Podcast
Questions and Answers
What was the primary goal of manifest destiny?
What was the primary goal of manifest destiny?
- Promoting the Populist Movement
- Establishing a federal regulatory agency
- Defending the Great Plains from settlers
- Expansion of the United States to the Pacific Ocean (correct)
What major piece of legislation helped fulfill America's commitment to manifest destiny?
What major piece of legislation helped fulfill America's commitment to manifest destiny?
- The Sherman Antitrust Act
- The Kansas-Nebraska Act
- The Morrill Act
- The Homestead Act (correct)
What was a primary cause of the Indian Wars between 1860 and 1890?
What was a primary cause of the Indian Wars between 1860 and 1890?
- The decline of the buffalo population
- Increased government regulation of railroads
- The establishment of time zones
- The movement of settlers onto the Great Plains (correct)
What was a key impact of the discovery of gold and silver in the mid-1800s?
What was a key impact of the discovery of gold and silver in the mid-1800s?
What was the last major conflict between Native Americans and the U.S. Army?
What was the last major conflict between Native Americans and the U.S. Army?
Which invention was crucial for settlers on the Great Plains to guard their property?
Which invention was crucial for settlers on the Great Plains to guard their property?
What best describes the Populist Movement of the 1890s?
What best describes the Populist Movement of the 1890s?
Which group could join the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) when it was founded?
Which group could join the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) when it was founded?
What was the purpose of Hawaii's annexation by the U.S.?
What was the purpose of Hawaii's annexation by the U.S.?
Which movement aimed to limit the power of big business and improve society during the early 20th century?
Which movement aimed to limit the power of big business and improve society during the early 20th century?
What did Jim Crow Laws enforce in the United States?
What did Jim Crow Laws enforce in the United States?
What was a common reason children worked in factories during this period?
What was a common reason children worked in factories during this period?
What policy did President Wilson advocate for regarding WWI?
What policy did President Wilson advocate for regarding WWI?
What was the major misconception regarding Yellow Journalism?
What was the major misconception regarding Yellow Journalism?
Which of the following statements about anti-suffragists is true?
Which of the following statements about anti-suffragists is true?
What was the main reason for American intervention in various Latin American countries between 1890 and 1917?
What was the main reason for American intervention in various Latin American countries between 1890 and 1917?
What economic change influenced American expansionism in the late nineteenth century?
What economic change influenced American expansionism in the late nineteenth century?
Which of the following industrial leaders argued for the necessity of expansion to support American industry?
Which of the following industrial leaders argued for the necessity of expansion to support American industry?
What was one of the main reasons U.S. businesses sought foreign markets in the late nineteenth century?
What was one of the main reasons U.S. businesses sought foreign markets in the late nineteenth century?
What role did American imperialism play in foreign relations with Latin America?
What role did American imperialism play in foreign relations with Latin America?
Which advancement was crucial for American industrial growth in the late nineteenth century?
Which advancement was crucial for American industrial growth in the late nineteenth century?
What was a potential consequence of failing to secure new foreign markets for U.S. goods?
What was a potential consequence of failing to secure new foreign markets for U.S. goods?
American imperialism is often attributed to which of the following causes?
American imperialism is often attributed to which of the following causes?
Which companies exemplified American corporate interests in Latin America during the period of expansion?
Which companies exemplified American corporate interests in Latin America during the period of expansion?
What demographic shift occurred in the United States during the late nineteenth century as a result of industrialization?
What demographic shift occurred in the United States during the late nineteenth century as a result of industrialization?
What was a major impact of the Progressive movement on American society?
What was a major impact of the Progressive movement on American society?
What is the best definition of nationalism?
What is the best definition of nationalism?
Which Supreme Court decision stated that segregation by law was constitutional, provided accommodations were equal?
Which Supreme Court decision stated that segregation by law was constitutional, provided accommodations were equal?
What was a significant consequence of Germany's policy of unrestricted submarine warfare?
What was a significant consequence of Germany's policy of unrestricted submarine warfare?
Who were muckrakers?
Who were muckrakers?
Why was imperialism considered a threat to international peace?
Why was imperialism considered a threat to international peace?
What was the primary message of the Zimmerman Telegram?
What was the primary message of the Zimmerman Telegram?
What diplomatic approach is associated with William Howard Taft?
What diplomatic approach is associated with William Howard Taft?
Which journalist is recognized for using photography to reveal extreme poverty among immigrants?
Which journalist is recognized for using photography to reveal extreme poverty among immigrants?
What was the purpose of the Selective Service Act?
What was the purpose of the Selective Service Act?
What did the 19th Amendment accomplish?
What did the 19th Amendment accomplish?
Which of the following statements accurately describes Yellow Journalism?
Which of the following statements accurately describes Yellow Journalism?
Who among the following was a muckraker that exposed the corrupt practices of the Standard Oil Company?
Who among the following was a muckraker that exposed the corrupt practices of the Standard Oil Company?
What did the Espionage and Sedition Act prohibit?
What did the Espionage and Sedition Act prohibit?
What role did the War Industries Board play during the war?
What role did the War Industries Board play during the war?
