Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average length of a kidney?
What is the average length of a kidney?
- 10 cm
- 12 cm (correct)
- 14 cm
- 16 cm
Which structure is found in the hilum of the kidney?
Which structure is found in the hilum of the kidney?
- Renal cortex
- Perirenal fat
- Renal arteries (correct)
- Ureter (correct)
Which of the following correctly describes the right kidney's position?
Which of the following correctly describes the right kidney's position?
- Only located in the lumbar region
- Higher than the left
- Lower than the left (correct)
- At the same level as the left
What are the coverings of the kidney?
What are the coverings of the kidney?
Which organ is positioned anteriorly to the left kidney?
Which organ is positioned anteriorly to the left kidney?
Which muscle is NOT related to the posterior surface of the kidney?
Which muscle is NOT related to the posterior surface of the kidney?
What is the approximate length of the ureters?
What is the approximate length of the ureters?
What is the main function of the ureters?
What is the main function of the ureters?
What differentiates the male urethra from the female urethra?
What differentiates the male urethra from the female urethra?
Where does the ureter open into the urinary bladder?
Where does the ureter open into the urinary bladder?
Which part of the male urethra is the longest?
Which part of the male urethra is the longest?
What is the normal capacity of the urinary bladder before discomfort is felt?
What is the normal capacity of the urinary bladder before discomfort is felt?
At which structure does the ureter meet a site of constriction?
At which structure does the ureter meet a site of constriction?
Which surface of the urinary bladder is directed posteriorly?
Which surface of the urinary bladder is directed posteriorly?
What is the length of the female urethra?
What is the length of the female urethra?
Which part of the male urethra is the narrowest?
Which part of the male urethra is the narrowest?
Flashcards
Ureters' length
Ureters' length
Ureters are approximately 25-30 cm long.
Ureter location
Ureter location
Ureters run from the kidneys to the bladder, with half of their course in the abdomen and half in the pelvis.
Ureter constrictions
Ureter constrictions
The ureter has three points of narrowing: the pelvi-ureteric junction, where it crosses the common iliac artery, and the uretero-vesical junction.
Urinary bladder capacity
Urinary bladder capacity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary bladder location
Urinary bladder location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male urethra segments
Male urethra segments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female urethra length
Female urethra length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter entry point to bladder
Ureter entry point to bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney location
Kidney location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney surfaces
Kidney surfaces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney structure (cortex and medulla)
Kidney structure (cortex and medulla)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney coverings
Kidney coverings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureters' function
Ureters' function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney relations (anterior)
Kidney relations (anterior)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney relations (posterior)
Kidney relations (posterior)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney size
Kidney size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Urinary System Overview
- The urinary system is composed of organs that filter blood, maintain fluid balance, and eliminate waste.
- Key organs include two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder, and one urethra.
Objectives of the Lecture
- Students should be able to list the organs of the urinary system.
- Students should be able to describe the anatomy of the kidney, including relationships to surrounding structures.
- Students should be able to describe the anatomy of the ureters, including constrictions.
- Students should be able to describe the anatomy of the urinary bladder.
- Students should be able to describe the anatomy of the male urethra, including its parts.
- Students should be able to describe the anatomy of the female urethra.
- Students should know the differences between the male and female urethra.
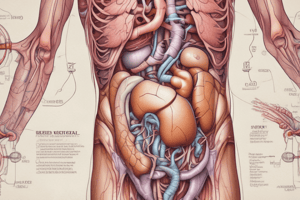
Kidney Anatomy
- Kidneys are located on either side of the vertebral column.
- Each kidney extends from the 12th thoracic vertebra to the 3rd lumbar vertebra.
- The right kidney is slightly lower than the left.
- The kidney is approximately 12 cm long, 6 cm wide, and 3 cm thick.
Kidney Structure
- The kidney has two surfaces, two borders, and two ends.
- The lateral border is convex, the medial border is convex at the ends and concave in the middle.
- The hilum is found in the middle of the medial border and provides passage for renal vessels, nerves, and the pelvis.
- The pelvis is a dilated sac that extends outside the hilum and connects with the ureter.
Kidney Relations (Anterior)
- Right kidney: suprarenal gland, duodenum, liver, colon, small intestine.
- Left kidney: suprarenal gland, spleen, pancreas, stomach, colon, and small intestine.
Kidney Relations (Posterior)
- Posterior relations of both kidneys: diaphragm, muscles of the posterior abdominal wall (psoas major, quadratus lumborum, transversus abdominis).
Kidney Coverings
- Fibrous capsule
- Perirenal fat
- Renal fascia
- Pararenal fat
Ureters
- Two muscular tubes that convey urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Each ureter is approximately 25 to 30 cm long.
- Half of the ureter's course is within the abdomen, and the other half is within the pelvis.
- The ureters are a continuation of the renal pelvis.
- Three constrictions during the ureter's course: pelvi-ureteric junction, crossing the common iliac artery, and uretero-vesical junction.
Urinary Bladder
- A hollow, muscular organ that serves as a reservoir for urine.
- Located in the pelvic cavity, behind the pubic bones.
- Shaped like a three-sided pyramid.
- Capacity is 220cc, but can accommodate up to 500cc.
- Apex is behind the upper part of the symphysis pubis and is continuous with the median umbilical ligament.
- Base is directed posteriorly.
- The bladder has three surfaces (one superior and two inferolateral) and a base. Each surface and base are triangular.
Bladder Related Structures
- Ureters enter the superolateral angle of the bladder base
- The inferior angle of the bladder transitions to the urethra.
- The male urethra is continuous with the prostatic part of the urethra.
- The female urethra is continuous with the urethra
Male Urethra
- 20 cm long, divided into three parts.
- Prostatic part: 3 cm, widest, begins at the neck of the urinary bladder, and houses the ejaculatory ducts.
- Membranous part: 1 cm, narrowest and shortest, surrounded by a sphincter,
- Spongy part: 16 cm, longest, passes through the penis, and opens by the external urethral orifice.
Female Urethra
- Very short, approximately 4 cm long
- Begins at the neck of the bladder.
- Its upper part is surrounded by sphincter urethra.
- Shorter, wider, and more dilatable than the male urethra.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.