Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the master system that controls bodily processes?
What is the master system that controls bodily processes?
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Endocrine system
- Nervous system (correct)
What is the message that travels through nerves called?
What is the message that travels through nerves called?
- Enzyme
- Antibody
- Hormone
- Nerve impulse (correct)
Which of the following is an example of a stimulus?
Which of the following is an example of a stimulus?
- Thinking
- Sleeping
- Breathing
- Feeling thirsty (correct)
What are the sense organs that detect stimuli called?
What are the sense organs that detect stimuli called?
What is the behavior caused by a stimulus called?
What is the behavior caused by a stimulus called?
Light, heat, and touch are examples of what kind of stimulus?
Light, heat, and touch are examples of what kind of stimulus?
What is the secretion of enzymes in the body considered?
What is the secretion of enzymes in the body considered?
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Which part of a neuron receives impulses?
Which part of a neuron receives impulses?
What type of neuron carries impulses from sensory organs to the spinal cord?
What type of neuron carries impulses from sensory organs to the spinal cord?
Which of the following is part of the central nervous system?
Which of the following is part of the central nervous system?
What protects the brain?
What protects the brain?
Which part of the brain controls heartbeat and breathing?
Which part of the brain controls heartbeat and breathing?
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
Which part of the spinal cord is made up of nerve fibers?
Which part of the spinal cord is made up of nerve fibers?
How many pairs of cranial nerves do humans have?
How many pairs of cranial nerves do humans have?
What type of nerve carries both motor and sensory impulses?
What type of nerve carries both motor and sensory impulses?
What are actions controlled by the brain called?
What are actions controlled by the brain called?
What controls reflex actions?
What controls reflex actions?
What is the path that an impulse takes in a reflex action called?
What is the path that an impulse takes in a reflex action called?
What is the primary role of the nervous system in the context of bodily functions?
What is the primary role of the nervous system in the context of bodily functions?
How does the brain contribute to responding to a stimulus, such as picking up a coin?
How does the brain contribute to responding to a stimulus, such as picking up a coin?
Which of the following best describes the coordination process facilitated by the nervous system?
Which of the following best describes the coordination process facilitated by the nervous system?
How does the nervous system facilitate complex actions like walking or smiling?
How does the nervous system facilitate complex actions like walking or smiling?
What distinguishes sensory neurons from motor neurons in terms of function?
What distinguishes sensory neurons from motor neurons in terms of function?
What role do association neurons play within the spinal cord?
What role do association neurons play within the spinal cord?
What is the role of the vertebral column in the central nervous system (CNS)?
What is the role of the vertebral column in the central nervous system (CNS)?
How do the grooves and ridges on the surface of the cerebrum contribute to its function?
How do the grooves and ridges on the surface of the cerebrum contribute to its function?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the cerebrum?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the cerebrum?
What is the likely outcome if the medulla oblongata is severely damaged?
What is the likely outcome if the medulla oblongata is severely damaged?
How is the spinal cord organized in terms of grey and white matter?
How is the spinal cord organized in terms of grey and white matter?
What is the main function of the nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system?
What is the main function of the nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system?
How do cranial nerves differ from spinal nerves in terms of origin?
How do cranial nerves differ from spinal nerves in terms of origin?
What is the defining characteristic of mixed nerves?
What is the defining characteristic of mixed nerves?
How does the brain's role differ in voluntary actions compared to reflex actions?
How does the brain's role differ in voluntary actions compared to reflex actions?
Which of the following is an example of an action that is primarily controlled by the spinal cord?
Which of the following is an example of an action that is primarily controlled by the spinal cord?
What is contained within the central canal of the spinal cord?
What is contained within the central canal of the spinal cord?
Which of the following best describes the role of spinal nerves?
Which of the following best describes the role of spinal nerves?
Which action best demonstrates the coordination function of the nervous system involving multiple organ systems?
Which action best demonstrates the coordination function of the nervous system involving multiple organ systems?
How does the nervous system’s coordination with the endocrine system enhance bodily functions?
