Podcast
Questions and Answers
What happens to mature neurons and myelin that have been damaged?
What happens to mature neurons and myelin that have been damaged?
- They regenerate and replace themselves
- They undergo apoptosis
- They do not divide or replace themselves (correct)
- They remain functional but do not divide
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
- Carry impulses away from the cell body
- Form the myelin that covers the neurons of the CNS
- Support the metabolic demands of the cell
- Transmit impulses to the cell body (correct)
Which type of neuron carries impulses from receptors in the periphery to the CNS?
Which type of neuron carries impulses from receptors in the periphery to the CNS?
- Interneurons
- Oligodendrocytes
- Sensory/afferent neurons (correct)
- Motor/efferent neurons
What is the role of interneurons?
What is the role of interneurons?
What is the term for the electrical events that travel along the entire neuron?
What is the term for the electrical events that travel along the entire neuron?
What is the difference between the inside and outside of a neuron in terms of electrical charge?
What is the difference between the inside and outside of a neuron in terms of electrical charge?
What is the function of Schwann cells in the PNS?
What is the function of Schwann cells in the PNS?
One of three components of the action potential in the neuron is the resting membrane potential (RMP) which is the membrane potential (or state of tension) inside a plasma membrane, measured relative to the fluid just outside in the absence of significant electrical activity.
One of three components of the action potential in the neuron is the resting membrane potential (RMP) which is the membrane potential (or state of tension) inside a plasma membrane, measured relative to the fluid just outside in the absence of significant electrical activity.
- C7 through T1 injuries allow individuals to straighten their arms, but they may result in impaired fine motor skills. Paraplegia usually results from injuries at the thoracic level. Trunk and lower body control are lost at T1, with return of sitting balance and abdominal muscle control from T9 through T12. Injuries in the lumbar and sacral segments result in loss of control of the lower extremities. Spinal cord injuries may affect bowel, bladder, and sexual function.
- C7 through T1 injuries allow individuals to straighten their arms, but they may result in impaired fine motor skills. Paraplegia usually results from injuries at the thoracic level. Trunk and lower body control are lost at T1, with return of sitting balance and abdominal muscle control from T9 through T12. Injuries in the lumbar and sacral segments result in loss of control of the lower extremities. Spinal cord injuries may affect bowel, bladder, and sexual function.
What is the primary function of the axon in a neuron?
What is the primary function of the axon in a neuron?
What type of cells form the myelin that covers neurons in the CNS?
What type of cells form the myelin that covers neurons in the CNS?
What is the term for the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of a neuron?
What is the term for the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of a neuron?
What is the function of motor neurons?
What is the function of motor neurons?
What is the role of gap junctions in the body?
What is the role of gap junctions in the body?
The cell body (soma) is filled with cytoplasm and contains organelles, including the nucleus, that support the metabolic demands of the cell.
The cell body (soma) is filled with cytoplasm and contains organelles, including the nucleus, that support the metabolic demands of the cell.
SNA supporting cells include neuroglia, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells.
SNA supporting cells include neuroglia, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells.
The SNS is responsible for increased heart rate, smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles, decreased GI movement and constriction of anal and bladder sphincter, vasoconstriction and elevated BP, increased respirations, pupil dilation, increased sweat gland secretion.
The SNS is responsible for increased heart rate, smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles, decreased GI movement and constriction of anal and bladder sphincter, vasoconstriction and elevated BP, increased respirations, pupil dilation, increased sweat gland secretion.
The PNS is responsible for decreased heart rate, constriction of bronchial smooth muscle, increased peristalsis of GI and bladder, relaxation of anal and urinary sphincter, vasodilation of arteries supplying external genitalia, constriction of pupils, increased pancreatic, salivary, and eye secretions.
The PNS is responsible for decreased heart rate, constriction of bronchial smooth muscle, increased peristalsis of GI and bladder, relaxation of anal and urinary sphincter, vasodilation of arteries supplying external genitalia, constriction of pupils, increased pancreatic, salivary, and eye secretions.
The BBB/Blood-Brain-Barrier protects the brain from foreign substances, hormones and neurotransmitters in the systemic circulation, and also protects against drastic environmental fluctuations.
The BBB/Blood-Brain-Barrier protects the brain from foreign substances, hormones and neurotransmitters in the systemic circulation, and also protects against drastic environmental fluctuations.
Increased ICP, respiratory depression/failure, and herniation of the brainstem may occur with TBI.
Increased ICP, respiratory depression/failure, and herniation of the brainstem may occur with TBI.
SCI responses range from mild paresthesia (abnormal sensation, such as burning, pricking, tickling, or tingling) to quadriplegia (paralysis of all four extremities).
SCI responses range from mild paresthesia (abnormal sensation, such as burning, pricking, tickling, or tingling) to quadriplegia (paralysis of all four extremities).
