Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of calcitonin produced by parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland?
What is the role of calcitonin produced by parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland?
- Controlling heart function
- Aiding in growth and development
- Regulating calcium homeostasis (correct)
- Maintaining basal metabolic rate
Which cells are primarily responsible for the production and secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4?
Which cells are primarily responsible for the production and secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4?
- Adrenal cells
- Parafollicular cells
- Thymic cells
- Follicular cells (correct)
Where are parafollicular cells predominantly located in the thyroid gland?
Where are parafollicular cells predominantly located in the thyroid gland?
- Upper part (correct)
- Isthmus
- Lower part
- Lateral lobes
Which artery supplies blood to the thyroid gland directly from the thyrocervical trunk?
Which artery supplies blood to the thyroid gland directly from the thyrocervical trunk?
What is the main function of follicular cells in the thyroid gland?
What is the main function of follicular cells in the thyroid gland?
Which structure connects the two lateral lobes of the thyroid gland?
Which structure connects the two lateral lobes of the thyroid gland?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Thyroid Gland Anatomy
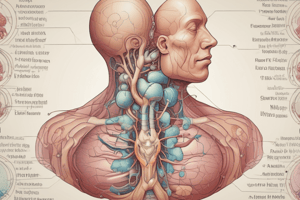
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the anterior neck, surrounded by the hyoid bone and the trachea. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by a central mass called the isthmus, which comes into continuity with the thyroglossal duct remnants. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism through its synthesis of three hormones: triiodothyronine (T3), tetraiodothyronine (T4), and calcitonin.
Structure
Follicular Cells
Follicular cells constitute about 95% of the total cell population of the thyroid gland. They are responsible for the production and secretion of T3 and T4 hormones, also known as thyroid hormones. These hormones play essential roles in maintaining basal metabolic rate, growth development, body temperature, heart function, etc..
Parafollicular Cells
Parafollicular cells, also known as parathyroidoid-producing cells or C cells, represent less than 5% of the total cell population and are more abundant in the upper part of the thyroid gland. These cells produce and secrete calcitonin, a peptide hormone involved in calcium homeostasis and regulation of insulin and glucagon levels.
Blood Supply
The thyroid gland receives blood from both sides via the superior thyroid artery and the inferior thyroid artery. The superior thyroid artery branches off the external carotid artery, while the inferior thyroid artery originates directly from the thyrocervical trunk. Both these blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to the thyroid gland, facilitating the various cellular processes within it.
In summary, the thyroid gland is a complex organ composed of follicular and parafollicular cells, each playing unique roles in the production of thyroid and calcitonin hormones. Its structure allows for efficient blood flow to support these vital functions, making it an integral component of human physiology.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.