How does the nervous system’s coordination with the endocrine system enhance bodily functions?
If the cerebrum were damaged, which of the following functions would be most directly affected?
If the cerebrum were damaged, which of the following functions would be most directly affected?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the necessity of coordination between the nervous and endocrine systems?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the necessity of coordination between the nervous and endocrine systems?
How does the structural organization of the spinal cord (grey vs. white matter) directly support its function in relaying information?
How does the structural organization of the spinal cord (grey vs. white matter) directly support its function in relaying information?
If a person were to experience damage that selectively impairs the function of association neurons in the spinal cord, which of the following outcomes would be most likely?
If a person were to experience damage that selectively impairs the function of association neurons in the spinal cord, which of the following outcomes would be most likely?
Which scenario exemplifies a response primarily mediated by the spinal cord, independent of direct brain involvement?
Which scenario exemplifies a response primarily mediated by the spinal cord, independent of direct brain involvement?
How does the folding of the cerebrum into grooves and ridges (gyri and sulci) enhance its functional capacity?
How does the folding of the cerebrum into grooves and ridges (gyri and sulci) enhance its functional capacity?
Which of the following actions illustrates the integrated function of multiple components within the nervous system?
Which of the following actions illustrates the integrated function of multiple components within the nervous system?
Damage to which specific area of the brain would result in the most immediate and life-threatening consequences?
Damage to which specific area of the brain would result in the most immediate and life-threatening consequences?
How does the arrangement of cranial and spinal nerves facilitate the overall function of the peripheral nervous system?
How does the arrangement of cranial and spinal nerves facilitate the overall function of the peripheral nervous system?
Which of the following is the MOST comprehensive description of the role of the nervous system in maintaining homeostasis?
Which of the following is the MOST comprehensive description of the role of the nervous system in maintaining homeostasis?
The nervous system controls and coordinates daily activities.
The nervous system controls and coordinates daily activities.
A 'stimulus' refers to any change in the internal or external environment.
A 'stimulus' refers to any change in the internal or external environment.
Receptors, such as eyes and ears, detect stimuli.
Receptors, such as eyes and ears, detect stimuli.
A response is the action caused by a stimulus.
A response is the action caused by a stimulus.
Secretion of enzymes inside the body is an example of an external stimulus.
Secretion of enzymes inside the body is an example of an external stimulus.
Coordination means body tissues and organs work independently of each other.
Coordination means body tissues and organs work independently of each other.
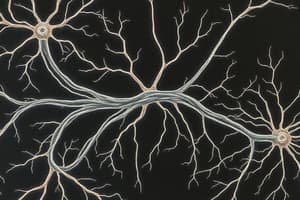
The neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
The neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Axons receive impulses and then pass them to the cell body.
Axons receive impulses and then pass them to the cell body.
Sensory neurons originate from the brain or spinal cord to the body parts.
Sensory neurons originate from the brain or spinal cord to the body parts.
Motor neurons exclusively connect sensory neurons within the spinal cord.
Motor neurons exclusively connect sensory neurons within the spinal cord.
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord.
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord.
The cerebellum is the uppermost and largest part of the brain.
The cerebellum is the uppermost and largest part of the brain.
The cerebrum controls mental activities like thinking and reasoning.
The cerebrum controls mental activities like thinking and reasoning.
The cerebellum maintains balance and coordinates muscular activity.
The cerebellum maintains balance and coordinates muscular activity.
Damage to the cerebrum can lead to death of an individual.
Damage to the cerebrum can lead to death of an individual.
The spinal cord conducts messages from the brain to the muscles.
The spinal cord conducts messages from the brain to the muscles.
There are 21 pairs of spinal nerves in humans.
There are 21 pairs of spinal nerves in humans.
Voluntary actions are actions controlled by the spinal cord.
Voluntary actions are actions controlled by the spinal cord.
Reflex actions are quick, automatic responses to a stimulus without brain involvement.
Reflex actions are quick, automatic responses to a stimulus without brain involvement.
The nervous system solely controls voluntary movements like walking and writing, independent of involuntary processes.
