Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a state?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a state?
- Control over a specific territory
- A set of permanent political institutions
- The ability to enforce its laws
- A shared language and culture (correct)
What is the main difference between a nation and a state?
What is the main difference between a nation and a state?
- States are always more powerful than nations.
- Nations are ruled by monarchs, while states are ruled by elected officials.
- Nations are always larger than states.
- States have a clear territory and boundaries, while nations may not. (correct)
Which of these is an example of a state's function in maintaining order?
Which of these is an example of a state's function in maintaining order?
- Negotiating a trade agreement with another country.
- Building a new school in a rural area.
- Creating and enforcing traffic laws. (correct)
- Providing financial aid to citizens in need.
What is the relationship between polity and state?
What is the relationship between polity and state?
Which of the following is NOT a key function of a polity?
Which of the following is NOT a key function of a polity?
Which of the following is NOT a key element of a polity?
Which of the following is NOT a key element of a polity?
Which of these describes a system of government where political power is concentrated in the hands of a few?
Which of these describes a system of government where political power is concentrated in the hands of a few?
What is the term for the shared beliefs and values that influence political behavior within a society?
What is the term for the shared beliefs and values that influence political behavior within a society?
Which of these is NOT a key aspect of how power operates in a polity?
Which of these is NOT a key aspect of how power operates in a polity?
What is the term for the right and capacity to influence or command the behavior of others?
What is the term for the right and capacity to influence or command the behavior of others?
What is the term for the belief that a government's power is justified and deserves to be obeyed?
What is the term for the belief that a government's power is justified and deserves to be obeyed?
Which form of government allows for the greatest citizen participation in decision-making?
Which form of government allows for the greatest citizen participation in decision-making?
What does the term "polity" refer to?
What does the term "polity" refer to?
Flashcards
Monarchy
Monarchy
A government system with a hereditary ruler like a king or queen.
Aristocracy
Aristocracy
A government where a small elite group holds power due to birth or wealth.
Nation-state
Nation-state
A political entity where the nation’s borders align with the state’s borders.
Public services
Public services
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resolving disputes
Resolving disputes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polity
Polity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sovereignty
Sovereignty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Legitimacy
Legitimacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Authority
Authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Power
Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Institutions
Institutions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political culture
Political culture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Democracy
Democracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Definition and Scope
- Polity refers to the form of government and its related institutions within a particular state. It encompasses the structures of power, the distribution of authority, and the processes by which decisions are made affecting the population.
- It examines various aspects of governance, including the relationships among different branches of government, the role of political parties, and public participation in decision-making.
- The study of polity integrates elements of political science, sociology, economics, and history to understand how power operates in society.
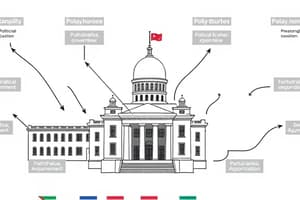
Elements of a Polity
- Sovereignty: The supreme and absolute power within a state in making and enforcing laws. It asserts authority over its own territory and citizens, and ideally, is recognized by other sovereign states.
- Legitimacy: The belief that a government's power is justified and deserves to be obeyed. This can stem from tradition, popular consent, law, or religious authority.
- Authority: The right and capacity to influence or command the behavior of others. Authority derives from legitimate power and is often backed by the use of legitimate force.
- Power: The ability to influence or control others, often even against their will. Power may be wielded by individuals, groups, or institutions.
- Institutions: The formal and informal structures that make up a polity, such as legislatures, executive branches, judiciaries, bureaucracies, political parties, and interest groups. These structures define roles, procedures, and responsibilities.
- Political culture: The shared values, beliefs, and attitudes towards politics and government that exist within a society.
- Political participation: The ways in which citizens engage in the political process, from voting to protesting, lobbying, or running for office.
Types of Polity
- Democracy: A system of government where supreme political authority is vested in the people, and citizens have a say in decision making, typically through elections and representation.
- Autocracy: A system of government where supreme political authority rests with a single individual, a small group, or a single ruling party, typically with restricted citizen participation.
- Oligarchy: A system of government where political power is concentrated in the hands of a small, often privileged, group of individuals.
- Monarchy: A system of government with a hereditary head of state, typically a king or queen, who holds significant political power.
- Aristocracy: A form of government where power is held by a small, elite group thought to be superior by virtue of birth, wealth, or ability.
Polity and State Relations
- State: The set of permanent political institutions, such as the army, police, and bureaucracy, that control a given territory. The state is frequently intertwined with the polity, yet they are distinct.
- Nation: A large group of people united by a common culture, ethnicity, history, language, or territory. This can sometimes coincide with a polity (state), but not always.
- Nation-state: An ideal that arises when the borders of a nation's people align with the political borders of the state.
- International relations: The interactions between different states and their polites on a global level.
Functions of Polity
- Maintaining order: A polity's primary function is to establish rules, enforce norms, and control conflicts to ensure social stability.
- Providing security: The protection of citizens and the state's territory from external threats as well as internal unrest.
- Providing public services: Polity structures often are responsible for providing essential services such as infrastructure, healthcare, education, and social welfare.
- Making and enforcing laws: Legislative bodies are critical for enacting laws that regulate the behavior of citizens and businesses.
- Resolving disputes: Polity mechanisms (like courts) help settle disagreements among citizens, groups, and the state itself.
- Setting and achieving societal goals: Polity policies and programs aim to address broad issues like economic development, environmental protection, or social justice.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.