Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primarily lines the primitive oral cavity or stomedeum?
What primarily lines the primitive oral cavity or stomedeum?
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Simple columnar epithelium
- Pseudostratified epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium (correct)
What is the primary role of the dental lamina during tooth development?
What is the primary role of the dental lamina during tooth development?
- To serve as the primordial for the ectodermal portion of deciduous teeth (correct)
- To form the root structure of teeth
- To provide blood supply to developing teeth
- To stimulate bone growth in the jaw
What happens to the dental lamina as teeth develop?
What happens to the dental lamina as teeth develop?
- It retains its initial connection to developing teeth
- It becomes entirely ossified into bone
- It transforms into enamel
- It loses connection and breaks up due to mesenchymal invasion (correct)
From where do the successors of deciduous teeth develop?
From where do the successors of deciduous teeth develop?
What shape does the enamel organ take as it develops?
What shape does the enamel organ take as it develops?
What shapes do the developmental stages of the enamel organ resemble?
What shapes do the developmental stages of the enamel organ resemble?
In the bud stage, what type of cells predominantly make up the enamel organ?
In the bud stage, what type of cells predominantly make up the enamel organ?
What is the role of the ectomesenchymal cells during the cap stage?
What is the role of the ectomesenchymal cells during the cap stage?
What substance is secreted by the cells in the center of the enamel organ during the cap stage?
What substance is secreted by the cells in the center of the enamel organ during the cap stage?
What primary function does the epithelium serve during the bell stage of tooth development?
What primary function does the epithelium serve during the bell stage of tooth development?
Flashcards
Dental Lamina
Dental Lamina
A band of epithelium that forms along the future dental arch, serving as a precursor for deciduous teeth.
Ectoderm
Ectoderm
The outer germ layer of embryonic tissue, giving rise to the oral cavity lining.
Ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme
Connective tissues arising from neural crest cells, crucial for tooth development.
Tooth Bud
Tooth Bud
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Papilla
Dental Papilla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel Organ
Enamel Organ
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deciduous Teeth
Deciduous Teeth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permanent Molars
Permanent Molars
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Pearls
Epithelial Pearls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tooth development
Tooth development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Sac
Dental Sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel Organ Shape Change
Enamel Organ Shape Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Lamina
Dental Lamina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bud Stage
Bud Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basement Membrane
Basement Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cap Stage
Cap Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Papilla
Dental Papilla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Follicle
Dental Follicle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stellate Reticulum
Stellate Reticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bell Stage
Bell Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer enamel epithelium
Outer enamel epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner enamel epithelium
Inner enamel epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial signal
Epithelial signal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Tooth Development and Growth
- The primitive oral cavity, or stomodeum, is lined with stratified squamous epithelium (ectoderm).
- Connective tissue underneath the oral ectoderm is made up of neural crest cells (ectomesenchyme).
- Tooth development starts in the anterior portion of the maxilla and mandible and progresses posteriorly.
- Epithelial cells proliferate rapidly in specific areas (dental lamina) of the oral ectoderm.
- Ectomesenchymal cells also proliferate, forming a horseshoe-shaped dental arch.
- This proliferation of cells leads to the formation of the dental lamina.
- The dental lamina is the primordium for the ectodermal portion of deciduous teeth during jaw development.
- Permanent molars develop directly from the distal extension of the dental lamina.
- Deciduous teeth successors form from a lingual extension of the free end of the dental lamina.
- As teeth develop, they lose their connection to the dental lamina, breaking up through mesenchymal invasion.
- Remnants of the dental lamina remain (epithelial pearls or islands) in the jaw and gingival regions.
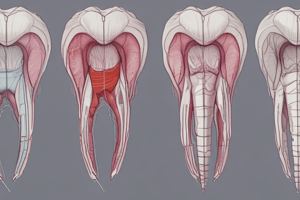
Stages of Tooth Development
- Bud Stage: Ectomesenchymal cells proliferate, forming a rounded swelling (the bud) corresponding to the future position of deciduous teeth.
- Cap Stage: Epithelium proliferates around the growing ball of ectomesenchymal cells. Ectomesenchymal cells become encapsulated.
- Bell Stage: Enamel organ shape resembles a bell. The epithelial cells are essential for regulating epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, controlling enamel organ morphogenesis and histodifferentiation.
- Four layers: Inner enamel epithelium, Outer enamel epithelium, Stellate reticulum, and Stratum intermedium develop.
- Root Formation (Hertwig's Root Sheath): After enamel and dentin formation, the root forms (Hertwig's root sheath). This sheath molds the root shape and begins dentin formation.
- Hertwig's epithelial root sheath(HERS) cells differentiate into cementoblasts.
- If the continuity of Hertwig's root sheath is broken, a defect in the root dentin wall may result.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.