The nervous system solely controls voluntary movements like walking and writing, independent of involuntary processes.
Neurons transmit messages through electrical impulses, with dendrites receiving impulses and axons transmitting them away from the cell body.
Neurons transmit messages through electrical impulses, with dendrites receiving impulses and axons transmitting them away from the cell body.
The central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain and spinal cord, with the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consisting of nerves linking the CNS to body organs.
The central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain and spinal cord, with the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consisting of nerves linking the CNS to body organs.
The cerebrum, located at the back of the head, primarily coordinates muscular activity and maintains balance; damage to this area leads to impaired cognitive functions.
The cerebrum, located at the back of the head, primarily coordinates muscular activity and maintains balance; damage to this area leads to impaired cognitive functions.
Reflex actions, controlled by the brain, are slower responses to stimuli, allowing for conscious decision-making before a reaction occurs.
Reflex actions, controlled by the brain, are slower responses to stimuli, allowing for conscious decision-making before a reaction occurs.
Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain to sensory organs, enabling the perception of stimuli like touch and sound.
Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain to sensory organs, enabling the perception of stimuli like touch and sound.
The brain stem, or medulla oblongata, controls voluntary actions like walking and writing, ensuring coordinated movement.
The brain stem, or medulla oblongata, controls voluntary actions like walking and writing, ensuring coordinated movement.
A nerve is composed of multiple neurons bundled together, each transmitting signals independently without interaction.
A nerve is composed of multiple neurons bundled together, each transmitting signals independently without interaction.
Spinal nerves emerge exclusively from the brain, transmitting signals to various body parts without involving the spinal cord.
Spinal nerves emerge exclusively from the brain, transmitting signals to various body parts without involving the spinal cord.
Internal stimuli include environmental factors such as light and touch, triggering responses like moving away from heat.
Internal stimuli include environmental factors such as light and touch, triggering responses like moving away from heat.
Association neurons directly connect sensory organs to muscles, creating a shortcut for immediate reflex responses.
Association neurons directly connect sensory organs to muscles, creating a shortcut for immediate reflex responses.
Increasing the surface area of the cerebrum is achieved through a smooth, uniform surface, maximizing neuron density.
Increasing the surface area of the cerebrum is achieved through a smooth, uniform surface, maximizing neuron density.
The spinal cord extends from the cerebrum and runs down the whole length of the backbone.
The spinal cord extends from the cerebrum and runs down the whole length of the backbone.
The actions which are controlled by the spinal cord are called voluntary actions.
The actions which are controlled by the spinal cord are called voluntary actions.
The eyes, ears, nose, skin and brain are receptors.
The eyes, ears, nose, skin and brain are receptors.
Secretion of enzymes in our body is an external stimulus
Secretion of enzymes in our body is an external stimulus
The brain is the main control centre of the peripheral nervous system.
The brain is the main control centre of the peripheral nervous system.
The tail or axon which is a long, tube-like part with fine terminal nerve endings, is not enveloped in a sheath called myelin sheath.
The tail or axon which is a long, tube-like part with fine terminal nerve endings, is not enveloped in a sheath called myelin sheath.
The master system that controls processes like respiration and digestion is called the ______ system.
The master system that controls processes like respiration and digestion is called the ______ system.
A message from eyes to the brain travels through ______.
A message from eyes to the brain travels through ______.
A message conducted along a nerve is called ______ impulse.
A message conducted along a nerve is called ______ impulse.
Any change in the internal or external environment of an organism is called a ______.
Any change in the internal or external environment of an organism is called a ______.
The eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue are examples of ______.
The eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue are examples of ______.
The brain and ______ cord coordinate information received from receptors.
The brain and ______ cord coordinate information received from receptors.
Muscles that respond to nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord are called ______.
Muscles that respond to nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord are called ______.
Pulling your hand away from a hot plate is a ______.
Pulling your hand away from a hot plate is a ______.
Factors within an organism are examples of ______ stimuli.
Factors within an organism are examples of ______ stimuli.
