Podcast
Questions and Answers
In cattle, which condition is LEAST likely to be an indication for rumen surgery?
In cattle, which condition is LEAST likely to be an indication for rumen surgery?
- Chronic re-occurring free gas bloat.
- Mild, self-resolving cases of grain overload. (correct)
- Suspected ruminal foreign body with hardware disease.
- Frothy bloat that is unresponsive to medical management.
During an exploratory rumenotomy in a cow, what would ultrasonography NOT be useful for visualizing?
During an exploratory rumenotomy in a cow, what would ultrasonography NOT be useful for visualizing?
- Fibrinous adhesions surrounding the rumen.
- Abscesses within the rumen or reticulum.
- Metallic foreign bodies within the reticulum. (correct)
- Inflammatory changes in the rumen wall.
What does measuring fibrinogen levels in cattle primarily help to identify?
What does measuring fibrinogen levels in cattle primarily help to identify?
- The severity of dehydration.
- The presence of a parasitic infection.
- Extent of liver damage.
- The presence and extent of inflammation. (correct)
When performing a left flank laparotomy for a rumenotomy in a mature dairy cow, how far ventral to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae should your skin incision be?
When performing a left flank laparotomy for a rumenotomy in a mature dairy cow, how far ventral to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae should your skin incision be?
What is the primary objective of suturing the rumen to the skin during a rumenotomy procedure?
What is the primary objective of suturing the rumen to the skin during a rumenotomy procedure?
Which suture pattern is recommended to suture the rumen to the skin during a rumenotomy?
Which suture pattern is recommended to suture the rumen to the skin during a rumenotomy?
When performing skin suturing fixation during a rumenotomy, in which direction should the suturing begin?
When performing skin suturing fixation during a rumenotomy, in which direction should the suturing begin?
During a rumenotomy using skin suturing fixation, what is the purpose of pulling the suture tight to invert skin edges?
During a rumenotomy using skin suturing fixation, what is the purpose of pulling the suture tight to invert skin edges?
What is a key consideration when making an incision into the rumen wall when using a rumenotomy board?
What is a key consideration when making an incision into the rumen wall when using a rumenotomy board?
What is the main purpose of Weingarth's frame when performing a rumenotomy?
What is the main purpose of Weingarth's frame when performing a rumenotomy?
What is an important consideration when preparing a patient for a rumen exploratory procedure?
What is an important consideration when preparing a patient for a rumen exploratory procedure?
In which direction should the incision be made in cattle when using the Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation method?
In which direction should the incision be made in cattle when using the Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation method?
During reticular exploration, what action can be taken to manage abscesses?
During reticular exploration, what action can be taken to manage abscesses?
What is the recommended closure technique for the rumen during a rumenotomy?
What is the recommended closure technique for the rumen during a rumenotomy?
What is the proper order of closure for a laparotomy?
What is the proper order of closure for a laparotomy?
What type of suture is typically used for a two layer muscle closure during a laparotomy?
What type of suture is typically used for a two layer muscle closure during a laparotomy?
What type of suture is typically used to close the skin during a laparotomy?
What type of suture is typically used to close the skin during a laparotomy?
What action should be taken during skin closer for a laparotomy to allow for proper ventral drainage?
What action should be taken during skin closer for a laparotomy to allow for proper ventral drainage?
Which local or regional anesthesia technique is not typically used in a left flank laparotomy?
Which local or regional anesthesia technique is not typically used in a left flank laparotomy?
Which of the following techniques involves suturing the rumen wall to the abdominal skin edges to create a sealed opening for exploration and removal of rumen contents?
Which of the following techniques involves suturing the rumen wall to the abdominal skin edges to create a sealed opening for exploration and removal of rumen contents?
Metals and magnets are not be imaged clearly by ___________.
Metals and magnets are not be imaged clearly by ___________.
In a 5 y/o Gelbvieh cow with intestinal obstruction, scant feces, and a distended rumen, why might oral-rumen intubation fail to decompress the rumen?
In a 5 y/o Gelbvieh cow with intestinal obstruction, scant feces, and a distended rumen, why might oral-rumen intubation fail to decompress the rumen?
What is the significance of a 'papple' shape upon examination of a cow?
What is the significance of a 'papple' shape upon examination of a cow?
During a rumenotomy, why is it crucial to perform copious lavage before releasing the rumen from the skin?
