Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the primary function of the distal radioulnar joint?
- To control multi-articular muscles of the hand
- To provide 2 degrees of freedom to the wrist complex
- To adjust the grip of the hand
- To facilitate forearm pronosupination (correct)
Which of the following bones are part of the proximal carpal row?
Which of the following bones are part of the proximal carpal row?
- Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum (correct)
- Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate
- Radius, Ulna, Radius
- Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate
What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
- Plane synovial joint
- Bicondylar joint
- Pivot joint
- Ellipsoid joint (correct)
What is the function of the pisiform bone?
What is the function of the pisiform bone?
How many degrees of freedom does the wrist complex have?
How many degrees of freedom does the wrist complex have?
What type of joint is the intercarpal/midcarpal joint?
What type of joint is the intercarpal/midcarpal joint?
What is the function of the radiocarpal joint?
What is the function of the radiocarpal joint?
What is the concave rule applied to in the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the concave rule applied to in the distal radioulnar joint?
What type of movement occurs during pronation in the distal radioulnar joint?
What type of movement occurs during pronation in the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the function of the wrist complex?
What is the function of the wrist complex?
Which of the following movements occurs in the sagittal plane?
Which of the following movements occurs in the sagittal plane?
What is the range of motion for ulnar/cubital deviation?
What is the range of motion for ulnar/cubital deviation?
In open kinematic chain, what is the direction of roll and glide in flexion?
In open kinematic chain, what is the direction of roll and glide in flexion?
Which of the following joints has a concave surface?
Which of the following joints has a concave surface?
What is the purpose of the convex rule in arthrokinematics?
What is the purpose of the convex rule in arthrokinematics?
Which movement occurs in the frontal plane?
Which movement occurs in the frontal plane?
What is the main difference between open kinematic chain and osteokinematics?
What is the main difference between open kinematic chain and osteokinematics?
What type of stability is provided by the capsule in the wrist?
What type of stability is provided by the capsule in the wrist?
What is the range of motion for palmar flexion?
What is the range of motion for palmar flexion?
Which of the following compartments contains the capitate and hamate bones?
Which of the following compartments contains the capitate and hamate bones?
What is the function of the synovial membrane in the wrist joint?
What is the function of the synovial membrane in the wrist joint?
What is a notable feature of the ligaments of the wrist?
What is a notable feature of the ligaments of the wrist?
What is the function of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the function of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the location of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the location of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the function of the scapholunate ligament?
What is the function of the scapholunate ligament?
What can be a result of an untreated scapholunate ligament injury?
What can be a result of an untreated scapholunate ligament injury?
What type of movements are facilitated by the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What type of movements are facilitated by the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the primary function of the ligaments in the wrist joint?
What is the primary function of the ligaments in the wrist joint?
What is the purpose of the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments?
What is the purpose of the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments?
What is the result of an injury to the scapholunate ligament?
What is the result of an injury to the scapholunate ligament?
Flashcards
What is the primary function of the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the primary function of the distal radioulnar joint?
The distal radioulnar joint's primary function is to allow the forearm to rotate, enabling movements like turning a doorknob.
Which bones make up the proximal carpal row?
Which bones make up the proximal carpal row?
The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones form the proximal row of carpal bones in the wrist.
What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
The radiocarpal joint, where the radius meets the carpal bones, is a type of joint that allows for movement in two directions.
What is the function of the pisiform bone?
What is the function of the pisiform bone?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many degrees of freedom does the wrist complex have?
How many degrees of freedom does the wrist complex have?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of joint is the intercarpal/midcarpal joint?
What type of joint is the intercarpal/midcarpal joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the radiocarpal joint?
What is the function of the radiocarpal joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the concave rule applied to in the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the concave rule applied to in the distal radioulnar joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of movement occurs during pronation in the distal radioulnar joint?
What type of movement occurs during pronation in the distal radioulnar joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the wrist complex?