What was a major economic challenge faced by the American economy in the late 1800s?
What was a major economic challenge faced by the American economy in the late 1800s?
What event is typically viewed as a turning point in American diplomacy?
What event is typically viewed as a turning point in American diplomacy?
What justification was used to align American colonialism with its political values?
What justification was used to align American colonialism with its political values?
Which of the following figures advocated for the idea of a 'new manifest destiny'?
Which of the following figures advocated for the idea of a 'new manifest destiny'?
Which of the following describes the sentiment of American workers in the late 1800s amidst economic instability?
Which of the following describes the sentiment of American workers in the late 1800s amidst economic instability?
One of the results of the Spanish American War was that the United States:
One of the results of the Spanish American War was that the United States:
What were two economic arguments in favor of American imperialism?
What were two economic arguments in favor of American imperialism?
Which characteristic described the American approach to imperialism following the Spanish American War?
Which characteristic described the American approach to imperialism following the Spanish American War?
Flashcards
What was the primary goal of Manifest Destiny?
What was the primary goal of Manifest Destiny?
A policy that promoted the expansion of the United States westward to the Pacific Ocean, driven by the belief that it was America's destiny.
How did the Homestead Act and the Transcontinental Railroad contribute to Manifest Destiny?
How did the Homestead Act and the Transcontinental Railroad contribute to Manifest Destiny?
The Homestead Act provided free land to settlers, while the transcontinental railroad facilitated transportation and settlement in the West.
What was the main cause of the Indian Wars (1860-1890)?
What was the main cause of the Indian Wars (1860-1890)?
The arrival of settlers onto the Great Plains disrupted Native American lands and way of life, leading to conflicts.
What mainly drove the population growth of California and Western territories in the mid-1800s?
What mainly drove the population growth of California and Western territories in the mid-1800s?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How did railroads affect the development of the United States in the late 19th century?
How did railroads affect the development of the United States in the late 19th century?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the relationship between corn production and corn prices?
What is the relationship between corn production and corn prices?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who won the Battle of Little Bighorn?
Who won the Battle of Little Bighorn?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What was the main factor in the decline of the buffalo population in the late 1800s?
What was the main factor in the decline of the buffalo population in the late 1800s?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labor Organization
Labor Organization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urbanization
Urbanization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progressive Movement
Progressive Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muckrakers
Muckrakers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plessy v. Ferguson
Plessy v. Ferguson
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nationalism
Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of Military Innovations in WWI
Impact of Military Innovations in WWI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yellow Journalism
Yellow Journalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open Door Policy
Open Door Policy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Big Stick Diplomacy
Big Stick Diplomacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moral Diplomacy
Moral Diplomacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dollar Diplomacy
Dollar Diplomacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Journalism
Journalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
War Industries Board
War Industries Board
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liberty Bonds
Liberty Bonds
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is annexation?
What is annexation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is yellow journalism?
What is yellow journalism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Isolationism?
What is Isolationism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Jim Crow Laws?
What are Jim Crow Laws?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is diplomacy?
What is diplomacy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What was the Progressive Movement?
What was the Progressive Movement?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is American Imperialism?
What is American Imperialism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What did President Wilson hope the Great War would be?
What did President Wilson hope the Great War would be?
Signup and view all the flashcards
American Imperialism
American Imperialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transformation of the American Economy
Transformation of the American Economy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Overproduction and Expansion
Overproduction and Expansion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economic Stagnation and Social Unrest
Economic Stagnation and Social Unrest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Targeting New Markets
Targeting New Markets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economic Imperialism in Latin America
Economic Imperialism in Latin America
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of American Imperialism on Diplomacy
Impact of American Imperialism on Diplomacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drivers of American Expansion
Drivers of American Expansion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economic Volatility in Late 1800s America
Economic Volatility in Late 1800s America
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of the Spanish-American War
Impact of the Spanish-American War
Signup and view all the flashcards
New Manifest Destiny
New Manifest Destiny
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economic Arguments for Imperialism
Economic Arguments for Imperialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Justification of American Colonialism
Justification of American Colonialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tension and Unpredictability of 'Exporting Democracy'
Tension and Unpredictability of 'Exporting Democracy'
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of Industrialization in Late 1800s America
Impact of Industrialization in Late 1800s America
Signup and view all the flashcards
American Imperialism in the Late 1800s
American Imperialism in the Late 1800s
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Manifest Destiny
- The primary goal of manifest destiny was westward expansion to the Pacific Ocean.
- The Homestead Act and transcontinental railroad completion helped fulfill this goal.
- Indian Wars (1860-1890) resulted from settlers moving onto the Great Plains.
- The discovery of gold and silver in the mid-1800s caused population growth in western territories.
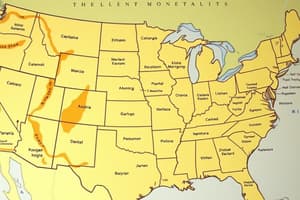
Federal Land Grants to Railroads
- The government provided land and loans to railroads.
- Loan amounts varied based on terrain. ($16,000 for level land, $32,000 for hilly land, $48,000 for mountain land)
- The map displays land granted to railroads by 1871.
