Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is one of the primary uses of remote sensing in archeology?
What is one of the primary uses of remote sensing in archeology?
- To discover underground water sources
- To design modern buildings
- To analyze soil composition
- To recognize prehistoric archeological patterns (correct)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of contours?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of contours?
- Contours can represent underwater topography
- Contours indicate constant elevation
- Contours are always parallel to each other (correct)
- Contours never cross each other
What does the term 'horizontal equivalent' refer to in contour mapping?
What does the term 'horizontal equivalent' refer to in contour mapping?
- The distance between two contour lines at different elevations
- The distance between two points at the same elevation (correct)
- The projection of a contour line on the horizontal plane
- The distance between a contour line and the nearest benchmark
Which method is commonly used for calculating areas in surveying?
Which method is commonly used for calculating areas in surveying?
What does the contour interval indicate in a contour map?
What does the contour interval indicate in a contour map?
How does the contour interval relate to the scale of a map?
How does the contour interval relate to the scale of a map?
What is the term for the horizontal distance between two consecutive contours?
What is the term for the horizontal distance between two consecutive contours?
Which instrument is primarily used to locate contour gradients?
Which instrument is primarily used to locate contour gradients?
Which statement is true regarding contour lines?
Which statement is true regarding contour lines?
What can be computed approximately using contour maps?
What can be computed approximately using contour maps?
What method involves the use of horizontal and vertical measurements for drawing contours?
What method involves the use of horizontal and vertical measurements for drawing contours?
Which of the following is NOT a use of contour maps?
Which of the following is NOT a use of contour maps?
Steep ground is indicated by contour lines that are:
Steep ground is indicated by contour lines that are:
What does a topographical map represent?
What does a topographical map represent?
Which method is considered the best for representing elevations on a map?
Which method is considered the best for representing elevations on a map?
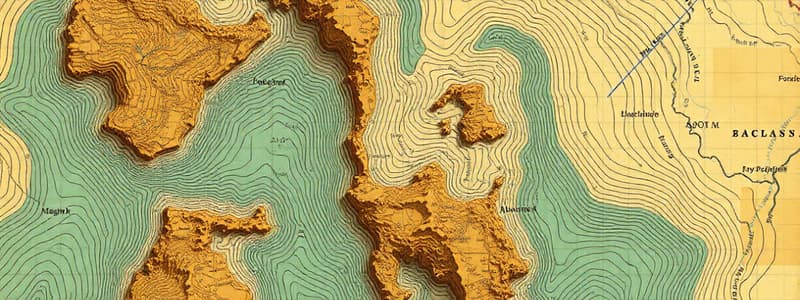
What is a contour line?
What is a contour line?
What is a contour interval?
What is a contour interval?
For which type of terrain should a larger contour interval be used?
For which type of terrain should a larger contour interval be used?
What happens if a small contour interval is adopted on a rough hilly ground?
What happens if a small contour interval is adopted on a rough hilly ground?
Which of the following features are NOT typically shown in topographical maps?
Which of the following features are NOT typically shown in topographical maps?
Why is it important to maintain a constant contour interval in a contour plan?
Why is it important to maintain a constant contour interval in a contour plan?
What is a primary characteristic of the Method of Squares?
What is a primary characteristic of the Method of Squares?
The Method of Cross Sections is most suitable for which of the following?
The Method of Cross Sections is most suitable for which of the following?
Which formula can be used to calculate the area of a triangle if the lengths of the sides are known?
Which formula can be used to calculate the area of a triangle if the lengths of the sides are known?
What is the purpose of the Average Ordinate Rule when determining areas?
What is the purpose of the Average Ordinate Rule when determining areas?
Which method is NOT part of the process for calculating areas based on field measurements?
Which method is NOT part of the process for calculating areas based on field measurements?
In tacheometric methods, what is the role of traverse stations?
In tacheometric methods, what is the role of traverse stations?
The formula for calculating the area using the Trapezoidal Rule primarily emphasizes which aspect?
The formula for calculating the area using the Trapezoidal Rule primarily emphasizes which aspect?
What does the variable 'd' represent in the area calculation formulas?
What does the variable 'd' represent in the area calculation formulas?
What is the formula for calculating the area using the Trapezoidal Rule?
What is the formula for calculating the area using the Trapezoidal Rule?
Which rule is stated to be more accurate in the content provided?
Which rule is stated to be more accurate in the content provided?
What is the area calculation formula for the Prismoidal Formula?
What is the area calculation formula for the Prismoidal Formula?
Which of the following is NOT an application of Remote Sensing?
Which of the following is NOT an application of Remote Sensing?
What kind of data is typically collected in Remote Sensing?
What kind of data is typically collected in Remote Sensing?
In the Simpson’s Rule formula, what factor is multiplied by the sum of odd ordinates?