Contusions, wounds, tumors, abscesses, and hemorrhages are common causes of astrogliosis which is when astrocytes respond to local tissue injury through proliferation forming a glial scar (astrogliosis).
Contusions, wounds, tumors, abscesses, and hemorrhages are common causes of astrogliosis which is when astrocytes respond to local tissue injury through proliferation forming a glial scar (astrogliosis).
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders resulting from damage to upper motor neurons that stem from an event that occurs during prenatal, perinatal, or postnatal periods and has 2 classifications which are motor dysfunction type and anatomic involvement.
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders resulting from damage to upper motor neurons that stem from an event that occurs during prenatal, perinatal, or postnatal periods and has 2 classifications which are motor dysfunction type and anatomic involvement.
What is the term that describes the swelling of neurons due to injury?
What is the term that describes the swelling of neurons due to injury?
Which part of the brain is responsible for conscious perception of touch, pressure, temp, and pain?
Which part of the brain is responsible for conscious perception of touch, pressure, temp, and pain?
What is the term for the phagocytosis and inflammatory responses caused by a dead neuron damaging neighboring cells?
What is the term for the phagocytosis and inflammatory responses caused by a dead neuron damaging neighboring cells?
What is the primary function of the occipital lobe?
What is the primary function of the occipital lobe?
What is the term for the decrease in neuron size due to injury or disease?
What is the term for the decrease in neuron size due to injury or disease?
What is a treatment of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) due to ischemic injury?
What is a treatment of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) due to ischemic injury?
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for reasoning, planning, speech, and movement?
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for reasoning, planning, speech, and movement?
What system (in the white matter) in the brain controls voluntary movement?
What system (in the white matter) in the brain controls voluntary movement?
Which of the following is a clinical manifestation of pressure injury?
Which of the following is a clinical manifestation of pressure injury?
What type of neurons have the capacity to regenerate, repair, and reinnervate?
What type of neurons have the capacity to regenerate, repair, and reinnervate?
Spastic cerebral palsy is characterized by the inability of muscles to:
Spastic cerebral palsy is characterized by the inability of muscles to:
What is status epilepticus characterized by?
What is status epilepticus characterized by?
What type of structures are formed in the nucleus or cytoplasm of neurons?
What type of structures are formed in the nucleus or cytoplasm of neurons?
Which part of the brain is responsible for conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli?
Which part of the brain is responsible for conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli?
What is a possible outcome of ischemic injury to neurologic tissue?
What is a possible outcome of ischemic injury to neurologic tissue?
What is a characteristic of Athetoid/dyskinetic cerebral palsy?
What is a characteristic of Athetoid/dyskinetic cerebral palsy?
What is a characteristic of Ataxic cerebral palsy?
What is a characteristic of Ataxic cerebral palsy?
A motor dysfunction classification of cerebral palsy is Ataxic which is the inability to control balance and coordination.
A motor dysfunction classification of cerebral palsy is Ataxic which is the inability to control balance and coordination.
Common symptoms of ICP include headache, vomiting, papilledema (swelling of the optic nerve), and mental deterioration.
Common symptoms of ICP include headache, vomiting, papilledema (swelling of the optic nerve), and mental deterioration.
- A 2 year old patient presents to the ER with lack of coordination and balance, impaired cognitive function, speech / seizure disorder, presence of abnormal movements/reflexes, and limited fine motor skills. The patients mother states that the patient was delayed in walking, sitting, and reaching for toys. What can the nurse suspect?
- A 2 year old patient presents to the ER with lack of coordination and balance, impaired cognitive function, speech / seizure disorder, presence of abnormal movements/reflexes, and limited fine motor skills. The patients mother states that the patient was delayed in walking, sitting, and reaching for toys. What can the nurse suspect?
- A patient presents to the ER with unilateral vision loss, altered color perception, nystagmus (irregular eye movements, pain, pseudobulbar affect (uncontrollable laughing or crying), cognitive loss, bladder and bowel disfunction, altered gait/balance, spasticity, paresthesias, slurred speech and fatigue. What could the nurse suspect?
- A patient presents to the ER with unilateral vision loss, altered color perception, nystagmus (irregular eye movements, pain, pseudobulbar affect (uncontrollable laughing or crying), cognitive loss, bladder and bowel disfunction, altered gait/balance, spasticity, paresthesias, slurred speech and fatigue. What could the nurse suspect?
- An infant is born and shows increased head circumference, scalp vein distention, bulging/enlarged fontanelles, separation on bony structures/suture line, prominent scalp veins, frontal bossing, sunset eyes, lethargy, hyperactive reflexes, and vomiting. The infant also presents with a shrill, high-pitched cry and her mother states she has had difficulty feeding. What can the nurse suspect?
