelings of discomfort during the VNG procedure?
What instruction should you give to the patient during the Spontaneous Nystagmus Vertical Saccades test?
What instruction should you give to the patient during the Spontaneous Nystagmus Vertical Saccades test?
What does instructing the patient to keep their eyes wide and blink as little as possible during the Ocular Counter Roll test help achieve?
What does instructing the patient to keep their eyes wide and blink as little as possible during the Ocular Counter Roll test help achieve?
If a patient expresses feelings of nausea during the VNG, what should you do?
If a patient expresses feelings of nausea during the VNG, what should you do?
What are the main instructions given to a patient during the Horizontal Saccades test?
What are the main instructions given to a patient during the Horizontal Saccades test?
During the Pursuits test, what is the patient instructed to do?
During the Pursuits test, what is the patient instructed to do?
Why might the goggles need to be recalibrated during VNG testing?
Why might the goggles need to be recalibrated during VNG testing?
What should be done if a patient feels dizzy or nauseous during the VNG test?
What should be done if a patient feels dizzy or nauseous during the VNG test?
What do you instruct the patient to do to eliminate interference from their eyelashes during testing?
What do you instruct the patient to do to eliminate interference from their eyelashes during testing?
What is the focus of the Antisaccades test?
What is the focus of the Antisaccades test?
What preparatory question should be asked before performing the OPK test?
What preparatory question should be asked before performing the OPK test?
What are the patient’s instructions regarding head movement during Saccadometry?
What are the patient’s instructions regarding head movement during Saccadometry?
What role does the heart rate play in compensating for a drop in blood pressure in patients with POTS?
What role does the heart rate play in compensating for a drop in blood pressure in patients with POTS?
In the context of autonomic disorders, how is orthostatic hypotension defined?
In the context of autonomic disorders, how is orthostatic hypotension defined?
Why is a heart rate increase alone not considered a pathology in patients with POTS?
Why is a heart rate increase alone not considered a pathology in patients with POTS?
What is the relationship between heart rate and blood pressure in a closed cardiovascular system?
What is the relationship between heart rate and blood pressure in a closed cardiovascular system?
How does dysautonomia affect a patient’s response to changes in body position?
How does dysautonomia affect a patient’s response to changes in body position?
What physiological mechanisms underpin tilt table therapy for autonomic disorders?
What physiological mechanisms underpin tilt table therapy for autonomic disorders?
What distinguishes POTS from orthostatic hypotension in terms of heart rate response?
What distinguishes POTS from orthostatic hypotension in terms of heart rate response?
What symptoms can result from a failure to maintain stable blood pressure in autonomic disorders?
What symptoms can result from a failure to maintain stable blood pressure in autonomic disorders?
What role does body mapping play in the blood shunting mechanisms of individuals with TBI and dysautonomia?
What role does body mapping play in the blood shunting mechanisms of individuals with TBI and dysautonomia?
How do vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive deficits impact the heart rate and blood pressure in individuals with TBI?
How do vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive deficits impact the heart rate and blood pressure in individuals with TBI?
What changes occur in autonomic symptoms when proprioceptive or vestibular systems are improved?
What changes occur in autonomic symptoms when proprioceptive or vestibular systems are improved?
What conditions must be met regarding blood pressure and heart rate when a patient lies down at a certain angle?
What conditions must be met regarding blood pressure and heart rate when a patient lies down at a certain angle?
Why is understanding the concept of decompensation important for managing patients with TBI and dysautonomia?
Why is understanding the concept of decompensation important for managing patients with TBI and dysautonomia?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
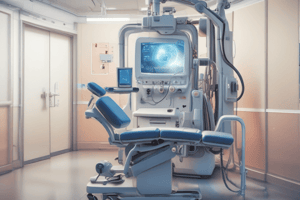
VNG Set-Up
- Launch OTOACCESS program; input patient details: first & last name, ID format: first two letters of first name, first letter of last name, and birth year.
- Select “Micromedical VNG” from the menu.
- Position patient chair 36 inches from the TV; align chair with ground markers for accuracy.
- Center patient in front of the TV; ensure the green dot is at eye level.
- Maintain cleanliness of goggles using antibacterial wipes; apply goggles on the patient securely.
- Start testing once goggles are fitted; patient's eyes will focus on the screen.
- Adjust clarity using side knobs; check TV and patient's eyes for optimal sharpness.
- Center on pupil using toggle; perform calibration as per instructions.
- Regularly check patient comfort and provide breaks as necessary.
Running VNG Procedures
- Ocular Counter Roll:
- Patient focuses on a green dot; perform calibration and torsion measures.
- Move patient’s head while keeping their eyes on the dot; maintain focus while minimizing blinks.
- Spontaneous Nystagmus Tests:
- Use black goggle cover for tests.
- Central Test: Instruct patient to focus on an imagined distant dot.
- Vertical Saccades: Guide patient through looking at frame dots upon verbal cues.
- Horizontal Saccades: Similar to vertical saccades but directed left and right.
- Gaze Stability:
- Instruct patient to keep eyes fixed while head remains still; conduct five tests.
