Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the fibrous capsule in the kidneys?
What is the primary function of the fibrous capsule in the kidneys?
- To filter blood and produce urine
- To stabilize the kidneys' position within the abdominal cavity
- To provide blood supply to the kidneys
- To cover the outer surface of the entire organ (correct)
Which connective tissue layer surrounding the kidneys contains adipose tissue?
Which connective tissue layer surrounding the kidneys contains adipose tissue?
- Perinephric fat (correct)
- Perirenal fascia
- Subcutaneous fat
- Fibrous capsule
Which of the following dimensions accurately describes a typical adult kidney?
Which of the following dimensions accurately describes a typical adult kidney?
- 14 cm long, 6 cm wide, 2.5 cm thick
- 10 cm long, 5.5 cm wide, 3 cm thick (correct)
- 12 cm long, 4 cm wide, 2 cm thick
- 8 cm long, 6 cm wide, 4 cm thick
What is the role of the renal fascia?
What is the role of the renal fascia?
How much does a typical adult kidney weigh?
How much does a typical adult kidney weigh?
What is the function of the afferent arterioles in the kidneys?
What is the function of the afferent arterioles in the kidneys?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the ureteral openings in the urinary bladder?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the ureteral openings in the urinary bladder?
Where do cortical radiate veins drain blood?
Where do cortical radiate veins drain blood?
What is the role of the urinary bladder in the urinary system?
What is the role of the urinary bladder in the urinary system?
Transitional epithelium lines which structure(s) of the urinary system?
Transitional epithelium lines which structure(s) of the urinary system?
Which structure is attached to the posterior abdominal wall and extends from the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
Which structure is attached to the posterior abdominal wall and extends from the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
Which structure directly receives blood from the renal artery?
Which structure directly receives blood from the renal artery?
What is the correct order of blood flow starting from the arcuate arteries?
What is the correct order of blood flow starting from the arcuate arteries?
Which capillaries help maintain the osmotic gradient in the renal medulla?
Which capillaries help maintain the osmotic gradient in the renal medulla?
What is the primary function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the primary function of the peritubular capillaries?
Into which structure do the efferent arterioles empty?
Into which structure do the efferent arterioles empty?
What is the role of interlobular arteries in the kidney?
What is the role of interlobular arteries in the kidney?
Where do the renal venules collect blood from?
Where do the renal venules collect blood from?
From which structure do the arcuate veins receive blood?
From which structure do the arcuate veins receive blood?
Where are the kidneys located in relation to the organs of the digestive tract?
Where are the kidneys located in relation to the organs of the digestive tract?
Which part of the body provides partial protection to the upper parts of the kidneys?
Which part of the body provides partial protection to the upper parts of the kidneys?
What space do the kidneys lie in?
What space do the kidneys lie in?
Which structures are involved in protecting and stabilizing each kidney?
Which structures are involved in protecting and stabilizing each kidney?
The kidneys are located on either side of which anatomical structure?
The kidneys are located on either side of which anatomical structure?
Which part of the urinary bladder acts as a funnel to channel urine into the urethra?
Which part of the urinary bladder acts as a funnel to channel urine into the urethra?
What is the primary role of the internal urethral sphincter?
What is the primary role of the internal urethral sphincter?
What structure in the urinary bladder disappears as the bladder fills?
What structure in the urinary bladder disappears as the bladder fills?
Where is the urethral entrance located in the urinary bladder?
Where is the urethral entrance located in the urinary bladder?
Which organ is not directly involved in urine transport, storage, or elimination?
Which organ is not directly involved in urine transport, storage, or elimination?
Which statement correctly describes the urinary bladder?
Which statement correctly describes the urinary bladder?
Which of the following segments of the renal tubule directly connects to the Bowman's capsule?
Which of the following segments of the renal tubule directly connects to the Bowman's capsule?
Where are the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and distal convoluted tubule (DCT) primarily located?
Where are the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and distal convoluted tubule (DCT) primarily located?
What is the main role of the loop of Henle within the nephron?
What is the main role of the loop of Henle within the nephron?
Approximately how many nephrons are found in each kidney?
Approximately how many nephrons are found in each kidney?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the nephrons?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the nephrons?
What surrounds the glomerulus in the nephron?
What surrounds the glomerulus in the nephron?
Which structure is NOT part of the blood supply to the kidneys?
Which structure is NOT part of the blood supply to the kidneys?
How much cardiac output do the kidneys receive?
How much cardiac output do the kidneys receive?
Through which artery does blood enter the kidneys?
Through which artery does blood enter the kidneys?
Where does the filtrate flow after passing through the distal convoluted tubule?
Where does the filtrate flow after passing through the distal convoluted tubule?
Which body fluids collected during dissection can reveal drugs ingested by the victim in the hours before death?
Which body fluids collected during dissection can reveal drugs ingested by the victim in the hours before death?
What information can urinalysis provide in forensic investigations?