- An infant is born and shows increased head circumference, scalp vein distention, bulging/enlarged fontanelles, separation on bony structures/suture line, prominent scalp veins, frontal bossing, sunset eyes, lethargy, hyperactive reflexes, and vomiting. The infant also presents with a shrill, high-pitched cry and her mother states she has had difficulty feeding. What can the nurse suspect?
- A patient presents to the ER with increased BP, Altered HR (tachy then brady), mostly bradycardic, decreased LOC, papilledema, decreased respiration, and increased temp. What can the nurse suspect?
- A patient presents to the ER with increased BP, Altered HR (tachy then brady), mostly bradycardic, decreased LOC, papilledema, decreased respiration, and increased temp. What can the nurse suspect?
__________ affects the hemi-section of the spinal cord usually resulting from stabbing or gunshot injury to one side of the cord.
__________ affects the hemi-section of the spinal cord usually resulting from stabbing or gunshot injury to one side of the cord.
- Patient presents to the ER with tremors of the hands, arms, legs, and face while their body is at rest; slowed shuffling movement, stooped posture, muscle rigidity which is causing feeding difficulties, monotone speech, and stiff expression. What could the nurse suspect?
- Patient presents to the ER with tremors of the hands, arms, legs, and face while their body is at rest; slowed shuffling movement, stooped posture, muscle rigidity which is causing feeding difficulties, monotone speech, and stiff expression. What could the nurse suspect?
Which drugs are used to control muscle spasms in Cerebral Palsy?
Which drugs are used to control muscle spasms in Cerebral Palsy?
Which form of multiple sclerosis is characterized by slow, chronic deterioration and no remissions?
Which form of multiple sclerosis is characterized by slow, chronic deterioration and no remissions?
What provides evidence for immunopathology in patients with multiple sclerosis?
What provides evidence for immunopathology in patients with multiple sclerosis?
What type of immune response predominance is seen in multiple sclerosis patients?
What type of immune response predominance is seen in multiple sclerosis patients?
What is the initial presentation of multiple sclerosis before it progresses to other forms?
What is the initial presentation of multiple sclerosis before it progresses to other forms?
Which form of multiple sclerosis is most common and is characterized by periods of acute neuro symptoms (flare-ups, exacerbations, relapses) alternating with periods of remissions?
Which form of multiple sclerosis is most common and is characterized by periods of acute neuro symptoms (flare-ups, exacerbations, relapses) alternating with periods of remissions?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cerebral Palsy
- Cerebral Palsy has no known cure, but drugs like Lamotrigine and Valproate are used to control seizures.
- Botulinum toxin A, Dantrolene, and Baclofen are used to control muscle spasms.
Multiple Sclerosis
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a disease characterized by the degeneration of myelin (demyelination) in CNS neurons.
- Presence of IgG and IgM in the CSF provides evidence for immunopathology and predominance of the Th1 immune response.
- MS can present in different forms, including:
- Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS): the initial presentation of MS.
- Relapsing-remitting (RR): characterized by periods of acute neuro symptoms alternating with periods of remissions.
- Primary progressive: slow, chronic deterioration of neuro function with occasional plateaus.
- Secondary progressive: initially presents with RR characteristics, followed by a pattern of slow chronic deterioration.
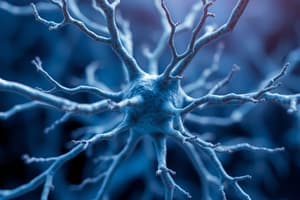
Neuron Function
- The axon carries impulses away from the cell body.
- The cell body (soma) is filled with cytoplasm and contains organelles, including the nucleus, that support the metabolic demands of the cell.
- Dendrites are multiple, branched extensions of the cell body that transmit impulses to the cell body.
- Sensory/afferent neurons carry impulses from receptors in the periphery to the CNS.
- Motor/efferent neurons carry signals away from the CNS to targets in the body that regulate activity.
- Interneurons provide connections between and transmit signals between afferent and efferent neurons.
Neuroglia and Supporting Cells
- Neuroglia form the myelin that covers the neurons of the CNS.
- SNA supporting cells include neuroglia, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells.
- PNS supporting cells include Schwann cells, which stimulate myelin production and maintenance.
Action Potentials
- Action potentials are electrical events that travel along the entire neuron, allowing charged ions to flood through channels in the semipermeable membrane around the neuron.
- Membrane potential is the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of the cell.
Synapses
- Electrical synapses transmit impulses by passing current-carrying ions through small openings known as gap junctions.
- Chemical synapse is a small gap between neurons or between neurons and other cells, transmitting impulses via stimulation of neurotransmitters.
Injuries and Conditions
- Chromatolysis is the swelling of neurons due to injury.
- Atrophy is a decrease in neuron size.
- Neuronophagia is phagocytosis and inflammatory responses caused by a dead neuron damaging neighboring cells.
- Ischemic injury occurs when there is inadequate perfusion to neurologic tissue and can lead to ICP.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.