Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary reason why the eardrum can appear opaque in middle ear effusion (OME)?
What is the primary reason why the eardrum can appear opaque in middle ear effusion (OME)?
- The eardrum is thickened due to a build-up of earwax.
- The presence of a thick mucoid fluid in the middle ear. (correct)
- The presence of air bubbles in the middle ear.
- The eardrum is inflamed and red.
How does the appearance of the eardrum in a patient with OME differ from a normal eardrum?
How does the appearance of the eardrum in a patient with OME differ from a normal eardrum?
- The eardrum in OME will have a distinct bulge, indicating fluid buildup.
- The eardrum in OME is often visibly red and inflamed.
- The eardrum in OME is typically transparent and clear.
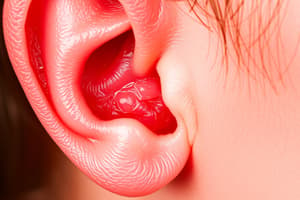
- The eardrum in OME may appear thicker and less transparent, with a possible yellowish hue. (correct)
Why is it challenging to diagnose OME in children?
Why is it challenging to diagnose OME in children?
- Children's eardrums are less susceptible to fluid buildup, making diagnosis difficult.
- Children often have difficulty describing their hearing loss.
- Children are often moving around, making it difficult to get a clear view of the eardrum. (correct)
- Children's eardrums are smaller and more delicate, making examination difficult.
What is the typical treatment approach for OME in most cases?
What is the typical treatment approach for OME in most cases?
According to the provided information, what percentage of children with middle ear effusion (OME) experience a resolution of their condition within 3 months?
According to the provided information, what percentage of children with middle ear effusion (OME) experience a resolution of their condition within 3 months?
What are the potential problems associated with persistent or prolonged OME?
What are the potential problems associated with persistent or prolonged OME?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of OME?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of OME?
What is the meaning of the acronym OME as used in the provided text?
What is the meaning of the acronym OME as used in the provided text?
What condition occurs when the eustachian tube does not open normally?
What condition occurs when the eustachian tube does not open normally?
Which of the following is a common symptom of acute otitis media?
Which of the following is a common symptom of acute otitis media?
Which age group is most commonly affected by ear infections?
Which age group is most commonly affected by ear infections?
What is one potential systemic symptom of acute otitis media?
What is one potential systemic symptom of acute otitis media?
What does otorrhoea refer to in the context of ear infections?
What does otorrhoea refer to in the context of ear infections?
Which of the following factors is least likely to contribute to eustachian tube dysfunction?
Which of the following factors is least likely to contribute to eustachian tube dysfunction?
What might ear tugging indicate in toddlers?
What might ear tugging indicate in toddlers?
What typically follows a common cold in children leading to ear infections?
What typically follows a common cold in children leading to ear infections?
What type of epithelium lines the eustachian tube?
What type of epithelium lines the eustachian tube?
What function do the cilia in the eustachian tube serve?
What function do the cilia in the eustachian tube serve?
Which part of the eustachian tube is composed of cartilage?
Which part of the eustachian tube is composed of cartilage?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for opening and closing the cartilaginous portion of the eustachian tube?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for opening and closing the cartilaginous portion of the eustachian tube?
What happens to toxic substances inhaled into the respiratory tract?
What happens to toxic substances inhaled into the respiratory tract?
What type of tissue is found in the bony portion of the eustachian tube?
What type of tissue is found in the bony portion of the eustachian tube?
Which structure does the eustachian tube connect to?
Which structure does the eustachian tube connect to?
What is the primary role of mucus in the respiratory tract?
What is the primary role of mucus in the respiratory tract?
What is the primary purpose of forming a seal with the ear canal during pneumatic otoscopy?
What is the primary purpose of forming a seal with the ear canal during pneumatic otoscopy?
What occurs to a normal eardrum when air is puffed in during pneumatic otoscopy?
What occurs to a normal eardrum when air is puffed in during pneumatic otoscopy?
How does acute otitis media (AOM) affect eardrum mobility when air is puffed in?
How does acute otitis media (AOM) affect eardrum mobility when air is puffed in?
What does a lack of movement in the eardrum during pneumatic otoscopy typically indicate?
What does a lack of movement in the eardrum during pneumatic otoscopy typically indicate?
What is tympanometry used to measure?
What is tympanometry used to measure?
In the context of otoscopy, what does OME stand for?
In the context of otoscopy, what does OME stand for?
What is a characteristic finding in tympanic membrane (eardrum) mobility in OME?
What is a characteristic finding in tympanic membrane (eardrum) mobility in OME?
What happens to the eardrum when air is released during pneumatic otoscopy in OME?
What happens to the eardrum when air is released during pneumatic otoscopy in OME?
What is the primary reason thick mucoid fluid in the middle ear inhibits eardrum vibration?
What is the primary reason thick mucoid fluid in the middle ear inhibits eardrum vibration?
What is the function of the flanges on an ear tube?
What is the function of the flanges on an ear tube?
What typically happens to tympanostomy tubes after a certain period?
What typically happens to tympanostomy tubes after a certain period?
During a tympanostomy procedure, which material is primarily suctioned out?
During a tympanostomy procedure, which material is primarily suctioned out?