In the Simpson’s Rule formula, what factor is multiplied by the sum of odd ordinates?
What does $D$ represent in the context of the volume calculation formulas?
What does $D$ represent in the context of the volume calculation formulas?
What element is NOT part of the area calculation in the trapezoidal formula?
What element is NOT part of the area calculation in the trapezoidal formula?
Flashcards
Contour Line
Contour Line
An imaginary line joining points with the same elevation on a topographical map.
Topographical Map
Topographical Map
A map showing both horizontal and vertical details of the ground.
Contour Interval
Contour Interval
Vertical distance between two consecutive contour lines.
Topographical Survey
Topographical Survey
Signup and view all the flashcards
Level Surface
Level Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Representation Method
Representation Method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Undulating Ground
Undulating Ground
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ground Features
Ground Features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contour Map
Contour Map
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Equivalent
Horizontal Equivalent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contour Gradient
Contour Gradient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Direct Contouring
Direct Contouring
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steep Slope on Contour Map
Steep Slope on Contour Map
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gentle Slope on Contour Map
Gentle Slope on Contour Map
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contour Lines Crossing
Contour Lines Crossing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Method of Squares
Method of Squares
Signup and view all the flashcards
Method of Cross Sections
Method of Cross Sections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tacheometric Methods
Tacheometric Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Area Calculation: Triangulation
Area Calculation: Triangulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Average Ordinate Rule
Average Ordinate Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Area Calculation: Planimeter
Area Calculation: Planimeter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Area Calculation: Offsets
Area Calculation: Offsets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Area calculation: Trapezoidal Rule
Area calculation: Trapezoidal Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a contour?
What is a contour?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Remote sensing
Remote sensing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mid-ordinate rule
Mid-ordinate rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simpson's rule
Simpson's rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trapezoidal rule
Trapezoidal rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Interval (d)
Common Interval (d)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ordinate (O)
Ordinate (O)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volume Calculation using Trapezoidal Rule
Volume Calculation using Trapezoidal Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volume Calculation using Prismoidal Formula
Volume Calculation using Prismoidal Formula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Applications of Remote Sensing
Applications of Remote Sensing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Unit III: Mapping & Sensing
- Mapping & Sensing: Includes contour lines and remote sensing
- Relative Positions: Points on a map are represented by relative positions
- Importance: Mapping importance increases when relative heights of features are represented along with horizontal positions
- Topographical Maps: Show ground features like rivers, ponds, valleys, slopes, depressions, roads, railways, vegetation, etc.
- Symbolic Notations: Used in topographical surveys for horizontal and vertical controls
Contour Lines
- Definition: Imaginary lines connecting points with the same elevation
- Best Method: Representing elevations on topographical maps
- Contour Interval: Vertical distance between consecutive contours
- Constant Interval: Keeps the plan consistent
- Map Appearance: Proper contour interval choice is crucial for clear visual representation
- Considerations: The choice of a suitable contour interval depends factors such as ground roughness, map scale, and intended use.
Methods of Contouring
- Direct Method: Measures horizontal and vertical distances to determine elevation points and connect them to form contours
- Indirect Method:
- Method of Squares: The area is gridded into squares, the reduced levels of corners are determined, and contours are drawn by interpolation
- Method of Cross-Sections: A traverse is run, cross-sections are projected, and levels are determined at various points. Contours are then interpolated
- Tacheometric Methods: A network of radial lines is drawn, observations from traverse stations are made, and elevations and distances are calculated.
Computations of Areas
- Methods:
- Dividing into Triangles/Squares: Calculate areas based on triangles or squares that divide the area within the boundary
- Planimeter: Instruments/tools are used to measure the irregular area
- Areas by Offsets (from base line): Methods based on measurements from a baseline:
- Ordinate Rule
- Average Ordinate Rule
- Trapezoidal Rule
- Simpson's Rule
Volumes
- Formulas: Calculate volumes for different shaped areas
- Trapezoidal Formula
- Prismoidal Formula/Simpson's Rule
Remote Sensing
- Definition: Collecting and interpreting information about a target without physical contact
- Methods/Techniques: Aircraft, satellites, cameras, scanners, and radar
- Applications:
- Environmental: Weather forecasting, pollution monitoring, and global warming
- Mineral Exploration: Locating and mapping mineral deposits
- Hazard Identification: Detecting natural hazards
- Archaeology: Identifying and mapping prehistoric sites
- Information Collection: High sophisticated sensing devices (e.g., sensors, cameras, etc.) used for data gathering
Characteristics of Contours
- Contours of Different Elevations: Contours do not intersect except for cliffs
- Steep Slopes: Closely spaced contours indicate steep slopes
- Gentle Slopes: Widely spaced contours represent gentle slopes
- Valley/Ridge Lines: Contours cross valley/ridge lines at right angles
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.