Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following accurately describes the anatomical location of the thyroid gland?
Which of the following accurately describes the anatomical location of the thyroid gland?
- Inferior to the cricoid cartilage and posterior to the esophagus.
- Lateral to the larynx and posterior to the carotid arteries.
- Immediately inferior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx and anterior to the trachea. (correct)
- Superior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx and anterior to the trachea.
Which structural component connects the left and right lobes of the thyroid gland?
Which structural component connects the left and right lobes of the thyroid gland?
- The thyroglossal duct
- The isthmus (correct)
- The cricoid cartilage
- The hyoid bone
What type of cells primarily form the walls of thyroid follicles?
What type of cells primarily form the walls of thyroid follicles?
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells
- Stratified squamous epithelial cells
- Simple cuboidal epithelial cells (correct)
- Transitional epithelial cells
What is the primary component of the colloid found within the central lumen of thyroid follicles?
What is the primary component of the colloid found within the central lumen of thyroid follicles?
Which of the following describes the change in follicular cells during periods of high thyroid activity?
Which of the following describes the change in follicular cells during periods of high thyroid activity?
Which hormone is produced by the parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid?
Which hormone is produced by the parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid?
Among thyroid hormones, which one is also known as tetraiodothyronine?
Among thyroid hormones, which one is also known as tetraiodothyronine?
What key element is essential for the thyroid gland to produce its hormones?
What key element is essential for the thyroid gland to produce its hormones?
Which of the following thyroid hormones contains three iodine atoms?
Which of the following thyroid hormones contains three iodine atoms?
Thyroglobulin (TG) is initially synthesized in which cellular structure?
Thyroglobulin (TG) is initially synthesized in which cellular structure?
What is the role of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) in the synthesis of thyroid hormones?
What is the role of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) in the synthesis of thyroid hormones?
How are T4 and T3 transported from the follicular cell into the bloodstream?
How are T4 and T3 transported from the follicular cell into the bloodstream?
Which of the following directly stimulates all steps in thyroid hormone production?
Which of the following directly stimulates all steps in thyroid hormone production?
Which hormone initiates the process of thyroid hormone secretion by stimulating the anterior pituitary?
Which hormone initiates the process of thyroid hormone secretion by stimulating the anterior pituitary?
Which of the following is a direct effect of TSH on the thyroid gland?
Which of the following is a direct effect of TSH on the thyroid gland?
How do elevated levels of T3 and T4 affect TSH secretion?
How do elevated levels of T3 and T4 affect TSH secretion?
What is the primary effect of thyroid hormones on general metabolism?
What is the primary effect of thyroid hormones on general metabolism?
How do normal physiological levels of thyroid hormones affect protein metabolism?
How do normal physiological levels of thyroid hormones affect protein metabolism?
Which of the following describes the effect of thyroid hormones on intestinal glucose absorption?
Which of the following describes the effect of thyroid hormones on intestinal glucose absorption?
How do thyroid hormones affect lipid metabolism?
How do thyroid hormones affect lipid metabolism?
What role do thyroid hormones play in physical growth?
What role do thyroid hormones play in physical growth?
For which aspect of mental development are thyroid hormones essential?
For which aspect of mental development are thyroid hormones essential?
What is the primary effect of thyroid hormones on the cardiovascular system?
What is the primary effect of thyroid hormones on the cardiovascular system?
How do thyroid hormones affect the respiratory system?
How do thyroid hormones affect the respiratory system?
What is a common symptom of iodine deficiency?
What is a common symptom of iodine deficiency?
What are the typical characteristics of cretinism related to physical features?
What are the typical characteristics of cretinism related to physical features?
How does cretinism typically affect mental capacity?
How does cretinism typically affect mental capacity?
What is a key difference between cretinism and dwarfism in terms of mental capacity?
What is a key difference between cretinism and dwarfism in terms of mental capacity?
What condition is also characterized by mucin accumulation and swelling?
What condition is also characterized by mucin accumulation and swelling?
Flashcards
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
A butterfly-shaped gland located inferior to the larynx and anterior to the trachea.
Isthmus
Isthmus
Connects the left and right lobes of the thyroid gland at the anterior midline.