During a rumenotomy, why is it crucial to perform copious lavage before releasing the rumen from the skin?
When performing reticular exploration during a rumenotomy, what anatomical landmark is palpated to identify potential obstructions?
When performing reticular exploration during a rumenotomy, what anatomical landmark is palpated to identify potential obstructions?
After completing a reticular exploration during a rumenotomy, what prophylactic measure is typically taken before closure?
After completing a reticular exploration during a rumenotomy, what prophylactic measure is typically taken before closure?
A surgeon with shorter arms may have difficulty with reticular exploration due to instrument and reach limitations. To compensate, they may need to make their initial skin incision:
A surgeon with shorter arms may have difficulty with reticular exploration due to instrument and reach limitations. To compensate, they may need to make their initial skin incision:
In the Stay Suture Rumenotomy technique, what gauge of nylon suture is recommended for anchoring the rumen wall to the incision?
In the Stay Suture Rumenotomy technique, what gauge of nylon suture is recommended for anchoring the rumen wall to the incision?
How many sutures should be placed in the rumen walls in the Stay Suture Rumenotomy technique?
How many sutures should be placed in the rumen walls in the Stay Suture Rumenotomy technique?
Flashcards
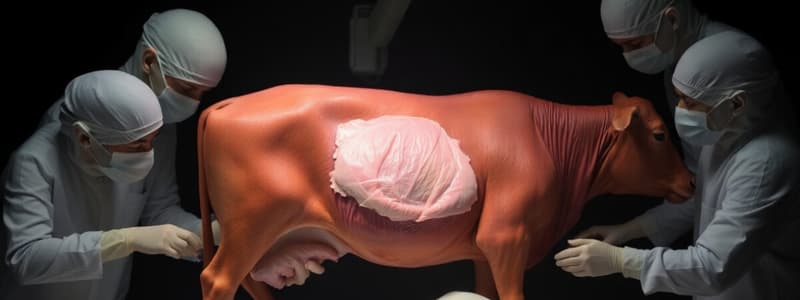
Rumenotomy
Rumenotomy
Surgical entry to the rumen to access its contents.
Indications for Rumen Surgery
Indications for Rumen Surgery
Frothy bloat, Free gas bloat, Ruminal foreign bodies, Hardware disease, Vagal indigestion, Grain overload, Toxin ingestion
Left Flank Laparotomy
Left Flank Laparotomy
A surgical approach through the left flank to access the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound Rumen Findings
Ultrasound Rumen Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Measuring Fibrinogen
Measuring Fibrinogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steps of Rumenotomy
Steps of Rumenotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Flank Laparotomy Anesthesia
Left Flank Laparotomy Anesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Flank Laparotomy - Skin Incision
Left Flank Laparotomy - Skin Incision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rumenotomy Fixation method
Rumenotomy Fixation method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goals of Rumenotomy
Goals of Rumenotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rumenotomy Retractor
Rumenotomy Retractor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Suturing Fixation
Skin Suturing Fixation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation
Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stay Suture Rumenotomy
Stay Suture Rumenotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weingarth's Ring Rumenotomy
Weingarth's Ring Rumenotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rumen Exploratory preparation
Rumen Exploratory preparation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explore dorsal and ventral rumen sac for:
Explore dorsal and ventral rumen sac for:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Exploration
Reticular Exploration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rumenotomy Closure
Rumenotomy Closure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abdomen Wall Closure
Abdomen Wall Closure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Rumen Evaluation and Surgery is covered in VCS 878 by Miesner
Indications for Rumen Surgery
- Rumen surgery may be indicated to gain Access to the Rumen
- Some Access to Rumen indications include: Frothy bloat, Free gas bloat/Chronic re-occurring bloat, Ruminal foreign bodies (Hardware disease, other), Vagal indigestion, Grain overload, Toxin ingestion, Experimental/Research
- Rumen surgery can be useful for making a rumen donor (rumen canula)
Ultrasonography
- Ultrasound findings (Braun, 2003) can show inflammatory fibrinous changes and abscesses
- Magnets and other foreign bodies cannot be imaged with ultrasound
Measuring Fibrinogen
- Fibrinogen can be measured by heat precipitating from plasma and measuring the difference of TP between samples; normal is less than 500 grams.
- A "coffee cup" method involves using 130°F H₂O for 3 minutes.
- The difference between TP measurements estimates fibrinogen.