[Blank] means that body tissues and organs work together to perform their functions appropriately.
[Blank] means that body tissues and organs work together to perform their functions appropriately.
The basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the ______.
The basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the ______.
The ______ of a neuron receive impulses.
The ______ of a neuron receive impulses.
The ______ transmit the impulse away from the cell body.
The ______ transmit the impulse away from the cell body.
Sensory neurons carry impulses from the body parts to the spinal cord or the ______.
Sensory neurons carry impulses from the body parts to the spinal cord or the ______.
[Blank] neurons carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to the body parts.
[Blank] neurons carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to the body parts.
The brain and spinal cord make up the ______ nervous system.
The brain and spinal cord make up the ______ nervous system.
The brain lies protected inside the ______.
The brain lies protected inside the ______.
The ______ is the uppermost and largest part of the brain and controls mental activities.
The ______ is the uppermost and largest part of the brain and controls mental activities.
The ______ maintains balance of the body and coordinates muscular activity.
The ______ maintains balance of the body and coordinates muscular activity.
Actions controlled by the brain are called ______ actions.
Actions controlled by the brain are called ______ actions.
The master system that controls and coordinates body processes like respiration and digestion is called the ______ system.
The master system that controls and coordinates body processes like respiration and digestion is called the ______ system.
A ______ is any change in the internal or external environment that can be detected by an organism.
A ______ is any change in the internal or external environment that can be detected by an organism.
Organs such as the eyes, ears, and skin that detect a stimulus are called ______.
Organs such as the eyes, ears, and skin that detect a stimulus are called ______.
The ______ and spinal cord are the main organs that coordinate information received from receptors in the body.
The ______ and spinal cord are the main organs that coordinate information received from receptors in the body.
The behaviour caused by a stimulus is known as a ______.
The behaviour caused by a stimulus is known as a ______.
Environmental factors like light, heat, and touch are examples of ______ stimuli.
Environmental factors like light, heat, and touch are examples of ______ stimuli.
Secretion of enzymes and hormones within the body is considered an ______ stimulus.
Secretion of enzymes and hormones within the body is considered an ______ stimulus.
[Blank] is the process where body tissues and organs work together to perform their functions appropriately to fulfill the needs of the whole body.
[Blank] is the process where body tissues and organs work together to perform their functions appropriately to fulfill the needs of the whole body.
The nervous system coordinates muscles, controls responses to stimuli, and works closely with the ______ system, which secretes hormones.
The nervous system coordinates muscles, controls responses to stimuli, and works closely with the ______ system, which secretes hormones.
The basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system is a special cell called a ______ or a neuron.
The basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system is a special cell called a ______ or a neuron.
The short, cytoplasmic branching structures that arise from the cell body of a neuron are called ______.
The short, cytoplasmic branching structures that arise from the cell body of a neuron are called ______.
The long, tube-like part of a neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body is the ______.
The long, tube-like part of a neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body is the ______.
Neurons that carry impulses from sensory organs to the spinal cord or brain are called ______ neurons.
Neurons that carry impulses from sensory organs to the spinal cord or brain are called ______ neurons.
[Blank] neurons carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands.
[Blank] neurons carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands.
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons within the spinal cord are known as ______ neurons.
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons within the spinal cord are known as ______ neurons.
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the ______ and spinal cord.
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the ______ and spinal cord.
The ______ nervous system (PNS) includes the nerves arising from the spinal cord and brain, linking the CNS with various body organs.
The ______ nervous system (PNS) includes the nerves arising from the spinal cord and brain, linking the CNS with various body organs.
The actions controlled by the brain, such as riding a bicycle or dancing, are called ______ actions.
The actions controlled by the brain, such as riding a bicycle or dancing, are called ______ actions.
Actions under the control of the spinal cord, which are quick and automatic responses to a stimulus without brain involvement, are called ______ actions.
Actions under the control of the spinal cord, which are quick and automatic responses to a stimulus without brain involvement, are called ______ actions.