Thyroid Follicles
Thyroid Follicles
Spherical structures composing the thyroid gland.
Follicular Cells
Follicular Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Lumen
Central Lumen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parafollicular Cells
Parafollicular Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin (CT)
Calcitonin (CT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroglobulin (TG)
Thyroglobulin (TG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO)
Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feedback Control
Feedback Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Hormones' Effect on Metabolism
Thyroid Hormones' Effect on Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Metabolism: Normal
Protein Metabolism: Normal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Metabolism: Excess
Protein Metabolism: Excess
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical Growth
Physical Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development of Teeth
Development of Teeth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mental Growth
Mental Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sexual Growth
Sexual Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary Hypothyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Graves' Disease
Graves' Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
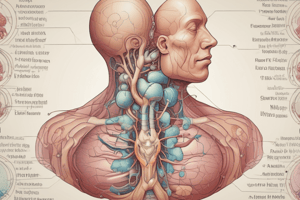
Thyroid Gland Structure
- A butterfly-shaped gland weighing 20–40 g.
- Located immediately inferior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx and anterior to the trachea.
- Composed of left and right lobes connected at the anterior midline by a narrow isthmus.
Histological Level
- Spherical structures called thyroid follicles compose the thyroid gland.
- Simple cuboidal epithelial cells, known as follicular cells, form the follicle wall.
- Follicular cells secrete thyroid hormones and surround a central lumen.
- The central lumen contains protein-rich fluid termed colloid.
- Follicular cells become columnar during high activity and flat when inactive.
- C (clear) cells, also named parafollicular cells, are large, pale cells that lie in between the follicles.
- C (clear) cells (parafollicular cells) produce the hormone calcitonin (CT).
Thyroid Hormones
- Thyroxin (tetraiodothyronin or T4) is a thyroid hormone.
- Triiodothyronin (T3)is a thyroid hormone.
- Calcitonin, a calcium-lowering hormone, is a thyroid hormone.
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones
- Thyroglobulin (TG) is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of thyroid follicular cells.
- TG is then transported into the follicular lumen.
- Two iodide molecules are transported into the follicular cell by the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS).
- Iodide diffuses to the apical surface and is transported into the follicular lumen by the pendrin (P) carrier.
- Thyroid peroxidase(TPO) oxidizes iodide.
- The oxidized iodide is linked to tyrosine residues in TG to form diiodotyrosine (DIT) and monoiodotyrosine (MIT) molecules.
- Within TG, T4 is formed from two DIT molecules.
- T3 is formed from one DIT and one MIT molecule.
- TG containing T4 and T3 is resorbed into the follicular cell via endocytosis.
- Lysosomal enzymes degrade TG to release T4 and T3 molecules.
- T4 and T3 molecules then move across the basolateral membrane of the follicular cell into the adjacent capillaries.
- Iodine is required by the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones.
- All steps in thyroid hormone production are stimulated by TSH.
Control of Thyroid Function
- Secretion of thyroid hormones is regulated by: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
- TRH is secreted from the median eminence of the hypothalamus (neurosecretion).
- TRH reaches the anterior pituitary through the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal circulation to stimulate TSH secretion.
- Secretion of thyroid hormones is regulated by: Thyrotropin (thyroid stimulating hormone = TSH)
- TSH is secreted by the basophil cells of the anterior pituitary.
- TSH increases the size, vascularity, and function of the thyroid gland.
- Secretion of thyroid hormones is regulated by: Thyroid hormones level in the blood (feedback control)
- T4 & T3 in plasma inhibit TSH secretion by direct inhibition of the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus.
Functions of Thyroid Hormones
- Thyroid hormones increase the rates of the chemical reactions of many cells in the body (the metabolic rate).
- Thyroid hormones increase O2 consumption and heat production and increase body temperature.
- Normal physiological levels of thyroid hormones stimulate protein synthesis and growth (anabolic effect).
- Excess thyroid hormones cause protein catabolism.
- Intestinal absorption of glucose increases due to thyroid hormones.
- Liver glycogenolysis increases due to thyroid hormones.
