Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main requirement for the function of the vertebral column?
What is the main requirement for the function of the vertebral column?
- Mobility
- Rigidity and plasticity (correct)
- Stability
- Flexibility
What is the role of the ligamentous and muscular tighteners in the vertebral column?
What is the role of the ligamentous and muscular tighteners in the vertebral column?
- To maintain equilibrium shape (correct)
- To provide flexibility
- To reduce stability
- To adjust the shape of the vertebral column
What is the analogy used to describe the vertebral column?
What is the analogy used to describe the vertebral column?
- A tower
- A ship's mast (correct)
- A building
- A tree trunk
What is the function of the shoulder girdle in the vertebral column?
What is the function of the shoulder girdle in the vertebral column?
What is the result of the muscular tighteners adapting their tension in the vertebral column?
What is the result of the muscular tighteners adapting their tension in the vertebral column?
What is the effect of the vertebral column's plasticity?
What is the effect of the vertebral column's plasticity?
What is the characteristic of the curve of the vertebral column of a baby?
What is the characteristic of the curve of the vertebral column of a baby?
What is the name of the curve formed in the thoracic and sacral regions?
What is the name of the curve formed in the thoracic and sacral regions?
What are the two main parts of a typical vertebra?
What are the two main parts of a typical vertebra?
What is the function of the vertical trabecular system in the vertebral body?
What is the function of the vertical trabecular system in the vertebral body?
What is the part of the vertebral arch that divides it into two parts?
What is the part of the vertebral arch that divides it into two parts?
What is the name of the bony structure that forms a rim around the discal surface of the vertebral body?
What is the name of the bony structure that forms a rim around the discal surface of the vertebral body?
What is one of the main requirements for the vertebral column?
What is one of the main requirements for the vertebral column?
How many vertebrae make up the vertebral column?
How many vertebrae make up the vertebral column?
What is the term for a curve in the vertebral column with a posterior convexity?
What is the term for a curve in the vertebral column with a posterior convexity?
How many nerve roots are there in the vertebral column?
How many nerve roots are there in the vertebral column?
What is the function of the vertebral column in relation to the head and internal organs?
What is the function of the vertebral column in relation to the head and internal organs?
How many fused vertebrae are there in the vertebral column?
How many fused vertebrae are there in the vertebral column?
Where is the area of weakness typically located in the body?
Where is the area of weakness typically located in the body?
What is the area of strength characterized by?
What is the area of strength characterized by?
How many columns make up the entire spine?
How many columns make up the entire spine?
What is the major column made up of?
What is the major column made up of?
What is the relationship between the number of curvatures and resistance to axial compression forces?
What is the relationship between the number of curvatures and resistance to axial compression forces?
What is the Delmas index a measure of?
What is the Delmas index a measure of?
What is the formula for the Delmas index?
What is the formula for the Delmas index?
What is the purpose of the spinal curvatures?
What is the purpose of the spinal curvatures?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
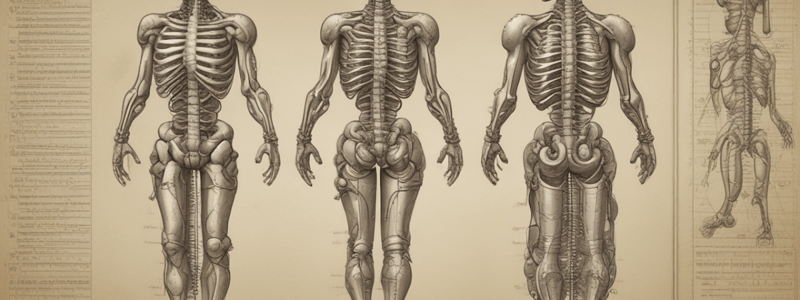
Vertebral Column Structure and Function
- The vertebral column requires two main properties to function: rigidity and plasticity.
- Rigidity refers to its ability to maintain its shape and provide support, similar to a ship's mast.
- Plasticity allows it to adapt to changes in shape while maintaining its rigidity.
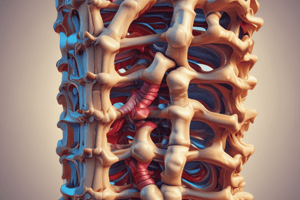
Typical Vertebra Structure
- A typical vertebra consists of two main parts: the vertebral body and the posterior arch.
- The vertebral body is built like a short bone, with a dense bony cortex surrounding a spongy bone.
- It has superior and inferior surfaces, discal surfaces, which are thick and partly cartilaginous.
- The vertebral body has vertical, oblique, and horizontal trabecular systems that correspond to the stresses placed on it.
Functions of the Vertebral Column
- Provide a base of support for the head and internal organs.
- Offer a stable base for the attachment of ligaments, bones, and muscles of the extremities, rib cage, and pelvis.
- Act as a link between the upper and lower extremities.
- Provide mobility for the trunk.
- Protect the spinal cord.
Structure of the Vertebral Column
- The vertebral column consists of 33 vertebrae and 23 intervertebral disks.
- There are 24 distinct vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar) and 9 fused vertebrae (5 sacral, 4 coccygeal).
- The vertebral column has 31 nerve roots (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral).
Primary and Secondary Curves
- The vertebral column has primary and secondary curves.
- The primary curves are kyphotic (thoracic and sacral) and develop in infancy.
- The secondary curves are lordotic (cervical and lumbar) and develop in infancy.
Stability and Mobility
- The vertebral column has three columns: one major column (anterior) and two minor columns (posterior).
- The spinal curvatures increase resistance to axial compression forces.
- The resistance of a curved column is directly proportional to the number of curvatures + 1, as quantified by the Delmas index.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.