Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of intercostal muscles in the respiratory system?
What is the role of intercostal muscles in the respiratory system?
Intercostal muscles help expand and relax the ribcage, providing support for the pleural cavity.
Explain the significance of the pleural cavity for lung function.
Explain the significance of the pleural cavity for lung function.
The pleural cavity creates an airtight environment essential for the lungs to inflate and deflate properly.
Describe the function of ciliated cells in the respiratory tract.
Describe the function of ciliated cells in the respiratory tract.
Ciliated cells sweep away dust and foreign particles from the trachea and bronchi, helping to keep airways clear.
What do goblet cells produce, and what is their main function?
What do goblet cells produce, and what is their main function?
How can excessive mucus production affect respiration?
How can excessive mucus production affect respiration?
What role does the nasal cavity play in the respiratory system?
What role does the nasal cavity play in the respiratory system?
How does the pharynx serve both the respiratory and digestive systems?
How does the pharynx serve both the respiratory and digestive systems?
What is the function of the larynx in the respiratory system?
What is the function of the larynx in the respiratory system?
Describe the function of the epiglottis during the breathing process.
Describe the function of the epiglottis during the breathing process.
How does the structure of the trachea differ from that of the esophagus?
How does the structure of the trachea differ from that of the esophagus?
What is the importance of bronchi and bronchioles in the respiratory system?
What is the importance of bronchi and bronchioles in the respiratory system?
Explain the role of alveoli in gas exchange.
Explain the role of alveoli in gas exchange.
What function does the diaphragm serve in the breathing process?
What function does the diaphragm serve in the breathing process?
Flashcards
Nasal Cavity function
Nasal Cavity function
Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air; contains olfactory receptors.
Pharynx function
Pharynx function
A shared passageway for air, food, and water.
Larynx function
Larynx function
Voice box containing vocal cords for sound production.
Epiglottis function
Epiglottis function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea Structure
Trachea Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchioles Structure
Bronchioles Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli function
Alveoli function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm function
Diaphragm function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercostal Muscles
Intercostal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural Cavity
Pleural Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ciliated Cells
Ciliated Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goblet Cells' Mucus
Goblet Cells' Mucus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pneumonia Risk
Pneumonia Risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Upper Respiratory System
- Nasal Cavity: Warms, moistens, and filters inhaled air. Holds olfactory receptors for smell. Unlike the mouth, air entering the nasal cavity is filtered, warmed, and moistened.
- Pharynx: A common passageway for air, food, and water. Connects the nose, mouth, and throat. Part of both the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Larynx (Voice Box): Houses the vocal cords, enabling sound production. Located in the middle of the neck, behind the esophagus.
- Epiglottis: A flap of cartilage that covers the trachea (windpipe) during swallowing to prevent food from entering the lungs. It stays open during breathing to allow air into the larynx.
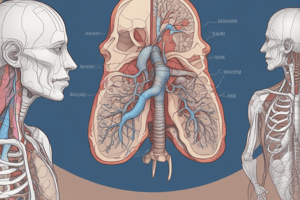
- Trachea (Windpipe): A tube that carries air from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. Lined with goblet cells that produce mucus. Cilia sweep trapped particles away. Cartilage rings provide structural support to maintain an open pathway. The trachea's rigid structure contrasts with the esophagus's collapsible nature.
Lower Respiratory System
- Bronchi: Branches from the trachea, with cartilage rings for structural support. They decrease in size as they branch into smaller tubes.
- Bronchioles: The smallest branches of the bronchi, lack cartilage rings, and are susceptible to collapse with damage, smoking.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs (oxygen and carbon dioxide). Their thin walls facilitate rapid diffusion. Susceptible to damage from smoking, without them, gas exchange is impaired, leading to rapid fatigue. Alveoli contain fluid, which can cause edema if damaged.
- Diaphragm: A large, dome-shaped muscle that contracts to expand the chest cavity, drawing air into the lungs. Relaxes to expel air. Lies under the ribs.
- Intercostal Muscles: Muscles between the ribs, assist in expanding and contracting the rib cage during breathing.
- Pleural Membrane: Forms an airtight sac around the lungs, crucial for proper inflation and deflation. The pressure within this cavity allows efficient lung function. A punctured pleural cavity disrupts this pressure, leading to lung collapse.
Cells of the Respiratory System
- Ciliated Cells: Line the trachea and bronchi. Cilia sweep away trapped dust and pathogens.
- Goblet Cells: Produce mucus, trapping foreign material. The mucus produced can expand significantly when needed. Excessive mucus production, however, can lead to respiratory problems.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.