Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average rate of urine production?
What is the average rate of urine production?
- 2 ml / minute
- 5 ml / minute
- 0.5 ml / minute
- 1 ml / minute (correct)
Which part of the kidney is responsible for the production of urine?
Which part of the kidney is responsible for the production of urine?
- Cortex (correct)
- Medulla
- Collecting ducts
- Fibrous capsule
What is the function of the ureters?
What is the function of the ureters?
- Transportation of urine (correct)
- Storage of urine
- Production of urine
- Filration of blood
What is the length of the ureter?
What is the length of the ureter?
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
What is the type of epithelium that lines the mucosa of the urinary bladder?
What is the type of epithelium that lines the mucosa of the urinary bladder?
What is the name of the triangular area in the urinary bladder?
What is the name of the triangular area in the urinary bladder?
At rest, what is the angle between the urethra and the base of the urinary bladder?
At rest, what is the angle between the urethra and the base of the urinary bladder?
What is nocturnal enuresis characterized by?
What is nocturnal enuresis characterized by?
What is the primary mechanism of stress urinary incontinence?
What is the primary mechanism of stress urinary incontinence?
What is urgency urinary incontinence characterized by?
What is urgency urinary incontinence characterized by?
What is the term used to describe the observation of an involuntary droplet of urine leaving the urethra?
What is the term used to describe the observation of an involuntary droplet of urine leaving the urethra?
What is the result of rotational descent of the urethra below the symphysis pubis?
What is the result of rotational descent of the urethra below the symphysis pubis?
What is the term used to describe the sudden, compelling desire to pass urine which is difficult to defer?
What is the term used to describe the sudden, compelling desire to pass urine which is difficult to defer?
What is the primary function of the neurological control in the bladder?
What is the primary function of the neurological control in the bladder?
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to increased intra-urethral pressure?
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to increased intra-urethral pressure?
What is the significance of the posterior urethro-vesical angle of 90-100°?
What is the significance of the posterior urethro-vesical angle of 90-100°?
Which type of urinary incontinence is characterized by an involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency and effort or physical exertion?
Which type of urinary incontinence is characterized by an involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency and effort or physical exertion?
What is the primary function of the hammock theory in the mechanism of continence?
What is the primary function of the hammock theory in the mechanism of continence?
What is the term used to describe the normal ability of a person to store urine temporarily with conscious control over the time and place of micturition?
What is the term used to describe the normal ability of a person to store urine temporarily with conscious control over the time and place of micturition?
What is the significance of the intra-abdominal situation of both the bladder and upper part of the urethra in the mechanism of continence?
What is the significance of the intra-abdominal situation of both the bladder and upper part of the urethra in the mechanism of continence?
What is the term used to describe the involuntary loss of urine on effort or physical exertion?
What is the term used to describe the involuntary loss of urine on effort or physical exertion?
What is the approximate length of the urethra?
What is the approximate length of the urethra?
What is the primary function of the urethra?
What is the primary function of the urethra?
At what volume is the first mild desire to void commonly felt?
At what volume is the first mild desire to void commonly felt?
What is the primary mechanism of continence at rest?
What is the primary mechanism of continence at rest?
What is the internal meatus of the urethra?
What is the internal meatus of the urethra?
What is the role of the detrusor muscle in the micturition cycle?
What is the role of the detrusor muscle in the micturition cycle?
What is the primary function of the pubourethral ligaments?
What is the primary function of the pubourethral ligaments?
What is the name of the muscle that forms the lower part of the extrinsic urethral sphincter?
What is the name of the muscle that forms the lower part of the extrinsic urethral sphincter?
What is the primary contributing factor to increase intraabdominal pressure in urinary incontinence?
What is the primary contributing factor to increase intraabdominal pressure in urinary incontinence?
What is the primary goal of non-surgical management in urinary incontinence?
What is the primary goal of non-surgical management in urinary incontinence?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a patient with urinary incontinence?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a patient with urinary incontinence?
What is the purpose of the cough stress test in assessing urinary incontinence?
What is the purpose of the cough stress test in assessing urinary incontinence?
What is the recommended duration of pelvic floor muscle training in non-surgical management of urinary incontinence?
What is the recommended duration of pelvic floor muscle training in non-surgical management of urinary incontinence?
What is the primary indication for surgical treatment in urinary incontinence?
What is the primary indication for surgical treatment in urinary incontinence?
What is the recommended approach for managing mixed incontinence?