What information can urinalysis provide in forensic investigations?
What can hair analysis reveal in a forensic investigation?
What can hair analysis reveal in a forensic investigation?
How can the position of the body at a crime scene be useful?
How can the position of the body at a crime scene be useful?
Which combination of exhibits collected during a dissection helps determine chronic exposure to substances?
Which combination of exhibits collected during a dissection helps determine chronic exposure to substances?
Which scenario would most likely be classified as accidental based on the provided example?
Which scenario would most likely be classified as accidental based on the provided example?
Which structure within the kidney is bound to the outer surfaces of the structures within the renal sinus?
Which structure within the kidney is bound to the outer surfaces of the structures within the renal sinus?
Which of the following correctly describes the renal pyramids?
Which of the following correctly describes the renal pyramids?
What does the major calyx consist of?
What does the major calyx consist of?
Where do the ducts from the renal papilla discharge urine into?
Where do the ducts from the renal papilla discharge urine into?
What is the superficial portion of the kidney that comes into contact with the renal capsule?
What is the superficial portion of the kidney that comes into contact with the renal capsule?
Which structure is the large, funnel-shaped chamber within the kidney?
Which structure is the large, funnel-shaped chamber within the kidney?
Which of the following structures stabilizes the positions of the ureter, renal blood vessels, and nerves?
Which of the following structures stabilizes the positions of the ureter, renal blood vessels, and nerves?
Which structure is described as being reddish brown and granular?
Which structure is described as being reddish brown and granular?
Which structure within the kidney is directly responsible for urine production?
Which structure within the kidney is directly responsible for urine production?
The renal pelvis is connected to which of the following structures?
The renal pelvis is connected to which of the following structures?
What is the function of the renal papilla?
What is the function of the renal papilla?
Which structure is described as a cavity within the kidney?
Which structure is described as a cavity within the kidney?
Which part of the kidney is the apex of the renal pyramid directed towards?
Which part of the kidney is the apex of the renal pyramid directed towards?
Which structure fills most of the renal sinus?
Which structure fills most of the renal sinus?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Nephron Components
- A nephron consists of a cup-like Bowman's capsule in the renal cortex and a coiled renal tubule that extends from the capsule.
- The renal tubule consists of three sections: the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), the loop of Henle, and the distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
- The PCT and DCT are located in the renal cortex, while the loop of Henle curves in and out of the renal medulla.
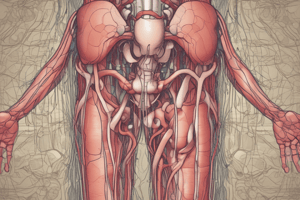
Blood Supply to the Kidneys
- Kidneys receive 20-25% of total cardiac output.
- 1200 mL of blood flows through kidneys each minute.
- Kidney receives blood through the renal artery.
- The renal artery branches into:
- Interlobar arteries
- Arcuate arteries
- Interlobular arteries
- Afferent arterioles
- Glomerulus
- Efferent arterioles
- Peritubular capillaries
- Vasa recta
- Renal venules
- Arcuate veins
- Interlobar veins
- Renal vein
Glomerulus
- A network of capillaries
- Site of filtration of blood to form urine
Renal Cortex and Medulla
- The renal cortex is the outer region of the kidney
- The renal medulla is the inner region of the kidney
- The renal cortex is reddish brown and granular
- The renal medulla contains renal pyramids
Renal Pyramids
- Cone-shaped structures in the renal medulla
- Connected to minor calyces
- Ducts discharge urine into minor calyces
Renal Sinus
- Internal cavity within kidney
- Lined by fibrous renal capsule
- Stabilizes positions of ureter, renal blood vessels, and nerves
Ureter
- A pair of muscular tubes
- Extends from kidneys to urinary bladder
- Begins at renal pelvis
- Is retroperitoneal, attached to posterior abdominal wall
- Penetrates posterior wall of the urinary bladder
- Passes through bladder wall at oblique angle
- Ureteral openings are slit-like rather than rounded
Urinary Bladder
- A hollow, muscular organ
- Functions as temporary reservoir for urine storage
- Full bladder can contain 1 liter of urine
- Has folds (rugae) that disappear as the bladder fills
- Trigone of the urinary bladder is a triangular area bounded by ureteral openings and entrance to urethra
Kidney Protection
- Each kidney is protected and stabilized by three concentric layers of connective tissue:
- Fibrous capsule
- Perinephric fat
- Renal fascia
Urinary System Structures
- Peritoneum
- Urinary bladder
- Pubic symphysis
- Prostate gland
- External urethral sphincter
- Spongy urethra
- External urethral orifice
- Urethra
- Urogenital diaphragm
- Left ureter
- Rectum
Kidney Location
- Located on either side of the vertebral column
- High along the back wall of the abdominal cavity, posterior to the digestive tract's organs
- Protected by muscle, fat, and ribs
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.