Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two subdivisions that arise from the primary epithelial band?
What are the two subdivisions that arise from the primary epithelial band?
- Cemental lamina and periodontal lamina
- Dental lamina and gingival lamina
- Dental lamina and vestibular lamina (correct)
- Enamel lamina and dentin lamina
Where do the epithelial thickenings or placodes form within the primary epithelial band?
Where do the epithelial thickenings or placodes form within the primary epithelial band?
- In the dental arches of the upper and lower jaws
- In the alveolar process (correct)
- In the vestibular lamina
- In the ectomesenchyme
What is the term used to describe the morphology of the developing tooth during the three stages of tooth development?
What is the term used to describe the morphology of the developing tooth during the three stages of tooth development?
- Early, intermediate, and late
- Initiation, morphodifferentiation, and apposition
- Formative, proliferative, and appositional
- Bud, cap, and bell (correct)
During which stage of tooth development is a tooth bud characterized?
During which stage of tooth development is a tooth bud characterized?
What is the term used to describe the increase in cellular density next to the epithelial outgrowth?
What is the term used to describe the increase in cellular density next to the epithelial outgrowth?
What is the role of the dental lamina in tooth formation?
What is the role of the dental lamina in tooth formation?
How many local thickenings or placodes form on the dental lamina in each alveolar process?
How many local thickenings or placodes form on the dental lamina in each alveolar process?
What is the shape of the cells in the concavity of the cap during the cap stage?
What is the shape of the cells in the concavity of the cap during the cap stage?
What forms around the epithelial thickenings or placodes during tooth development?
What forms around the epithelial thickenings or placodes during tooth development?
What forms from the interaction of the enamel organ and dental papilla?
What forms from the interaction of the enamel organ and dental papilla?
During the bud stage, what happens to the epithelial cells?
During the bud stage, what happens to the epithelial cells?
What is the name of the stage where the enamel organ looks like a cap?
What is the name of the stage where the enamel organ looks like a cap?
What is the term used to describe the cells in the convex portion of the cap?
What is the term used to describe the cells in the convex portion of the cap?
What is the name of the structure that forms from the interaction of the epithelial bud and ectomesenchyme?
What is the name of the structure that forms from the interaction of the epithelial bud and ectomesenchyme?
What is the function of the fluid in the stellate reticulum?
What is the function of the fluid in the stellate reticulum?
What is the term given to the cells in the center of the enamel organ that synthesize glycosaminoglycans?
What is the term given to the cells in the center of the enamel organ that synthesize glycosaminoglycans?
What is the shape of the enamel organ in the bell stage?
What is the shape of the enamel organ in the bell stage?
What is the function of the primary enamel knot?
What is the function of the primary enamel knot?
What is the term given to the structure formed by the cells in the centre of the concavity of the ‘cap’?
What is the term given to the structure formed by the cells in the centre of the concavity of the ‘cap’?
What is the characteristic of the dental papilla in the cap stage?
What is the characteristic of the dental papilla in the cap stage?
What is the significance of the bell stage?
What is the significance of the bell stage?
Where does the formation of the organic matrix of dentin begin?
Where does the formation of the organic matrix of dentin begin?
What is the direction of the mineralization of the dentin matrix?
What is the direction of the mineralization of the dentin matrix?
What happens to the inner enamel epithelial cells after the first layer of dentin is formed?
What happens to the inner enamel epithelial cells after the first layer of dentin is formed?
What is the direction of the enamel formation from the dentinoenamel junction?
What is the direction of the enamel formation from the dentinoenamel junction?
What type of cells produce the organic matrix of enamel?
What type of cells produce the organic matrix of enamel?
What is the term for the line separating the newly differentiated odontoblasts and the inner enamel epithelium?
What is the term for the line separating the newly differentiated odontoblasts and the inner enamel epithelium?
What is the sequence of events in the formation of the dentinoenamel junction?
What is the sequence of events in the formation of the dentinoenamel junction?
What is the result of the differentiation of odontoblasts and ameloblasts?
What is the result of the differentiation of odontoblasts and ameloblasts?