What is the recommended approach for managing mixed incontinence?
What is the purpose of voiding diaries in assessing urinary incontinence?
What is the purpose of voiding diaries in assessing urinary incontinence?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
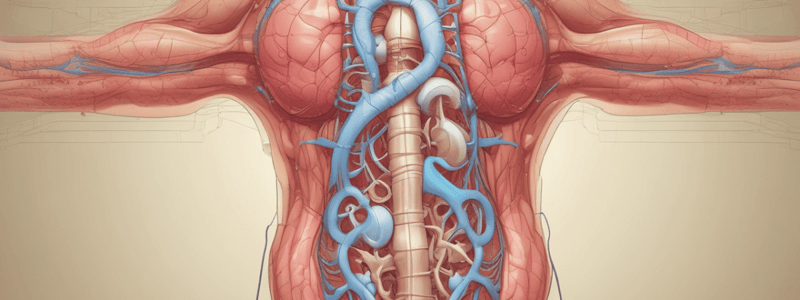
Urinary Tract
- The urinary tract consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra.
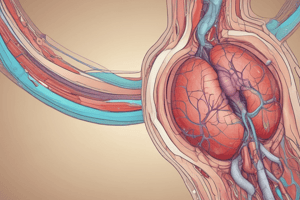
The Kidney
- The kidney has two parts: right and left.
- The kidney has a fibrous capsule, cortex, medulla, collecting ducts, and pelvis.
- The kidney's blood supply comes from the renal artery and renal vein.
- The kidney's function is to produce urine, with an average production of 1ml per minute.
The Ureter
- There are two ureters, one for each kidney.
- The ureter is a hollow muscular canal that is 25cm long.
- The ureter starts at the pelvis of the kidney and ends at the urinary bladder.
- The ureter has abdominal and pelvic parts.
- The ureter's function is to transport urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
The Urinary Bladder
- The urinary bladder is a midline hollow sac that lies directly behind the pubic symphysis.
- The bladder has three layers: mucosa (inner), musculosa (middle), and serosa (outer).
- The bladder has a dome, trigone, and relations with the uterus, cervix, and vagina.
- The bladder's function is to store urine.
The Urethra
- The urethra is a fibromuscular tube that is 3-4cm long.
- The urethra has two openings: internal meatus and external meatus.
- The urethra has intrinsic and extrinsic sphincters.
- The urethra's function is to transport urine from the bladder to outside the body.
Micturition Cycle
- The micturition cycle has two phases: filling and voiding.
- During the filling phase, the detrusor muscle is relaxed, and the sensation of fullness becomes more consciously apparent with increasing stored volume.
- During the voiding phase, the levator ani and urethral sphincter muscles relax, and the detrusor muscle contracts.
Mechanism of Continence
- At rest, continence is maintained by low intra-vesical pressure and intra-urethral pressure.
- Factors maintaining low intra-vesical pressure include passive and active factors.
- Factors increasing intra-urethral pressure include the mucosal seal, vascular cushion, urethral sphincters, and the hammock theory.
- The posterior urethro-vesical angle of 90-100° also helps maintain continence.
Mechanism of Continence at Stress
- Continence is maintained during stress by equally transmitted pressure on both the bladder and urethra.
- Additional factors that help maintain continence during stress include the extrinsic striated muscles, the hammock, and kinking of the urinary bladder neck.
Urinary Incontinence
- Urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine.
- Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine on effort or physical exertion.
- Urgency urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency.
- Mixed urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine associated with both urgency and effort.
- Nocturnal enuresis is the involuntary loss of urine during sleep.
Female Urinary Incontinence
- Female urinary incontinence can be classified into transurethral, extraurethral, and functional categories.
Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine on effort or physical exertion.
- The mechanism of incontinence involves anatomic and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency factors.
- Urethral hypermobility is a common cause of stress urinary incontinence.
Urgency Urinary Incontinence
- Urgency urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency.
- Contributing factors include weak tissues, pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, and increased intraabdominal pressure.
- Assessment involves a detailed history, examination, and investigations such as urine analysis, voiding diaries, and pad test.
Management
- Non-surgical management is the first step in managing urinary incontinence.
- Non-surgical management includes lifestyle interventions, physical therapies, behavioral therapies, and devices.
- Surgical treatment is considered if non-surgical management is not effective.
- The type of treatment depends on the type of incontinence.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.