What condition can develop if an infection in the middle ear spreads to the mastoid bone?
What condition can develop if an infection in the middle ear spreads to the mastoid bone?
How long do ear tubes generally remain in the eardrum?
How long do ear tubes generally remain in the eardrum?
What does a CT scan reveal if there is fluid or infection present in the middle ear and mastoid area?
What does a CT scan reveal if there is fluid or infection present in the middle ear and mastoid area?
What is a potential outcome if an ear tube were to migrate into the middle ear space?
What is a potential outcome if an ear tube were to migrate into the middle ear space?
What symptom may indicate a serious infection in the middle ear and mastoid area?
What symptom may indicate a serious infection in the middle ear and mastoid area?
What is the primary treatment approach for mastoiditis?
What is the primary treatment approach for mastoiditis?
What happens when the outer flange is not present on some types of ear tubes?
What happens when the outer flange is not present on some types of ear tubes?
Which of the following best describes the material the ear tube is primarily made of?
Which of the following best describes the material the ear tube is primarily made of?
How can pus from an infection in the middle ear affect the appearance of the outer ear?
How can pus from an infection in the middle ear affect the appearance of the outer ear?
What is the name of the surgery that may be necessary to clear pus from the mastoid area?
What is the name of the surgery that may be necessary to clear pus from the mastoid area?
Which muscle is associated with the mastoid bone?
Which muscle is associated with the mastoid bone?
Which of the following might NOT be a consequence of untreated mastoiditis?
Which of the following might NOT be a consequence of untreated mastoiditis?
Flashcards
Eustachian Tube
Eustachian Tube
A canal that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
Ciliated Respiratory Epithelium
Ciliated Respiratory Epithelium
Tissue lining with tiny hair-like structures that help move mucus.
Function of Cilia
Function of Cilia
Cilia beat to move mucus and trapped particles out of the respiratory tract.
Mucus
Mucus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bony Portion of Eustachian Tube
Bony Portion of Eustachian Tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cartilaginous Portion of Eustachian Tube
Cartilaginous Portion of Eustachian Tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levator Veli Palatini
Levator Veli Palatini
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tensor Veli Palatini
Tensor Veli Palatini
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patulous eustachian tube
Patulous eustachian tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute otitis media
Acute otitis media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common symptoms of ear infections
Common symptoms of ear infections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper respiratory infections
Upper respiratory infections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Febrile response
Febrile response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ear tugging in toddlers
Ear tugging in toddlers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eardrum Appearance
Eardrum Appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Self-limiting Nature
Self-limiting Nature
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE)
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Persistence Rate
Persistence Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of Hearing Loss
Impact of Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Observation Strategy
Observation Strategy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of OME
Symptoms of OME
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucoid fluid
Mucoid fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eardrum vibration
Eardrum vibration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Armstrong grommet
Armstrong grommet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ear tube procedure
Ear tube procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flanges of ear tubes
Flanges of ear tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tympanostomy tube lifespan
Tympanostomy tube lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratin debris
Keratin debris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer flange absence
Outer flange absence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Ear Space
Middle Ear Space
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Scan in Ear Diagnosis
CT Scan in Ear Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serious Acute Infection
Serious Acute Infection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastoidectomy
Mastoidectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Mastoiditis
Symptoms of Mastoiditis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role of Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
Role of Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pneumatic otoscopy
Pneumatic otoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tympanic membrane mobility
Tympanic membrane mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eardrum tension
Eardrum tension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tympanometry
Tympanometry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type A tympanogram
Type A tympanogram
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ear canal seal
Ear canal seal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Understanding Otitis Media and Ear Disorders
- Otitis media is inflammation or infection of the middle ear.
- Hiss is someone's name who discovered how ears are formed during embryogenesis.
- Primordial embryological tissue forms the pina (auricle).
- Cauliflower ear is a cosmetic issue.
- Keloids are hypertrophic or excessive scarring.
- Keloids are more common in African Canadian and African American populations.
- Keloids tend to form following superficial trauma.
- Otitis media is common and frequently causes visits to healthcare providers.
Otitis Media Subtypes
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM): An actual acute infectious disease. This presents with signs and symptoms of acute inflammation, such as fever and pain.
- Chronic Supportive Otitis Media (COME): A different entity. There is middle ear effusion (fluid) but without signs/symptoms of acute inflammation.
- Subacute Otitis Media: A state between acute and chronic otitis media.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): Middle ear effusion without signs or symptoms of acute inflammation. This is often asymptomatic.
Pathophysiology of Otitis Media
- The eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
- The eustachian tube is important for equalizing air pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere to prevent discomfort.
- Obstruction or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can lead to pressure imbalance, resulting in fluid buildup in the middle ear.
- Upper respiratory infections are common causes of OME, as nasal congestion and inflammation can interfere with eustachian tube function.
- Allergies and other conditions that cause inflammation can contribute to eustachian tube dysfunction.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Otitis Media
- Otitis media can be diagnosed by observing signs and symptoms and examining the eardrum.
- The presence of fluid or pus behind the eardrum can be a significant indicator.
- Treatments for AOM may include antibiotics to address bacterial infection.
- For OME, observation and management to allow inflammation to clear is often the best approach.
- Ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes) can be used in cases of repeated AOM or persistent OME.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.