- For example, if the initial TP is 9.5 and post-heat treated TP is 8, then estimated fibrinogen is about 1.5 grams.
Radiography
- Radiography is a potential diagnostic tool.
5 y/o Gelbvieh Cow Case
- A 5 y/o Gelbvieh Cow, presents with a complaint of intestinal obstruction
- Exam findings include that the cow is Alert, has a Papple shape, Normal TPR
- In the case the cow has scant/no Feces in rectum and large rumen and the cow cannot decompress with Oral-rumen intubation
- Ultrasound and Bloodwork are part of the case's plan
Rumenotomy
- Part of the dorsal rumen sac is exteriorized through the laparotomy incision
- Starting at the dorsal aspect of the incision, the rumen is sutured to the skin in a Cushing-type pattern to form a seal
- Partial thickness bites should be taken through the rumen wall
- After seal is created between rumen and skin, the rumen is incised leaving approximately 3 cm at the dorsal and ventral part
Left Flank Laparotomy
- Anesthesia for left flank laparotomy can be standing procedure, using Local or regional anesthesia
- Local or regional anesthesia may include a Proximal / Distal Paravertebral nerve block, Inverted L-block, or Line block with 2% Lidocaine HCI
- A skin incision (~20cm dorsoventral) is made in the left paralumbar fossa
- The incision is made approximately 4 cm (hand width) caudal and parallel to the last rib
- Make the incision approximately 6 to 8 cm ventral to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae
- Surgeons with short arms may require the incision to be more cranial and ventral for full reticular exploratory
Rumenotomy - Methods and Goals
- Rumenotomy methods include skin fixation techniques and rumen boards
- Rumenotomy goals include to avoid peritoneal contamination and to gain access to rumen
Skin Suturing Fixation
- The dorsal sac of rumen is exteriorized through left flank incision
- Rumen was sutured to skin using #2 silk in a continuous Connell pattern
- Suturing began midway down caudal part of incision and continued in a clockwise direction
- Suture pulled tight to invert skin edges under rumen for good seal
Rumenotomy Board
- For the rumenotomy board method, the incision should be made in a fold of rumen wall starting ventrally, placing hooks as the incision is made
Other Rumenotomy Variations
- Other methods include Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation, Stay Suture Rumenotomy, Weingarth's Ring Rumenotomy
Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation
- Rumen is exteriorized through incision and firmly anchored to skin dorsally and ventrally by towel clamps
- Rumen was opened and towel clamps placed cranially and caudally
- Additional clamps placed between these clamps
- The rumen edges were made to overlap the skin edges by 2-3 cm
Stay Suture Rumenotomy
- Rumen is exteriorized through incision
- Rumen wall anchored to incision dorsally, ventrally, cranially, and caudally by 4 sutures using #2 nylon
- Rumen exploratory is performed using rumen shroud
Weingarth's Ring Rumenotomy
- Weingarth's frame was fixed to dorsal commissure of the incision
- As rumen wall was incised, hooks placed into cut edge of rumen wall and hooked to frame
Rumen Exploratory
- It is difficult to explore cattle with a full rumen
- A 24 hour fast prior to rumenotomy can help as well as evacuating part of the rumen mat
- The dorsal and ventral rumen sacs should be explored
- A Rumen Exploratory can reveal Grain overload, Frothy / Free gas bloat, Sand accumulation, Rumenal foreign bodies, Rumenitis
Reticular Exploration
- Reticular Exploration can be difficult for surgeons with short arms
- Placement of body wall incision is critical and Rumen board techniques can limit the reach
- A main indication for Reticular Exploration is Hardware disease
- Check for adhesions of reticulum to body wall as well as palpate for abscesses
- Abscesses can be lanced into the reticulum and Ultrasound can be helpful for the exploration
- Palpate reticuloomasal orifice for Obstructing foreign bodies
- A magnet should be placed on the way out
Rumenotomy Closure
- A 2 layer inverting closure should be completed with absorbable suture
- Copious lavage should be done prior to releasing the rumen from skin
- Perform a routine abdominal wall closure
Laparotomy Closure
- A 2 layer muscle closure should be performed using #3 chromic gut for Peritoneum & Transverse abdominus and Internal & External abdominal oblique muscles
- Skin is routinely closed with Ford Interlocking pattern with #3 Braunamid
- An interrupted suture should be placed at bottom of incision to allow ventral drainage if needed
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.