Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
- To provide a cushion for tooth movement
- To form the bulk of the tooth's structure
- To protect the enamel from abrasion
- To connect the root of the tooth to the alveolar bone (correct)
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the dental tissues?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the dental tissues?
- Dentin
- Salivary glands (correct)
- Pulp
- Enamel
What is the significance of understanding enamel development in oral health?
What is the significance of understanding enamel development in oral health?
- It is irrelevant to clinical practices
- It allows for effective management of tooth decay (correct)
- It helps in preventing gum disease
- It aids in diagnosing systemic diseases
Which component of the tooth is primarily responsible for sensation?
Which component of the tooth is primarily responsible for sensation?
What aspect of oral embryology relates to the eruption and exfoliation of teeth?
What aspect of oral embryology relates to the eruption and exfoliation of teeth?
In what way does the alveolar bone maintain oral health?
In what way does the alveolar bone maintain oral health?
How does the oral mucosa contribute to oral health?
How does the oral mucosa contribute to oral health?
What role does cementum play in dental anatomy?
What role does cementum play in dental anatomy?
Which stage of tooth development is NOT mentioned in the overview?
Which stage of tooth development is NOT mentioned in the overview?
What is the primary role of the dental lamina during tooth development?
What is the primary role of the dental lamina during tooth development?
Which structure forms in conjunction with the dental lamina during initiation at week 7?
Which structure forms in conjunction with the dental lamina during initiation at week 7?
What is the significance of the basement membrane in tooth development?
What is the significance of the basement membrane in tooth development?
During which developmental stage is the seed for ectodermic structures planted?
During which developmental stage is the seed for ectodermic structures planted?
What key development occurs in week 7 of tooth formation?
What key development occurs in week 7 of tooth formation?
What is the result of the formation of the vestibular lamina?
What is the result of the formation of the vestibular lamina?
What aspect of embryogenesis does research focus on with stem cells today?
What aspect of embryogenesis does research focus on with stem cells today?
Which of the following is a stage in tooth development?
Which of the following is a stage in tooth development?
What cellular components are involved in the process of tooth development?
What cellular components are involved in the process of tooth development?
How long has the study of morphological aspects in dental development been ongoing?
How long has the study of morphological aspects in dental development been ongoing?
What is the primary role of the outer enamel epithelium (OEE)?
What is the primary role of the outer enamel epithelium (OEE)?
Which cells are responsible for facilitating amelogenesis?
Which cells are responsible for facilitating amelogenesis?
The inner enamel epithelium (IEE) is primarily composed of what type of cells?
The inner enamel epithelium (IEE) is primarily composed of what type of cells?
During which stage does the differentiation of ectomesenchyme cells into odontoblasts occur?
During which stage does the differentiation of ectomesenchyme cells into odontoblasts occur?
What characterizes the stratum intermedium (SI) in terms of its cell type?
What characterizes the stratum intermedium (SI) in terms of its cell type?
What is the main product of differentiation from the dental papilla's pulpal cells?
What is the main product of differentiation from the dental papilla's pulpal cells?
What is the primary characteristic developed during the morphogenesis transition between the bud and cap stages?
What is the primary characteristic developed during the morphogenesis transition between the bud and cap stages?
What process is characterized by cellular differentiation in the enamel organ prior to crown formation?
What process is characterized by cellular differentiation in the enamel organ prior to crown formation?
Which structure acts as a key signaling center for cusp shape and outline during morphogenesis?
Which structure acts as a key signaling center for cusp shape and outline during morphogenesis?
Which layer of the enamel organ is comprised of star-shaped cells?
Which layer of the enamel organ is comprised of star-shaped cells?
What significant change occurs to the enamel organ during the bell stage?
What significant change occurs to the enamel organ during the bell stage?
Which cell type is responsible for carrying out dentinogenesis?
Which cell type is responsible for carrying out dentinogenesis?
In which part of the bell stage is the crown outline visible in vertical cross-section?
In which part of the bell stage is the crown outline visible in vertical cross-section?
What layer forms a protective barrier during the early stages of tooth development?
What layer forms a protective barrier during the early stages of tooth development?
What cellular process occurs during the bell stage involving the enamel organ and dental papilla?
What cellular process occurs during the bell stage involving the enamel organ and dental papilla?
What is the first tooth to erupt that also corresponds to the first tooth to form?
What is the first tooth to erupt that also corresponds to the first tooth to form?
Which visual characteristic is associated with the early bell stage of tooth development?
Which visual characteristic is associated with the early bell stage of tooth development?
What does the separation of the enamel organ from the dental lamina signify?
What does the separation of the enamel organ from the dental lamina signify?
What is the main focus of further discussion mentioned for the histodifferentiation process?
What is the main focus of further discussion mentioned for the histodifferentiation process?
What morphological change follows after the cap stage in tooth development?
What morphological change follows after the cap stage in tooth development?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
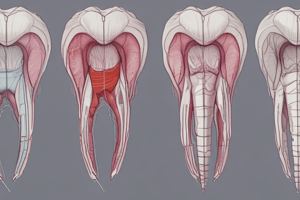
Stages of Tooth Development
- Dental Lamina: Forms in week 6-7 from oral epithelial cells in the mandibular and maxillary prominences. Divides into the dental lamina and the vestibular lamina.
- Vestibular Lamina: Forms adjacent to the dental lamina in week 7. Will give rise to the vestibule (space between teeth and lip).
- Bud Stage: The first stage of tooth development. The dental lamina thickens and starts to bud into the underlying ectomesenchyme. This is characterized by morphogenesis, the development of morphological characteristics. The enamel knot forms and plays a key role in cusp shape and outline.
- Cap Stage: The bud continues to grow and invaginates, forming a cap-like structure. This is the stage where the shape of the future tooth crown becomes more defined.
- Bell Stage: The cap further develops into a bell shape and detaches from the dental lamina. The outline of the tooth crown (including occlusal and cusp details) is now visible.
- Early Bell Stage: Cellular differentiation occurs inside the enamel organ and dental papilla. The cells differentiate into various cell types ready to form the different tissue structures of the tooth.
- Late Bell Stage: The bell stage is ready for crown formation (odontogenesis).
Histo-differentiation in the Bell Stage
- Enamel Organ:
- Outer Enamel Epithelium (OEE): Cuboidal cells that play a key role in the eruption process.
- Stellate Reticulum (SR): Star-shaped cells inside the OEE that facilitate amelogenesis.
- Stratum Intermedium (SI): Thickened cell layer inside the inner enamel epithelium that also facilitates amelogenesis.
- Inner Enamel Epithelium (IEE): Tall columnar cells that eventually differentiate into ameloblasts.
- Dental Papilla:
- Odontoblasts: Cells along the periphery of the dental papilla that are responsible for dentinogenesis.
- Pulpal Cells: Cells in the center of the dental papilla that eventually become the pulp of the tooth.
Clinical Significance of Oral Embryology
- Understanding oral tissue development allows for:
- Identifying healthy and abnormal oral tissues: By knowing the normal developmental stages and their timing, abnormalities can be identified earlier.
- Diagnosing and preventing oral disease: Understanding how different tissues develop helps to understand how diseases can arise and how they can be prevented.
- Managing disease and healing: Understanding the underlying developmental mechanisms can aid in the development of treatments for oral diseases.
- Upstanding how enamel develops: Knowing the process of amelogenesis allows for better understanding of how enamel is formed and how it can be affected by diseases, treatments, or even dietary factors.
- Understanding how material bond/adhere: Understanding the composition and structure of different oral tissues can contribute to the effective development and use of dental materials.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.