The path that an impulse takes in a reflex action is called a ______ arc.
The path that an impulse takes in a reflex action is called a ______ arc.
What is the master system that controls processes like respiration and digestion in our body?
What is the master system that controls processes like respiration and digestion in our body?
What is the message conducted along a nerve called?
What is the message conducted along a nerve called?
What is any change in the internal or external environment of an organism called?
What is any change in the internal or external environment of an organism called?
Name two examples of external stimuli.
Name two examples of external stimuli.
What are the eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue referred to as?
What are the eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue referred to as?
What two organs coordinate information received from receptors?
What two organs coordinate information received from receptors?
What type of behavior is caused by a stimulus?
What type of behavior is caused by a stimulus?
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system called?
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system called?
Name the three main parts of a nerve cell.
Name the three main parts of a nerve cell.
What is the function of sensory neurons?
What is the function of sensory neurons?
Name the two main parts of the human central nervous system.
Name the two main parts of the human central nervous system.
What are the three main centers of the brain?
What are the three main centers of the brain?
Which part of the brain controls mental activities and voluntary actions?
Which part of the brain controls mental activities and voluntary actions?
Which part of the brain maintains balance and coordinates muscular activity?
Which part of the brain maintains balance and coordinates muscular activity?
Are actions such as riding a bicycle considered voluntary or reflex actions?
Are actions such as riding a bicycle considered voluntary or reflex actions?
Describe the two primary functions of the brain when responding to a stimulus, such as picking up a coin.
Describe the two primary functions of the brain when responding to a stimulus, such as picking up a coin.
How do sensory neurons and motor neurons work together in response to an external stimulus, like touching a hot surface?
How do sensory neurons and motor neurons work together in response to an external stimulus, like touching a hot surface?
Explain how the structure of the cerebrum, with its grooves and ridges, contributes to its function.
Explain how the structure of the cerebrum, with its grooves and ridges, contributes to its function.
What is the role of the myelin sheath in some neurons, and how does it affect nerve impulse transmission?
What is the role of the myelin sheath in some neurons, and how does it affect nerve impulse transmission?
Differentiate between cranial and spinal nerves based on their origin and general function.
Differentiate between cranial and spinal nerves based on their origin and general function.
If the medulla oblongata is damaged, what critical bodily functions are most likely to be affected, and why?
If the medulla oblongata is damaged, what critical bodily functions are most likely to be affected, and why?
Explain how the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) work together to enable a voluntary action like writing.
Explain how the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) work together to enable a voluntary action like writing.
Describe the key differences between voluntary and reflex actions, emphasizing the role of the brain and spinal cord in each.
Describe the key differences between voluntary and reflex actions, emphasizing the role of the brain and spinal cord in each.
Describe how sensory receptors play a role in maintaining homeostasis.
Describe how sensory receptors play a role in maintaining homeostasis.
Why is coordination between different tissues and organs essential for the proper functioning of the body?
Why is coordination between different tissues and organs essential for the proper functioning of the body?
How does the arrangement of gray and white matter in the spinal cord contribute to its function of transmitting messages?
How does the arrangement of gray and white matter in the spinal cord contribute to its function of transmitting messages?
Explain the difference in function between afferent and efferent neurons in the context of a stimulus-response pathway.
Explain the difference in function between afferent and efferent neurons in the context of a stimulus-response pathway.
Describe how the cerebellum and cerebrum interact to produce a coordinated and balanced movement, such as riding a bicycle.
Describe how the cerebellum and cerebrum interact to produce a coordinated and balanced movement, such as riding a bicycle.
Explain why a mixed nerve is essential for effective communication between the brain and the body. Give an example.
Explain why a mixed nerve is essential for effective communication between the brain and the body. Give an example.
Describe what would happen if the association neurons in the spinal cord were damaged.
Describe what would happen if the association neurons in the spinal cord were damaged.
How does the structure of the cerebrum, with its grooves and ridges, contribute to its function in controlling mental activities and processing sensory information?
How does the structure of the cerebrum, with its grooves and ridges, contribute to its function in controlling mental activities and processing sensory information?