- Gluconeogenesis increases due to thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid hormones increase lipolysis (free fatty acids in plasma) and decrease cholesterol in the blood.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate linear growth of bone.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate the eruption and development of teeth.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate normal muscular development and function.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate growth of skin and hair follicles.
- Thyroid hormones are essential for CNS development, growth, and function during fetal life and in the first few years after birth.
- Thyroid hormones are essential for the myelination of nerve fibers.
- Thyroid hormones are essential for the development of synapses.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate gonadal functions.
- They are essential for the normal menstrual cycle and spermatogenesis & fertility.
- Thyroid hormones stimulate milk secretion during lactation.
- Thyroid hormones increase heart rate and strength of cardiac contraction.
- Thyroid hormones increase cardiac output due to increased stroke volume and heart rate.
- Thyroid hormones increase the number of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the heart.
- Respiration is increased due to increased body metabolism.
- Appetite is increased due to thyroid hormones.
- Intestinal motility is increased due to thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid hormones enhance wakefulness, alertness, & responsiveness to various stimuli.
- Thyroid hormones promote normal hydration and secretory activity of the skin.
Iodine Deficiency
- Iodine deficiency in diet can cause: -An enlarged thyroid (goiter).
Sexual Growth Retardation
- Sex organs remain infantile in sexual growth retardation.
Metabolism
- Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is decreased in slower metabolism.
- Those affected are sensitive to cold (cold intolerance).
- Serum cholesterol is increased in slower metabolism.
General Features
- Swollen eyelids with narrow palpebral fissures are present.
- Depressed nose with wide nostrils is present.
- Enlarged protruded tongue between thick lips are present.
- Bulging is due to muscle weakness, together with constipation.
- Skin is cold, pale, dry & coarse with scanty hair.
Cretinism vs Dwarfism
| Feature | Cretinism | Dwarfism |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Lack of thyroid hormone | Lack of growth hormone |
| Physical Growth | Short stature | Short stature |
| Mentality | Complete idiot | Normal |
| Sexuality | Sterile & impotent | Normal |
| Special Characters | Ugly face (discuss) | Nice facial characters |
Myxoedema (Hypothyroidism in Adults)
- Myx is mucin + edema is swelling.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Primary hypothyroidism is due to causes within the thyroid.
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Is an autoimmune destruction of the thyroid with lymphocytic infiltration.
- Secondary Hypothyroidism occurs.
- Hypothalamic Hypothyroidism is dueto a failureof hypothalamus to secrete TRH.
- Pituitary Hypothyroidism is due to failure of pituitary to secrete TSH.
Clinical Features of Hypothyroidism
- Low intolerance.
- Puff leths.
- Non(Prote ar spaces water ar S.
- Dec men.
- Rou.
- Constipation, decreased appetite.
Hyperthyroidism
- Graves' disease is toxic goiter and thyrotoxicosis.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
- Grave's disease: (1y hyperthyroidism).
- It is an autoimmune disease in which antibodies [Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI)] bind with TSH receptors result in the continuous stimulation of thyroid hormone production and secretion as well as thyroid growth (goiter).
- TSH-secreting tumor of the pituitary: (2ry hyperthyroidism).
- It is very rare.
Clinical Features of Hypothyroidism
- Increased basal metabolic rate (BMR).
- Intolerance to heat.
- Nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, insomnia.
- Hyperglycemia and decreased cholesterol.
- Weight loss despite increased food intake.
- Increased resting heart rate.
- Fine tremors in hands.
- Diarrhea.
- Excessive sweating, warm moist skin.
- Eye: lid retraction producing a staring look, and lid lag and exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeball.)
Primary Hypothyroidism
- Low T4
- Low TRH
- High TSH
Secondary Hyperthyroidism
- High T3 and T4 is present
- Low TRA
- Hig Tsh
Goiter
- A goiter can develop in all of the disorders except:
Disorder T4 TSH TRH Primary Hypothyroidism ↓ ↑ ↑ Pituitary Hypothyroidism ↓ ↓ ↑ Pituitary Hyperthyroidism ↑ ↑ ↓ Graves' Disease (Autoimmune) ↑ ↓ ↓
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.