- Pursuits:
- Patient follows a dot with their eyes only, avoiding head movement; execute both horizontal and vertical versions.
- Random Saccade:
- Similar instruction as pursuits; applied to horizontal and vertical configurations.
- OPK:
- Confirm seizure history; if present, skip test; else instruct patient to watch moving bars.
- Saccadometry:
- Look at center dot; when a new dot appears, shift gaze accordingly without head movement.
- Antisaccades:
- Instruct to look at center dot; upon dot appearance, shift to the opposing side equally before returning to center.
Troubleshooting Tips
- If cursor tracking is unstable, check for disturbances from eyelashes; instruct patient on eye positioning.
- Ensure no simultaneous blinking when starting the test to avoid data discrepancies.
- Correct significant data issues by recalibrating without starting over from scratch.
- Advise patient to remove mascara if it interferes with sensor detection of the pupil.
- Immediately pause testing if the patient experiences dizziness or nausea; wait for recovery before deciding on test continuation or termination.
- Consistently check on patient’s comfort and readiness to proceed throughout the testing session.
VNG Set-Up
- Launch OTOACCESS program; input patient details: first & last name, ID format: first two letters of first name, first letter of last name, and birth year.
- Select “Micromedical VNG” from the menu.
- Position patient chair 36 inches from the TV; align chair with ground markers for accuracy.
- Center patient in front of the TV; ensure the green dot is at eye level.
- Maintain cleanliness of goggles using antibacterial wipes; apply goggles on the patient securely.
- Start testing once goggles are fitted; patient's eyes will focus on the screen.
- Adjust clarity using side knobs; check TV and patient's eyes for optimal sharpness.
- Center on pupil using toggle; perform calibration as per instructions.
- Regularly check patient comfort and provide breaks as necessary.
Running VNG Procedures
- Ocular Counter Roll:
- Patient focuses on a green dot; perform calibration and torsion measures.
- Move patient’s head while keeping their eyes on the dot; maintain focus while minimizing blinks.
- Spontaneous Nystagmus Tests:
- Use black goggle cover for tests.
- Central Test: Instruct patient to focus on an imagined distant dot.
- Vertical Saccades: Guide patient through looking at frame dots upon verbal cues.
- Horizontal Saccades: Similar to vertical saccades but directed left and right.
- Gaze Stability:
- Instruct patient to keep eyes fixed while head remains still; conduct five tests.
- Pursuits:
- Patient follows a dot with their eyes only, avoiding head movement; execute both horizontal and vertical versions.
- Random Saccade:
- Similar instruction as pursuits; applied to horizontal and vertical configurations.
- OPK:
- Confirm seizure history; if present, skip test; else instruct patient to watch moving bars.
- Saccadometry:
- Look at center dot; when a new dot appears, shift gaze accordingly without head movement.
- Antisaccades:
- Instruct to look at center dot; upon dot appearance, shift to the opposing side equally before returning to center.
Troubleshooting Tips
- If cursor tracking is unstable, check for disturbances from eyelashes; instruct patient on eye positioning.
- Ensure no simultaneous blinking when starting the test to avoid data discrepancies.
- Correct significant data issues by recalibrating without starting over from scratch.
- Advise patient to remove mascara if it interferes with sensor detection of the pupil.
- Immediately pause testing if the patient experiences dizziness or nausea; wait for recovery before deciding on test continuation or termination.
- Consistently check on patient’s comfort and readiness to proceed throughout the testing session.
Tilt Table Therapy and Autonomic Disorders
- Tilt table therapy is primarily used to treat autonomic disorders, notably postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS).
- POTS is characterized by a significant increase in heart rate upon standing, serving as a compensatory mechanism for a drop in blood pressure.
- A stable blood pressure is crucial for maintaining consistent blood flow to the brain; fluctuations can lead to symptoms like dizziness or fainting.
Cardiovascular System Dynamics
- The cardiovascular system operates as a closed system, balancing heart rate and blood pressure.
- An increased heart rate compensates for decreased blood pressure to prevent dizziness or fainting.
- Distinction between POTS and orthostatic hypotension: in POTS, heart rate rises without a corresponding drop in blood pressure, while orthostatic hypotension involves a blood pressure decline without adequate compensation.
Orthostatic Hypotension
- Orthostatic hypotension occurs when systolic blood pressure drops by 20 points or diastolic by 10 points upon standing.
- Even minimal drops (5-10 points) can indicate a problem, highlighting the need for monitoring.
Physiological Mechanisms in TBI and Dysautonomia
- Body mapping theories suggest a lack of spatial awareness of body parts can hinder effective blood shunting.
- Individuals with dysautonomia often face vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive deficits that lead to mapping issues regarding the positioning of their bodies and heads.
- Improved awareness of body position can enhance autonomic symptoms and shunt blood more effectively when proprioceptive and vestibular systems are corrected.
Impact of Positioning
- When lying down, blood pressure and heart rate are typically stable; however, altering angles can induce compensatory shifts in the cardiovascular response, crucial for patients undergoing tilt table therapy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.