What influences the differentiation of odontoblasts?
What influences the differentiation of odontoblasts?
What is the outcome of the process of reciprocal induction?
What is the outcome of the process of reciprocal induction?
What is the significance of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath formation?
What is the significance of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath formation?
What is the composition of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath?
What is the composition of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath?
What is the role of the inner enamel epithelial layer of the sheath?
What is the role of the inner enamel epithelial layer of the sheath?
What occurs after the first layer of radicular dentin is formed?
What occurs after the first layer of radicular dentin is formed?
What is the significance of the cervical portion of the enamel organ?
What is the significance of the cervical portion of the enamel organ?
What is the relationship between the differentiation of ameloblasts and odontoblasts?
What is the relationship between the differentiation of ameloblasts and odontoblasts?
What marks the beginning of root development?
What marks the beginning of root development?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
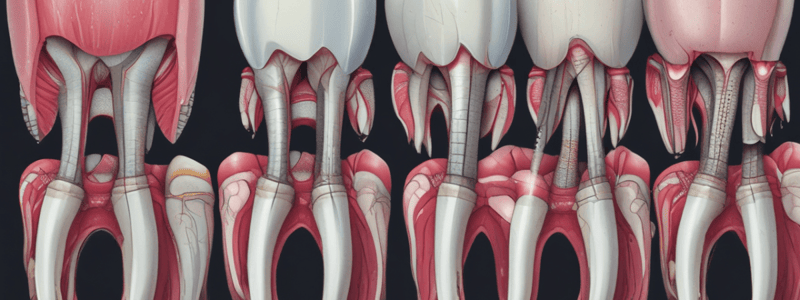
Enamel Organ Development
- Central cells of the enamel organ synthesize glycosaminoglycans, contributing to water absorption and stretching of intercellular bridges.
- These central cells appear star-shaped, known as the stellate reticulum, which protects enamel-forming cells by acting as a shock absorber.
- A knob-like enlargement in the concavity of the enamel organ is termed the primary enamel knot, which projects toward the dental papilla and contributes to the enamel cord structure.
Stages of Tooth Development
- Dental Papilla in Cap Stage: Cells become crowded and more vascularized.
- Dental Sac in Cap Stage: Appears more condensed and fibrous due to developmental changes.
- Enamel Organ in Bell Stage: Further invagination occurs, shaping the organ like a bell; final crown shape is achieved through morpho-differentiation of hard tissue-forming cells (ameloblasts and odontoblasts).
Initiation of Tooth Development
- Develops from ectoderm and ectomesenchyme; a thickened epithelium forms a continuous band (primary epithelial band) around the mouth corresponding to future dental arches.
- Localized thickenings or placodes lead to the formation of the dental lamina, which gives rise to future teeth.
- Ten epithelial thickenings correspond to future deciduous teeth, with ectomesenchymal cells accumulating around each thickening.
Stages in Formation of Tooth
- Bud Stage: Involves the formation of a tooth bud; odontoblasts differentiate and outline the dentinoenamel junction.
- Cap Stage: Tooth germ develops, leading to the formation of ameloblasts and odontoblasts; the enamel organ takes on a cap-like appearance with varying cell shapes.
Reciprocal Induction
- The differentiation of odontoblasts is influenced by inner enamel epithelium, establishing an interdependent relationship that leads to the formation of enamel and dentin through histodifferentiation.
Root Formation
- Begins after the dentinoenamel junction is established; Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath influences root shape, length, size, and root number while initiating radicular dentin formation.
- The inner enamel epithelial layer of the sheath prompts the differentiation of odontoblasts from the dental papilla, leading to the formation of the first layer of radicular dentin.
Condensation and Development
- The bud stage is marked by the epithelial incursion into the ectomesenchyme, leading to an increase in cellular density and condensation of ectomesenchymal cells around the epithelial bud.
- In the cap stage, unequal proliferation rates lead to distinct structural formation of the enamel organ, with cuboidal cells forming the outer enamel epithelium and columnar cells forming the inner enamel epithelium.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.