Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system?
- Blood
- Blood vessels
- Lungs (correct)
- Heart
What is the function of capillaries in the cardiovascular system?
What is the function of capillaries in the cardiovascular system?
- To facilitate exchange of substances between the bloodstream and surrounding tissues (correct)
- To carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
- To transport deoxygenated blood back towards the heart
- To regulate the heartbeat
Which layer of the heart is composed of cardiac muscle?
Which layer of the heart is composed of cardiac muscle?
- Myocardium (correct)
- Pericardium
- Epicardium
- Endocardium
What is the function of the valves in the heart?
What is the function of the valves in the heart?
Which chamber of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle?
Which chamber of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle?
What is the function of the myocardium?
What is the function of the myocardium?
Which layer of the heart wall provides a protective outer covering to the heart?
Which layer of the heart wall provides a protective outer covering to the heart?
What is the main function of the aortic valve?
What is the main function of the aortic valve?
Which coronary artery supplies blood to the lateral wall of the left ventricle?
Which coronary artery supplies blood to the lateral wall of the left ventricle?
Which coronary artery supplies blood to the posterior walls of both ventricles?
Which coronary artery supplies blood to the posterior walls of both ventricles?
Where is the AV Node located?
Where is the AV Node located?
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by sympathetic innervation of the heart?
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by sympathetic innervation of the heart?
Which of the following is responsible for maintaining the negative charge inside a nodal cell?
Which of the following is responsible for maintaining the negative charge inside a nodal cell?
What is the primary ion responsible for regulating the resting membrane potential of a nodal cell?
What is the primary ion responsible for regulating the resting membrane potential of a nodal cell?
What is autorhythmicity?
What is autorhythmicity?
What role does the SA node play in the spread of the action potential through the heart?
What role does the SA node play in the spread of the action potential through the heart?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the semilunar valves open and blood is forced into the arterial trunk?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the semilunar valves open and blood is forced into the arterial trunk?
What is the purpose of the refractory period in a neuron or muscle fiber?
What is the purpose of the refractory period in a neuron or muscle fiber?
What is the significance of ventricular balance in the heart?
What is the significance of ventricular balance in the heart?
What is the formula for calculating cardiac output?
What is the formula for calculating cardiac output?
Which of the following best defines cardiac reserve?
Which of the following best defines cardiac reserve?
What are chronotropic agents?
What are chronotropic agents?
Which of the following is a positive chronotropic agent?
Which of the following is a positive chronotropic agent?
Which of the following is a negative chronotropic agent?
Which of the following is a negative chronotropic agent?
How do autonomic reflexes alter heart rate?
How do autonomic reflexes alter heart rate?
What are the key extrinsic variables that raise and decrease heart rate?
What are the key extrinsic variables that raise and decrease heart rate?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
What is the primary function of the mitral valve?
What is the primary function of the mitral valve?
What is the main source of energy for cardiac muscle?
What is the main source of energy for cardiac muscle?
What is the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
What is the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
Which valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Which valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle?
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
What is the main source of energy for cardiac muscle?
What is the main source of energy for cardiac muscle?
What is the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
What is the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Components of the Cardiovascular System
- The lymphatic system is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system
Capillaries in the Cardiovascular System
- Capillaries are responsible for exchanging oxygen and nutrients with cells and removing waste products
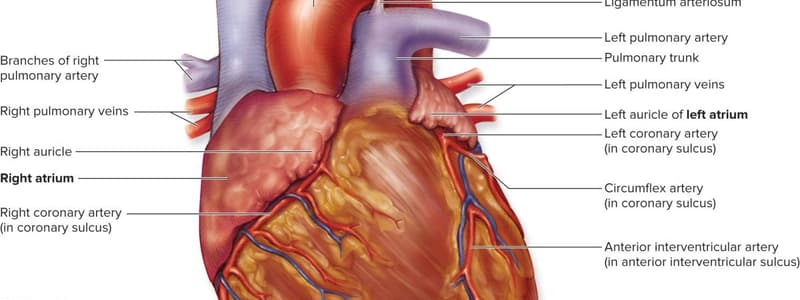
Heart Structure
- The myocardium is the layer of the heart composed of cardiac muscle
- The epicardium is the layer of the heart wall that provides a protective outer covering to the heart
Heart Valves
- The function of valves in the heart is to ensure one-way blood flow and prevent backflow
- The aortic valve allows blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta and prevents backflow
- The mitral valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle
Heart Chambers
- The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle
Blood Supply
- The obtuse marginal branch of the left circumflex artery supplies blood to the lateral wall of the left ventricle
- The posterior descending branch of the right coronary artery supplies blood to the posterior walls of both ventricles
Electrical Conduction
- The AV Node is located in the inferior portion of the right atrium
- The primary neurotransmitter released by sympathetic innervation of the heart is norepinephrine
- The negative charge inside a nodal cell is maintained by potassium ions
- The primary ion responsible for regulating the resting membrane potential of a nodal cell is potassium
- Autorhythmicity is the ability of certain cardiac cells to generate an electrical impulse spontaneously
- The SA node plays a role in the spread of the action potential through the heart by generating an electrical impulse that travels to the AV Node
Cardiac Cycle
- During the ejection phase of the cardiac cycle, the semilunar valves open and blood is forced into the arterial trunk
Refractory Period
- The refractory period in a neuron or muscle fiber is the period during which it cannot respond to a new stimulus
Cardiac Output
- Cardiac reserve is the difference between the maximum cardiac output and the resting cardiac output
- The formula for calculating cardiac output is cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume
- Chronotropic agents are substances that alter the heart rate
- Positive chronotropic agents increase heart rate, while negative chronotropic agents decrease heart rate
- Autonomic reflexes alter heart rate through the stimulation of the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system
- The key extrinsic variables that raise and decrease heart rate are sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation, respectively
Fibrous Skeleton
- The fibrous skeleton in the heart provides a framework for the attachment of the heart valves and separates the atria from the ventricles
Energy for Cardiac Muscle
- The primary source of energy for cardiac muscle is ATP derived from fatty acid oxidation
- Intercalated discs in cardiac muscle allow for the rapid transmission of electrical impulses between cells
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.