Late 19th Century Developments
- Settlers populated the Great Plains.
- Standard time zones were created.
- The first federal regulatory agency was established.
- Business management and finance methods were introduced.
- Railroads were important to U.S. development.
Corn Production and Prices
- Between 1870 and 1900, corn production and prices were correlated.
- Production increases were linked to price decreases.
Battle of Little Bighorn
- Native Americans led by Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse were victorious.
Buffalo Population Decline
- Over-hunting by white settlers led to the decline of the buffalo population.
Wounded Knee Massacre
- The last major Native American-U.S. Army conflict involved the Wounded Knee massacre.
Inventions and the Great Plains
- Barbed wire helped protect property from cattle drives.
Populist Movement
- A political coalition of farming interests opposed railroad and banking interests.
Yellow Journalism and Spanish-American War
- Yellow journalists stirred support using articles about the sinking of the Maine.
- Journalism articles promoted the Spanish-American War.
Industrial Workers of the World (IWW)
- Skilled and unskilled laborers, regardless of race/ ethnicity, immigrants, and women were part of the IWW.
- This included farmworkers.
Knights of Labor and American Federation of Labor (AFL)
- Both groups aimed to improve workers' conditions.
- Focus on better working conditions, higher wages, and safety measures.
Urbanization and Industrialization
- Rural populations migrated to urban areas.
- Railroad mileage and industrialization increased city populations.
- The percentage of the U.S. population in cities continuously rose.
Progressive Era Workplace Reforms
- Improvements in factory safety.
- Reduced work hours.
- Increased wages.
- Limits on child labor.
Muckrakers
- Investigative journalists and novelists exposed social and political corruption.
- Public was made aware of the harsh realities in poverty, politics and industry.
Plessy v. Ferguson
- The Supreme Court decision stated segregation by law was constitutional as long as accommodations were equal.
Progressive Movement Impact
- Increased government regulation of business.
Nationalism
- The belief that one's own nation is superior to others led to conflict among nations.
Imperialism Threat to Peace
- Competition for colonies resulted in conflict between nations.
Zimmerman Telegram
- The German foreign minister proposed an alliance with Mexico against the U.S.
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
- Germany's policy of attacking neutral ships.
- This was followed by the sinking of the Lusitania which led to United States entering World War 1.
WWI Military Innovations
- Poison gas
- Trench warfare
- Machine guns
- Submarines
- Airplanes
- Hand grenades
- Innovations led to high numbers of casualties.
US Presidents and Diplomacy
- William Howard Taft (Dollar Diplomacy)
- William McKinley (Open Door Policy)
- Theodore Roosevelt (Big Stick Diplomacy)
- Woodrow Wilson (Moral Diplomacy)
Constitutional Amendments
- 17th Amendment: Direct election of senators.
- 18th Amendment: Prohibition (repealed by the 21st).
- 19th Amendment: Women's right to vote.
Civil Rights Icons
- Booker T. Washington
- W.E.B. Du Bois
Progressive Reformers
- Ida Tarbell (Standard Oil corruption)
- Jacob Riis (immigrant poverty)
- Upton Sinclair (meatpacking industry)
- Ida B. Wells (lynching)
Progressive Groups
- Politicians (business reform)
- Muckrakers (exposing corruption)
- Conservationists (natural resource preservation)
- Women's rights advocates (protecting women, children, immigrants)
Terms & Definitions
War Industries Board - Coordinated private businesses for war supplies Liberty Bonds - Funded war efforts through loans to citizens Victory Gardens - Citizens grew their own food during the war Committee on Public Information - Created propaganda for the war Selective Service Act - Allowed for military drafting.
Espionage & Sedition Acts
- Restricted speech critical of the war effort.
- These restrictions impacted freedom of speech.
Annexation
- Formal act of a state claiming sovereignty over territory.
Hawaiian Planters
- Wanted to join the U.S to increase sugar crop sales.
Child Labor
- Children worked in mills/mines due to small size.
American Federation of Labor (AFL) & Industrial Workers of the World (IWW)
- Labor unions that still exist today.
Progressive Movement
- Series of social and political reforms aimed at business regulation, justice, and societal improvements.
Jim Crow Laws
- Laws that upheld segregation.
Isolationism
- Policy that avoided political and economic entanglements with other countries.
WWI Goal
- Woodrow Wilson's goal was a "war to end all wars"
American Imperialism in Asia and Latin America
- U.S. gained possession of many territories (Hawaii, Philippines, Puerto Rico, Guam, Samoa, etc.).
- Protectorates were established in Cuba, Panama, and the Dominican Republic.
- Took part in many interventions in other countries.
- The growth of American economy was related to the emergence as a major player in Asia and Latin America.
American Economy and Expansion
- The American economy transformed from family-owned businesses to large corporations (driven by industry and communication innovations like electricity).
- Industrial expansion created a demand for new markets and resources leading to American expansion.
Dawes Act
- The Dawes Act broke up tribal lands.
- The Dawes Act resulted in the loss of tribal land to non-natives.
- The Dawes Act aimed to assimilate Native Americans into mainstream American society.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.