Explain how the integrated function of sensory neurons, association neurons, and motor neurons allows for a coordinated response to external stimuli.
Explain how the integrated function of sensory neurons, association neurons, and motor neurons allows for a coordinated response to external stimuli.
Describe the potential consequences if the medulla oblongata is damaged, and explain why such damage is life-threatening.
Describe the potential consequences if the medulla oblongata is damaged, and explain why such damage is life-threatening.
How do cranial and spinal nerves act as a bridge between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, and what is the significance of having both types of nerves?
How do cranial and spinal nerves act as a bridge between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, and what is the significance of having both types of nerves?
Differentiate between the roles of the grey matter and white matter in the spinal cord, and explain how their arrangement contributes to the spinal cord's function.
Differentiate between the roles of the grey matter and white matter in the spinal cord, and explain how their arrangement contributes to the spinal cord's function.
Explain how the reflex arc operates in bypassing the brain to produce quick, automatic responses to stimuli, and provide an example of a situation where this is advantageous.
Explain how the reflex arc operates in bypassing the brain to produce quick, automatic responses to stimuli, and provide an example of a situation where this is advantageous.
Elaborate on the importance of coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system, providing an example of a physiological process that requires this coordination.
Elaborate on the importance of coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system, providing an example of a physiological process that requires this coordination.
Describe how the structure of a neuron facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses, detailing the roles of dendrites, cell body, and axon.
Describe how the structure of a neuron facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses, detailing the roles of dendrites, cell body, and axon.
Explain how the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is organized into sensory and motor divisions, and how these divisions work together to enable both the perception of stimuli and the execution of responses.
Explain how the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is organized into sensory and motor divisions, and how these divisions work together to enable both the perception of stimuli and the execution of responses.
How does the cerebellum contribute to both maintaining balance and coordinating muscular activity, and what might be the observable effects of damage to this region of the brain?
How does the cerebellum contribute to both maintaining balance and coordinating muscular activity, and what might be the observable effects of damage to this region of the brain?
Flashcards
Nervous System
Nervous System
A master system that controls and coordinates bodily processes.
Nerve Impulse
Nerve Impulse
A message conducted along a nerve.
Stimulus
Stimulus
Any change in the internal or external environment of an organism.
Receptors
Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response
Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Stimulus
External Stimulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Stimulus
Internal Stimulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coordination
Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuron
Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Body (Cyton)
Cell Body (Cyton)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dendrites
Dendrites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axon
Axon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Neurons
Sensory Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Neurons
Motor Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Association Neurons
Association Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain
Brain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voluntary Actions
Voluntary Actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex Actions
Reflex Actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nerve
Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebrum
Cerebrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata)
Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Nerves
Motor Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Nerves
Sensory Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed Nerves
Mixed Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex Arc
Reflex Arc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Spinal Cord?
Functions of Spinal Cord?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Coordination
Brain Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impulse (in neurons)
Impulse (in neurons)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous Coordination
Nervous Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Involuntary Process
Involuntary Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grooves and Ridges of Cerebrum
Grooves and Ridges of Cerebrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Stem
Brain Stem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelin Sheath
Myelin Sheath
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulus and Response
Stimulus and Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulus and Response Process
Stimulus and Response Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous System Functions
Nervous System Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Nerves
Function of Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The nervous system acts as a master system regulating processes such as respiration, digestion, and locomotion.
- Daily activities are coordinated and controlled by the nervous system.
- Following a nerve impulse, the brain sends messages to muscles to initiate action and ensures balance.
Stimulus and Response
- Thirst prompts drinking water, and pain in a fractured hand discourages movement.
- Receptors, including eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue, detect stimuli.
- The hot pan is an external stimulus example.
- Secretion of enzymes, hormones, and acids are internal stimuli.
Neuron Structure
- Bundles of nerve fibers (axons) are enclosed in a tubular sheath to form a nerve.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The cerebrum's surface is characterized by grooves and ridges to enhance surface area.
- The cerebrum is divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.