What is the function of the wrist complex?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which of the following movements occurs in the sagittal plane?
Which of the following movements occurs in the sagittal plane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the range of motion for ulnar/cubital deviation?
What is the range of motion for ulnar/cubital deviation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
In open kinematic chain, what is the direction of roll and glide in flexion?
In open kinematic chain, what is the direction of roll and glide in flexion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which of the following joints has a concave surface?
Which of the following joints has a concave surface?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the convex rule in arthrokinematics?
What is the purpose of the convex rule in arthrokinematics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which movement occurs in the frontal plane?
Which movement occurs in the frontal plane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main difference between open kinematic chain and osteokinematics?
What is the main difference between open kinematic chain and osteokinematics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of stability is provided by the capsule in the wrist?
What type of stability is provided by the capsule in the wrist?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the range of motion for palmar flexion?
What is the range of motion for palmar flexion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which of the following compartments contains the capitate and hamate bones?
Which of the following compartments contains the capitate and hamate bones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the synovial membrane in the wrist joint?
What is the function of the synovial membrane in the wrist joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a notable feature of the ligaments of the wrist?
What is a notable feature of the ligaments of the wrist?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the function of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the location of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What is the location of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the scapholunate ligament?
What is the function of the scapholunate ligament?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What can be a result of an untreated scapholunate ligament injury?
What can be a result of an untreated scapholunate ligament injury?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of movements are facilitated by the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
What type of movements are facilitated by the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the primary function of the ligaments in the wrist joint?
What is the primary function of the ligaments in the wrist joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments?
What is the purpose of the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the result of an injury to the scapholunate ligament?
What is the result of an injury to the scapholunate ligament?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
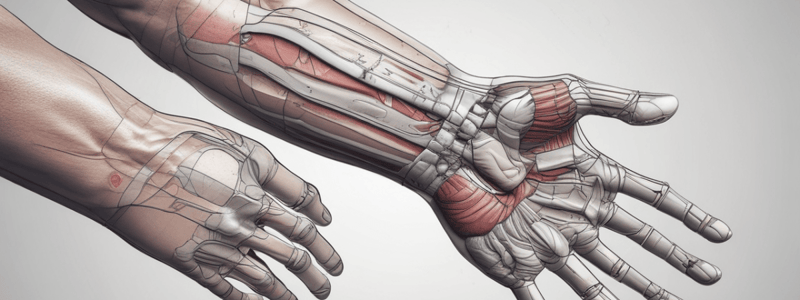
The Wrist Complex
- Functions: control of multi-articular muscles of the hand and fine adjustment of grip
- Degrees of freedom: 2 (radial/ulnar deviation, flexion/extension)
Joints of the Wrist Complex
- Distal radioulnar joint: pivot joint with concave rule (radius moves)
- Radiocarpal joint: ellipsoid joint with 2 axes, convex rule
- Midcarpal/intecarpal joints: plane synovial joints that interconnect each carpal bone
Intercarpal-Midcarpal Joints
- Compound joint with three or more articulation surfaces
- Two single functional units: proximal row (scaphoid-lunate-triquetrum) and distal row (trapezium-trapezoid-capitate-hamate)
Wrist Osteokinematics
- Movements:
- Palmar flexion: 85° transversal plane
- Dorsal flexion: 85° transversal plane
- Ulnar/cubital deviation: 35-40° frontal plane
- Radial deviation: 15° frontal plane
Wrist Arthrokinematics
- Open kinetic chain:
- Flexion/extension: roll anterior/gliding posterior
- Radial/ulnar deviation: roll radial/gliding ulnar
Wrist Stability
- Static stability: capsule, ligaments, and synovial membrane
- Dynamic stability: palmar and dorsal musculature of the wrist
The Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
- Load-bearing structure that stabilizes radiocarpal and ulnocarpal joints
- Prevents ulnocarpal abutment and facilitates complex wrist movements
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.